Your Parenchyma in plants images are available. Parenchyma in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Parenchyma in plants files here. Get all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for parenchyma in plants images information connected with to the parenchyma in plants topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Parenchyma In Plants. In plants parenchyma refers to a distinct tissue type that has thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide. They have only a primary cell wall and retain the ability for future cell division. Wikimedia) plant parenchyma cells are believed to be the precursor of differentiated and specialized cells and tissues. For information specific to plants, see ground tissue § parenchyma.
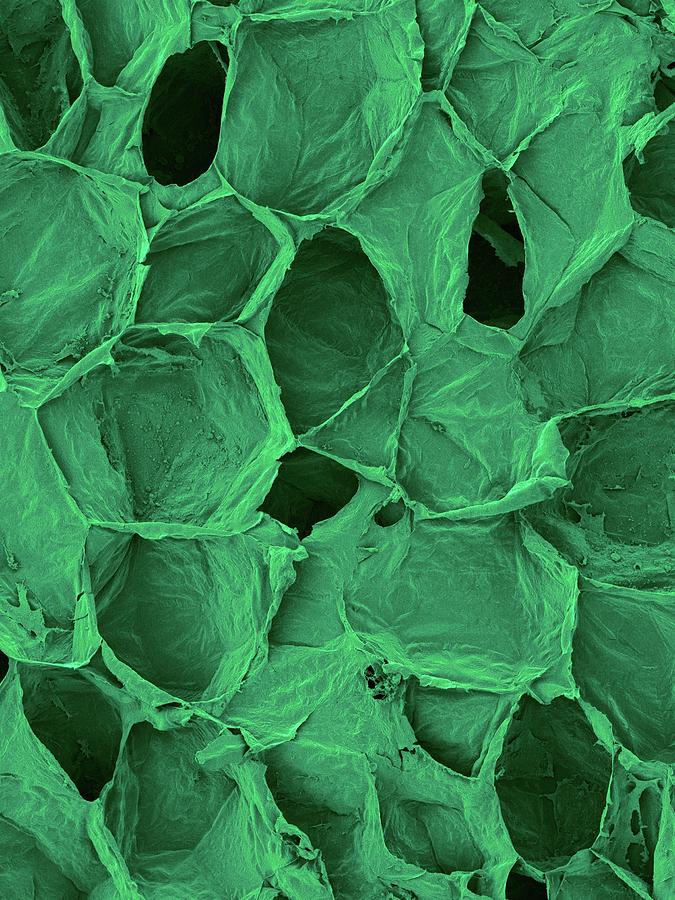
 Plant parenchyma cellulose walls, SEM Stock Image C032 From sciencephoto.com
Plant parenchyma cellulose walls, SEM Stock Image C032 From sciencephoto.com
It forms the major bulk of stem, roots, leaves, fruits and seeds. The cells are found in many places throughout plant bodies and, given that they are alive, are actively involved in photosynthesis , secretion , food storage, and other activities of plant life. It is defined as the functional tissues in all higher plants. Primary walls are common in parenchyma cells i.e., chlorophyllous and storing parenchyma. The storing parenchyma cells of phoenix, asparagus endosperm have extremely thick walls. Xylem parenchyma can be described as a component of the complex plant tissue xylem.
Ø they can also store ergastic substances like resins, tannins etc.
It is the least specialized among the permanent tissues. In contrast to collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells, parenchyma cells primarily consists of all of the simple, thin walled, undifferentiated cells which form a large majority of many plant tissues. It is also distributed in pith , medullary rays & packing tissue in xylem and phloem. Parenchyma is a specific type of ground tissue having thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide. Parenchyma cells are typically alive in maturity and conduct most of the plant�s metabolic functions, such as storage of energy (mainly in the form of starch and fats) and waste products (tannin, resins, gums, etc.), support for photosynthesis (as are the cells containing chlorophyll), gaseous exchange (which takes place in the intercellular spaces) and damage. It is defined as the functional tissues in all higher plants.
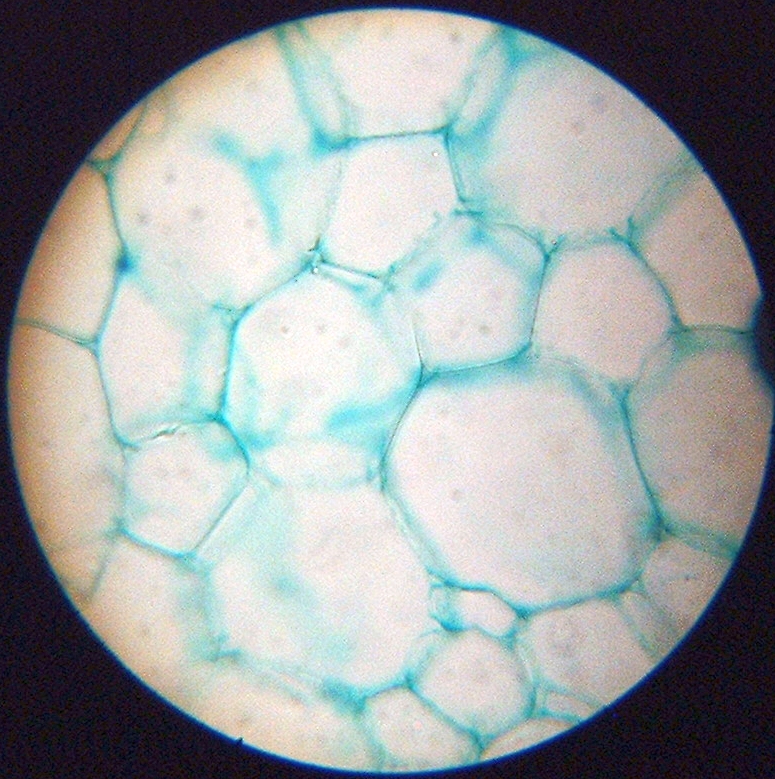
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Structure of parenchyma cell in plants (image source: Parenchyma cells are involved in the metabolic functions of the plant. The cells are found in many places throughout plant bodies and, given that they are alive, are actively involved in photosynthesis , secretion , food storage, and other activities of plant life. Collenchyma helps to provide strength to the plant’s stems, branches, leaves, and other structures. Parenchyma is a simple yet permanent tissue type that includes a major portion of the ground tissues for the plants with other having vascular ones.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Parenchyma in plants is found to be a living cell. In this tissue, only the parenchymatic cell type is present, which shows a thin primary cell wall. The cells provide mechanical support to the plant body. Parenchyma in plants is found to be a living cell. Ø they provide nourishment to the vascular tissues.
 Source: sciencefacts.net
Source: sciencefacts.net
8.1, 8.6) is a cell and tissue type in which the cells have only thin primary walls; In most plants, metabolic activity (such as respiration, digestion, and photosynthesis) occurs in these cells because they, unlike many of the other types of cells in the plant body, retain their protoplasts (the cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell. The cells have live nucleate protoplast concerned with various physiological activities in plants; In this tissue, only the parenchymatic cell type is present, which shows a thin primary cell wall. This strength allows plants to grow up without breaking from the weight of their own body.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Ø axial parenchyma and ray. Other articles where parenchyma cell is discussed: Structure of parenchyma cell in plants (image source: It is defined as the functional tissues in all higher plants. Ø they can also store ergastic substances like resins, tannins etc.
Source: sonuacademy.in
The cells provide mechanical support to the plant body. Provide mechanical rigidity to the plants; From the evolutionary point of view, the parenchymatic cell is regarded as the. Ø they provide nourishment to the vascular tissues. In terms of shape, they are classified to be isodiametric.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
In terms of shape, they are classified to be isodiametric. The storing parenchyma cells of phoenix, asparagus endosperm have extremely thick walls. In plants, parenchyma refers to a tissue composed of living cells, usually having only thin, primary cell walls and varying widely by morphology and metabolism. It is the least specialized among the permanent tissues. In contrast to collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells, parenchyma cells primarily consists of all of the simple, thin walled, undifferentiated cells which form a large majority of many plant tissues.
 Source: cronodon.com
Source: cronodon.com
In most plants, metabolic activity (such as respiration, digestion, and photosynthesis) occurs in these cells because they, unlike many of the other types of cells in the plant body, retain their protoplasts (the cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell. The parenchyma also acts as a storage tissue for food, air and water. From the evolutionary point of view, the parenchymatic cell is regarded as the. In plants, parenchyma refers to a tissue composed of living cells, usually having only thin, primary cell walls and varying widely by morphology and metabolism. It has a prominent and active protoplast and nucleus.
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
Parenchyma cells in plants are the formation of the bulk of the plant in the ground tissue, that have a special way to work in for storage of food or energy or water or even the waste material, photosynthesis, transport and exchange of gases. The cells are unspecialized, lack the characteristic wall of collenchyma and the secondary walls of sclerenchyma; In plants parenchyma refers to a distinct tissue type that has thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide. It is also distributed in pith , medullary rays & packing tissue in xylem and phloem. What is the function of collenchyma?
Source: thesaifworld.blogspot.com
In plants, parenchyma refers to a tissue composed of living cells, usually having only thin, primary cell walls and varying widely by morphology and metabolism. Parenchyma in plant cells is either polyhedral or isodiametric in shape. Parenchyma ( / pəˈrɛŋkɪmə /) is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. Parenchyma cells are typically alive in maturity and conduct most of the plant�s metabolic functions, such as storage of energy (mainly in the form of starch and fats) and waste products (tannin, resins, gums, etc.), support for photosynthesis (as are the cells containing chlorophyll), gaseous exchange (which takes place in the intercellular spaces) and damage. In plants parenchyma refers to a distinct tissue type that has thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Provide mechanical rigidity to the plants; Primary walls are common in parenchyma cells i.e., chlorophyllous and storing parenchyma. It is also distributed in pith , medullary rays & packing tissue in xylem and phloem. The cells have live nucleate protoplast concerned with various physiological activities in plants; Parenchyma cells in between the epidermis and pericycle in a root or shoot constitute the cortex, and tissue specialised for food storage commonly is parenchyma.
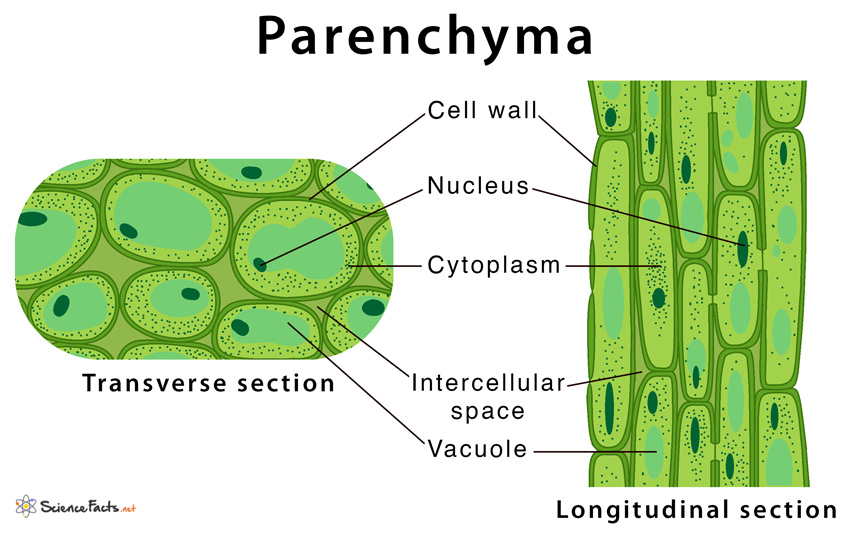 Source: sciencefacts.net
Source: sciencefacts.net
Other articles where parenchyma cell is discussed: In plants, parenchyma refers to a specific type of ground tissue with thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide. This strength allows plants to grow up without breaking from the weight of their own body. Parenchyma is a specific type of ground tissue having thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide. In this tissue, only the parenchymatic cell type is present, which shows a thin primary cell wall.
 Source: yaclass.in
Source: yaclass.in
Collenchyma helps to provide strength to the plant’s stems, branches, leaves, and other structures. It has a prominent and active protoplast and nucleus. The parenchyma is widely distributed in plant body such as stem , roots, leaves, flowers and fruits. In plants, parenchyma refers to a specific type of ground tissue with thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide. Parenchyma cells in between the epidermis and pericycle in a root or shoot constitute the cortex, and tissue specialised for food storage commonly is parenchyma.
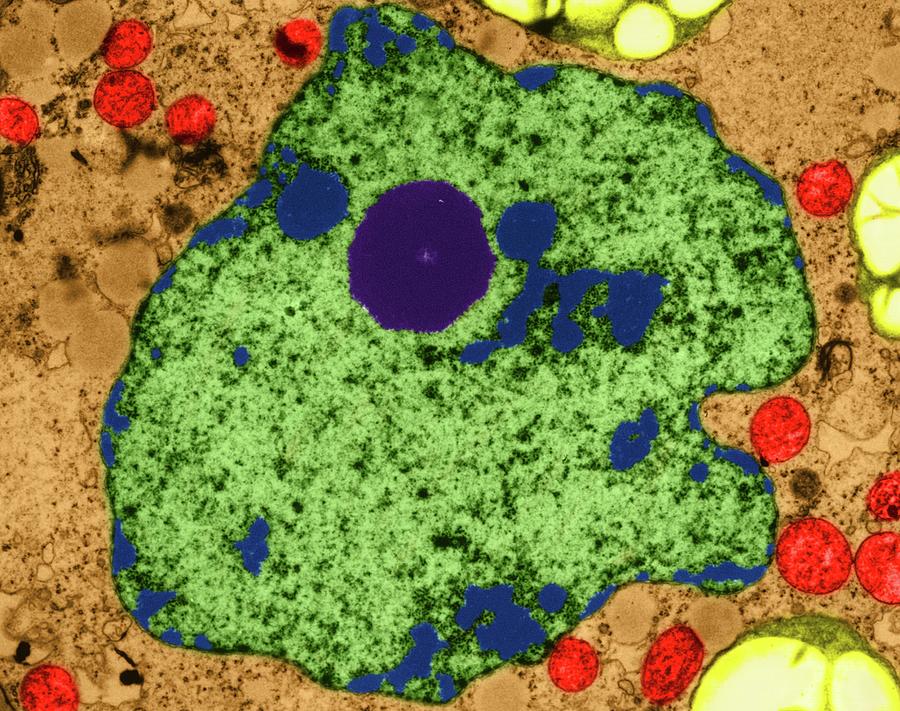 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Parenchyma cells are usually isodiametric or polyhedral in shape. Parenchyma is a simple yet permanent tissue type that includes a major portion of the ground tissues for the plants with other having vascular ones. Wikimedia) plant parenchyma cells are believed to be the precursor of differentiated and specialized cells and tissues. Parenchyma, the simple permanent ground tissues, form the bulk of the plant tissues, such as fruit pulp, the tender part of leaves and other plant organ. What is the function of collenchyma?
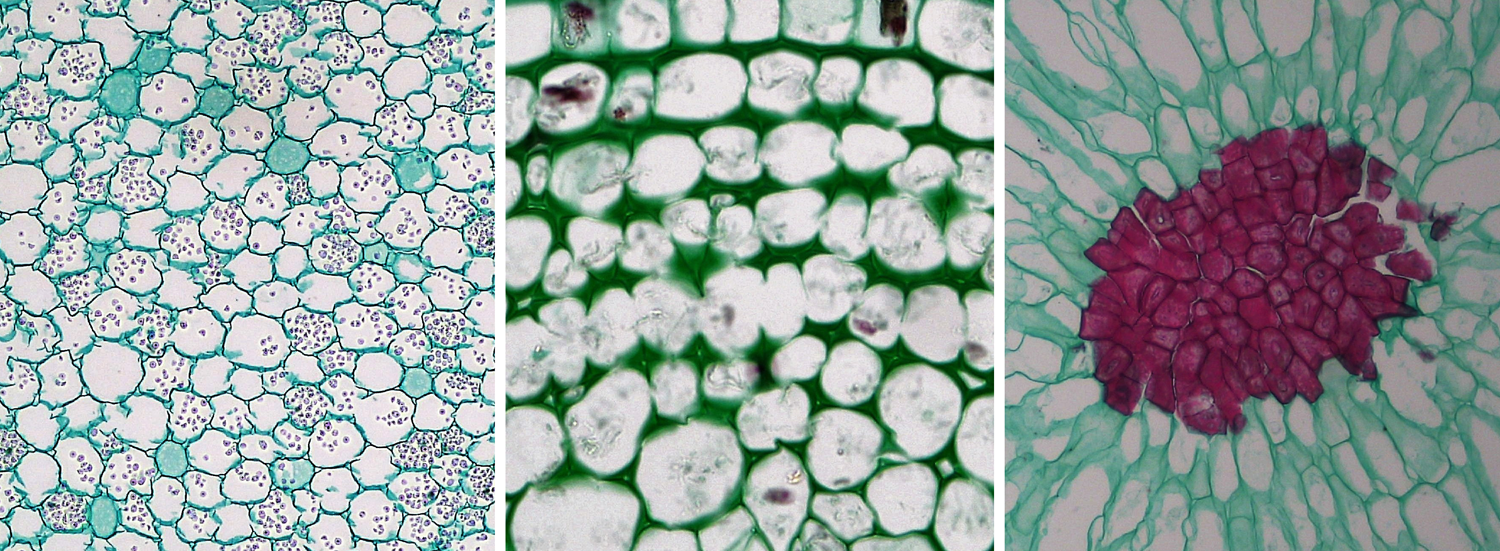 Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Ø they can also store ergastic substances like resins, tannins etc. Parenchyma tissue in plants position: Parenchyma cells contain a nucleus and when they are first formed, they are densely cytoplasmic and have several small vacuoles. Xylem parenchyma can be described as a component of the complex plant tissue xylem. It has a prominent and active protoplast and nucleus.
 Source: cronodon.com
Source: cronodon.com
The cells are found in many places throughout plant bodies and, given that they are alive, are actively involved in photosynthesis , secretion , food storage, and other activities of plant life. The cells provide mechanical support to the plant body. It is also distributed in pith , medullary rays & packing tissue in xylem and phloem. Parenchyma makes up most of the cells within leaves, flowers, and fruits. Ø they are the parenchyma cells occur in the vascular tissue of plants.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The cells have live nucleate protoplast concerned with various physiological activities in plants; Parenchyma in plants is discovered to be a living cell. In plants parenchyma refers to a distinct tissue type that has thin cell walls and the ability to grow and divide. Xylem parenchyma can be described as a component of the complex plant tissue xylem. Involved in photosynthesis and the exchange of gases through leaves.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Ø axial parenchyma and ray. Parenchyma ( / pəˈrɛŋkɪmə /) is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. They can likewise be oval, polygonal, lengthened, or round. The said cells are mostly concerned with the storage of fat and carbohydrate and transport of water. Pin by anything on plant tissue plant tissue epidermis cell.
 Source: sciencefacts.net
Source: sciencefacts.net
Other articles where parenchyma cell is discussed: From the evolutionary point of view, the parenchymatic cell is regarded as the. Parenchyma cells are usually isodiametric or polyhedral in shape. The said cells are mostly concerned with the storage of fat and carbohydrate and transport of water. In this tissue, only the parenchymatic cell type is present, which shows a thin primary cell wall.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title parenchyma in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.