Your Phenolics in plants images are available. Phenolics in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Phenolics in plants files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for phenolics in plants images information connected with to the phenolics in plants topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our site always provides you with hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Phenolics In Plants. Phenolics derived from amino acids and their precursors and some compounds which derived from shikimic acid pathway. For example, phenolics contribute to the bitterness and astringency of fruit and fruit juices, because of the interaction. They are ubiquitous in all plant organs and are therefore an integral part of the human diet. Classification of plant phenolics and 3.
 Simplified pathway of phenolic compound synthesis (adapted From researchgate.net
Simplified pathway of phenolic compound synthesis (adapted From researchgate.net
Some plant phenolics (for example, lignin, salicylic acid, and certain flavonoids) play pivotal roles in plant physiology. Simple flavonoids, phenolic acids, complex flavonoids and colored anthocyanins (figure 1). Phenolics are ubiquitous secondary metabolites found in plant. Plant phenolics can also modulate essential physiological processes such as transcriptional regulation and signal transduction. Phenolic compounds, the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, are found ubiquitously in algerian plant species. Flavonoids are the largest group of naturally occurring phenolic compounds, which occurs in different plant parts both in free state and as glycosides.
The compound classes based on the number of carbons and.
Phenolics play important roles in plant development, particularly in lignin and pigment biosynthesis. They are aromatic compounds synthesized by phenylpropanoid pathway. Phenolics derived from amino acids and their precursors and some compounds which derived from shikimic acid pathway. Notably, recent studies have reported new and surprising critical functions for plant phenolics, such as involvement in micronutrient. In relation to their chemical structure, these compounds contain at least one. Some plant phenolics (for example, lignin, salicylic acid, and certain flavonoids) play pivotal roles in plant physiology.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenolics derived from amino acids and their precursors and some compounds which derived from shikimic acid pathway. Phenolics play important roles in plant development, particularly in lignin and pigment biosynthesis. All phenolics could reduce integrity of dna and rna [47,49]. Some phenolics (i.e., ferulic acid and cinnamic acid) can inhibit protein synthesis.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Phenolics play important roles in plant development, particularly in lignin and pigment biosynthesis. Phenolics are widespread constituents of plant foods (fruits, vegetables, cereals, olive, legumes, chocolate, etc.) and beverages (tea, coffee, beer, wine, etc.), and partially responsible for the overall organoleptic properties of plant foods. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as contributing to plants’ colors. Phenolics are aromatic benzene ring compounds with one or more hydroxyl groups produced by plants mainly for protection against stress. Phenolics have been in the focus of many findings on plant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The functions of phenolic compounds in plant physiology and interactions with biotic and abiotic environments are difficult to overestimate. Phenolics derived from amino acids and their precursors and some compounds which derived from shikimic acid pathway. Phenolic compounds, or phenols, are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, biosynthesized via the pp, shikimate (sk), and phenylpropanoid (php) pathways in plants [277]. Others are proposed to be part of chemical defense, yet actual evidence is often lacking. They are ubiquitous in all plant organs and are therefore an integral part of the human diet.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
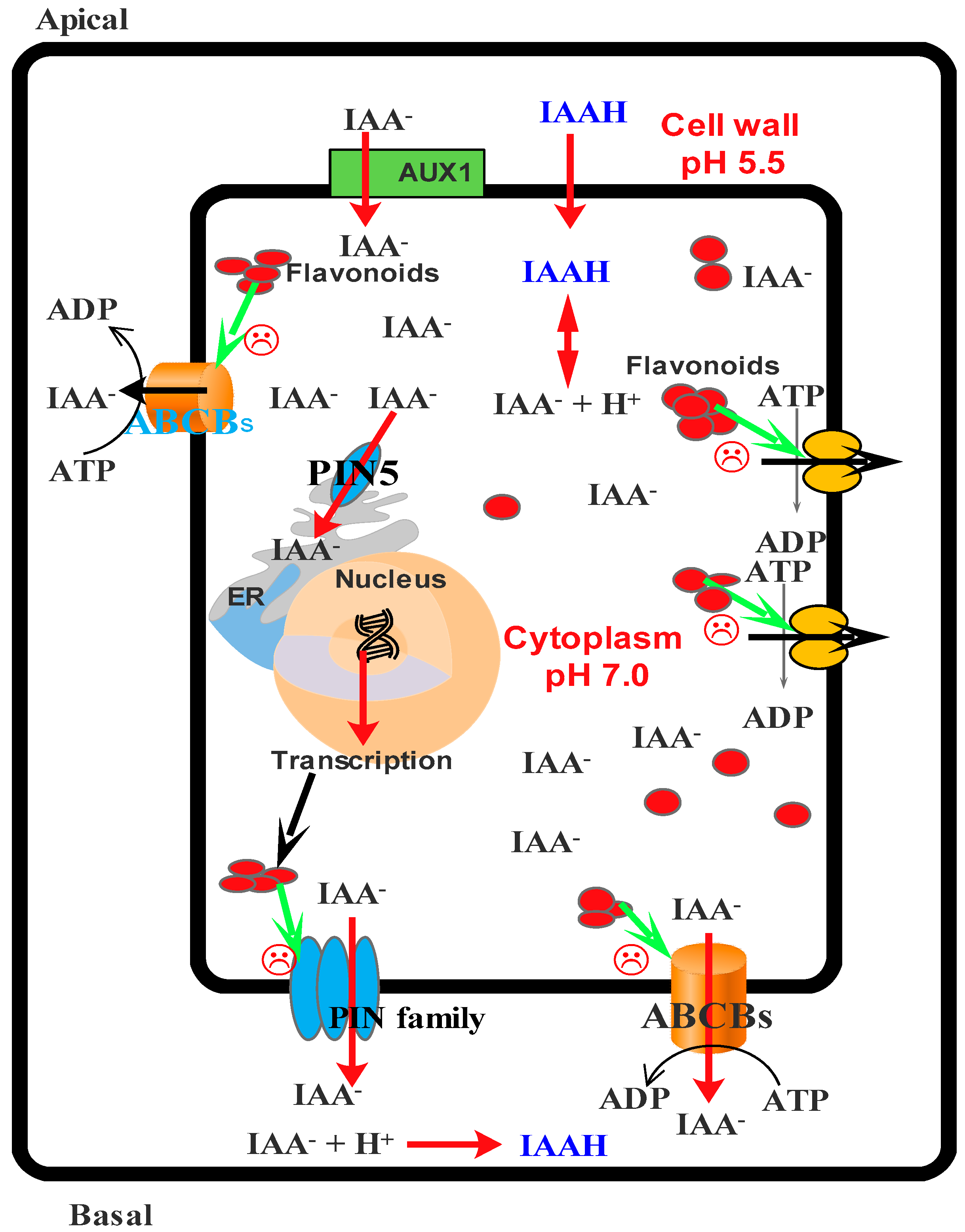
Lycopodiophyta (lycopods), pteridophyta (ferns and horsetails), angiosperms (flowering plants or magnoliophyta) and gymnosperms (conifers, cycads, ginkgo and gnetales). The functions of phenolic compounds in plant physiology and interactions with biotic and abiotic environments are difficult to overestimate. Phenolics derived from amino acids and their precursors and some compounds which derived from shikimic acid pathway. Classification of plant phenolics and 3. Some interesting effects of plant phenolics are also the ones associated with the growth hormone auxin.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenol itself is the simplest member of the class, although it is not found in plants. An additional role for flavonoids in functional pollen development has been observed. For example, phenolics contribute to the bitterness and astringency of fruit and fruit juices, because of the interaction. They also provide structural integrity and scaffolding support to plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In relation to their chemical structure, these compounds contain at least one. An additional role for flavonoids in functional pollen development has been observed. Phenol itself is the simplest member of the class, although it is not found in plants. All phenolics could reduce integrity of dna and rna [47,49]. Plant phenolics can also modulate essential physiological processes such as transcriptional regulation and signal transduction.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Notably, recent studies have reported new and surprising critical functions for plant phenolics, such as involvement in micronutrient. Flavonoids are the largest group of naturally occurring phenolic compounds, which occurs in different plant parts both in free state and as glycosides. Various phenolic acids have been found during the different stages of maturation 26 while growing conditions are known to have an impact on the phenolic acid content27. For example, phenolics contribute to the bitterness and astringency of fruit and fruit juices, because of the interaction. Phenolics phenolics are a huge and diverse group of aromatic compounds (containing benzene rings) usually with hydroxyl groups.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Some phenolics (i.e., ferulic acid and cinnamic acid) can inhibit protein synthesis. Phenolic compounds are mostly found in vascular plants (tracheophytes) i.e. Notably, recent studies have reported new and surprising critical functions for plant phenolics, such as involvement in micronutrient. In relation to their chemical structure, these compounds contain at least one. All phenolics could reduce integrity of dna and rna [47,49].
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Lycopodiophyta (lycopods), pteridophyta (ferns and horsetails), angiosperms (flowering plants or magnoliophyta) and gymnosperms (conifers, cycads, ginkgo and gnetales). They also provide structural integrity and scaffolding support to plants. Phenolics are widesp read constitu ents of plant foods (fruits, vegetables, cereals, olive, legumes, chocolate, etc.) and beverages (tea, coffee, beer, wine, etc. They are found to have many biological activities Flavanoids have role in functional pollen development in petunia plants.
 Source: quintaisimortais.blogspot.com
Source: quintaisimortais.blogspot.com
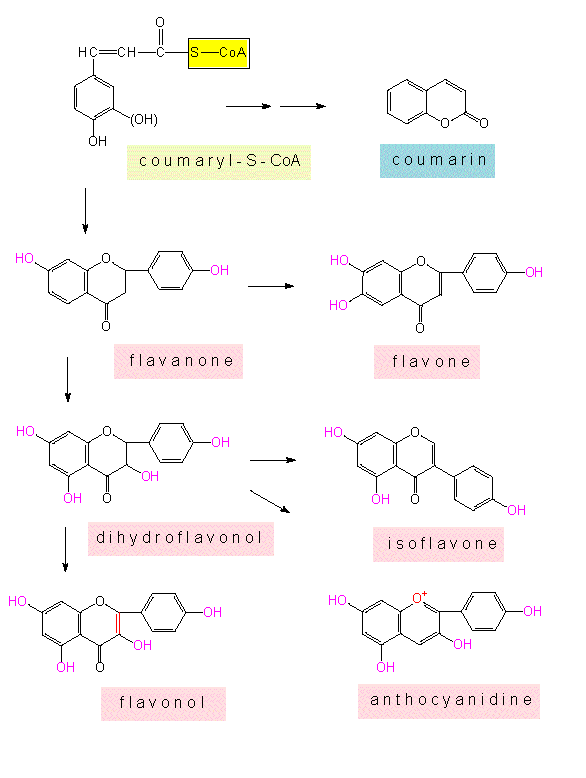
Flavonoids are the largest group of naturally occurring phenolic compounds, which occurs in different plant parts both in free state and as glycosides. Phenylpropanoids are a group of phenolics, it is a chemically diverse family of compounds ranging from simple phenolic acid to large and complex polymers such as tannins, lignin and flavonoid. However, in the vast majority of cases, phenolic compounds. Phenolics phenolics are a huge and diverse group of aromatic compounds (containing benzene rings) usually with hydroxyl groups. Phenolics are aromatic benzene ring compounds with one or more hydroxyl groups produced by plants mainly for protection against stress.
 Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
Some interesting effects of plant phenolics are also the ones associated with the growth hormone auxin. Thousands of organic compounds which contain one or more phenolic residue i.e., a functional hydroxyl group on a benzene ring are produced by plants and are called as phenolic compounds or plant phenolics. Phenolic compounds, the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, are found ubiquitously in algerian plant species. Flavanoids have role in functional pollen development in petunia plants. Phenolics play important roles in plant development, particularly in lignin and pigment biosynthesis.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Phenolics are widesp read constitu ents of plant foods (fruits, vegetables, cereals, olive, legumes, chocolate, etc.) and beverages (tea, coffee, beer, wine, etc. Plant phenolics can also modulate essential physiological processes such as transcriptional regulation and signal transduction. Phenolics have been in the focus of many findings on plant. For example, phenolics contribute to the bitterness and astringency of fruit and fruit juices, because of the interaction. Phenolics play important roles in plant development, particularly in lignin and pigment biosynthesis.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Phenolics have been in the focus of many findings on plant. Sativa can inhibit amino acid transport and protein synthesis, and the subsequent growth of treated plants. Phenolics are aromatic benzene ring compounds with one or more hydroxyl groups produced by plants mainly for protection against stress. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Importantly, phenolic phytoalexins, secreted by wounded or otherwise perturbed plants, repel or kill many microorganisms, and some pathogens can counteract or nullify these defences or.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
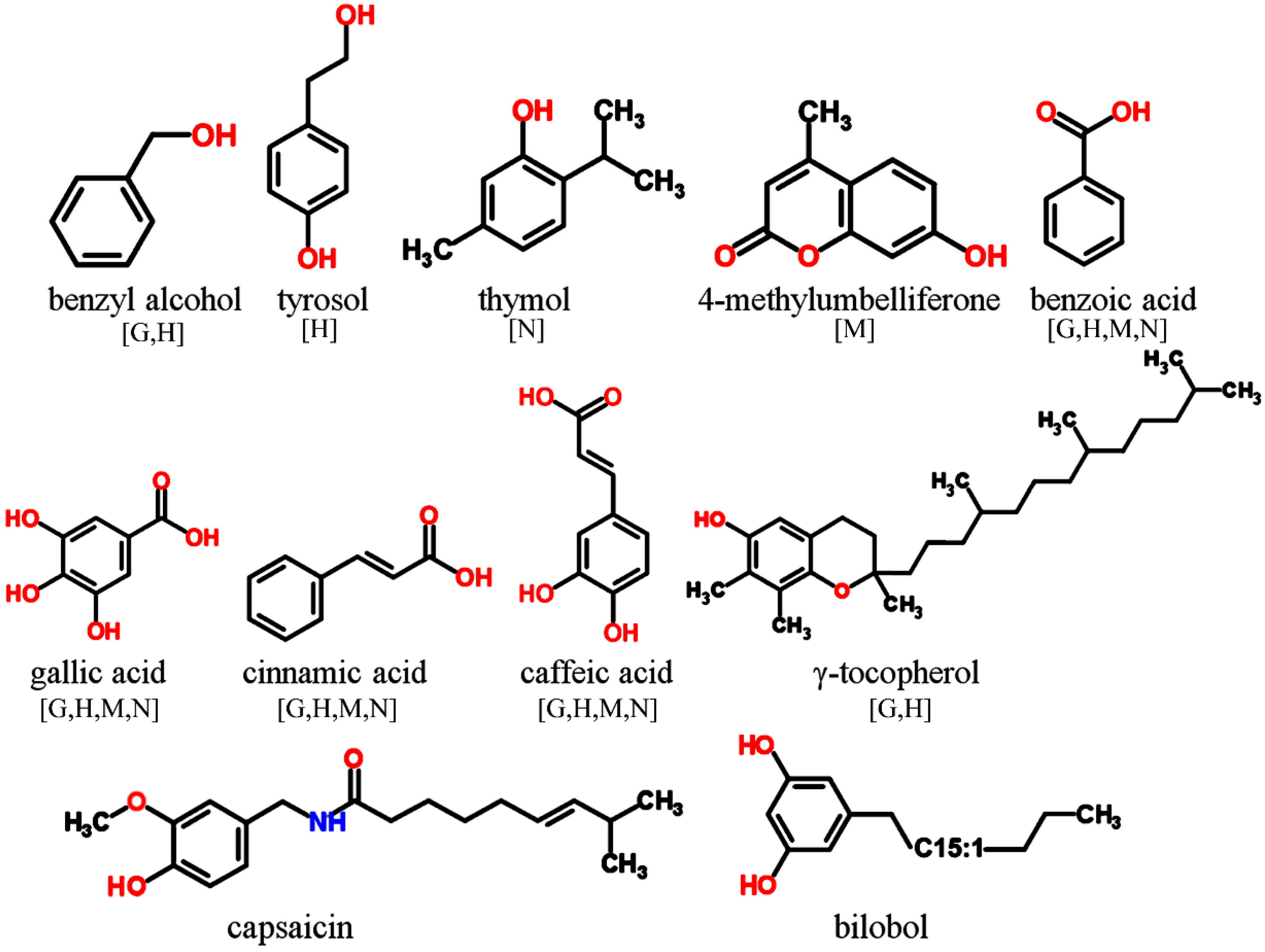
Phenolics derived from amino acids and their precursors and some compounds which derived from shikimic acid pathway. Each plant or plant product can be characterized by its unique phenolic profile however these extract are a complex mixture of phenolic compounds, sugars, fatty acids, and proteins. The compound classes based on the number of carbons and. They are ubiquitous in all plant organs and are therefore an integral part of the human diet. Lycopodiophyta (lycopods), pteridophyta (ferns and horsetails), angiosperms (flowering plants or magnoliophyta) and gymnosperms (conifers, cycads, ginkgo and gnetales).
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
In relation to their chemical structure, these compounds contain at least one. Others are proposed to be part of chemical defense, yet actual evidence is often lacking. They are aromatic compounds synthesized by phenylpropanoid pathway. The functions of phenolic compounds in plant physiology and interactions with biotic and abiotic environments are difficult to overestimate. Phenolics are the largest group of phytochemicals that account for most of the antioxidant activity in plants or plant products[3].
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Phenolic compounds, or phenols, are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, biosynthesized via the pp, shikimate (sk), and phenylpropanoid (php) pathways in plants [277]. Phenolics are often described as important in plant health and numerous studies have concluded they increase as a result of insect feeding, pathogen infection, or beneficial microorganism colonization. Phenolic compounds possess a common chemical structure comprising an aromatic ring with one or more hydroxyl substituents that can be divided into several classes, and the main groups of phenolic compounds include flavonoids, phenolic. Phenolic compounds are mostly found in vascular plants (tracheophytes) i.e. Phenolic compounds, or phenols, are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, biosynthesized via the pp, shikimate (sk), and phenylpropanoid (php) pathways in plants [277].
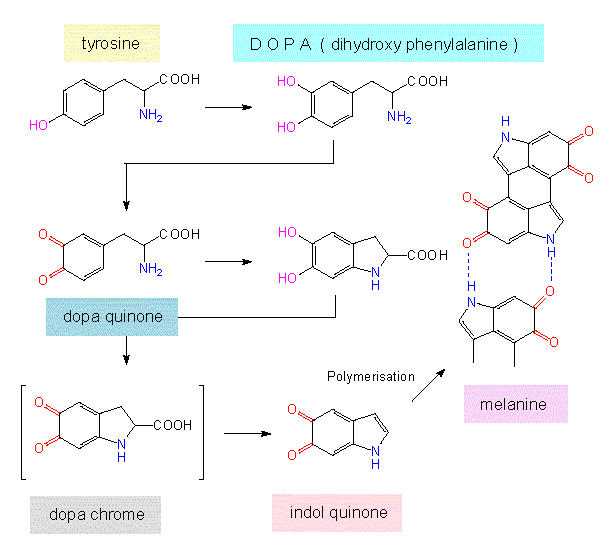 Source: s10.lite.msu.edu
Source: s10.lite.msu.edu
Phenolics are ubiquitous secondary metabolites found in plant. They are aromatic compounds synthesized by phenylpropanoid pathway. Phenolics are widespread constituents of plant foods (fruits, vegetables, An additional role for flavonoids in functional pollen development has been observed. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as contributing to plants’ colors.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Phenolics are ubiquitous secondary metabolites found in plant. Phenolic compounds, the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, are found ubiquitously in algerian plant species. Flavonoids are the largest group of naturally occurring phenolic compounds, which occurs in different plant parts both in free state and as glycosides. Sativa can inhibit amino acid transport and protein synthesis, and the subsequent growth of treated plants. The compound classes based on the number of carbons and.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title phenolics in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







