Your Pith in plants images are ready. Pith in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Pith in plants files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for pith in plants images information related to the pith in plants interest, you have come to the right site. Our site always provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
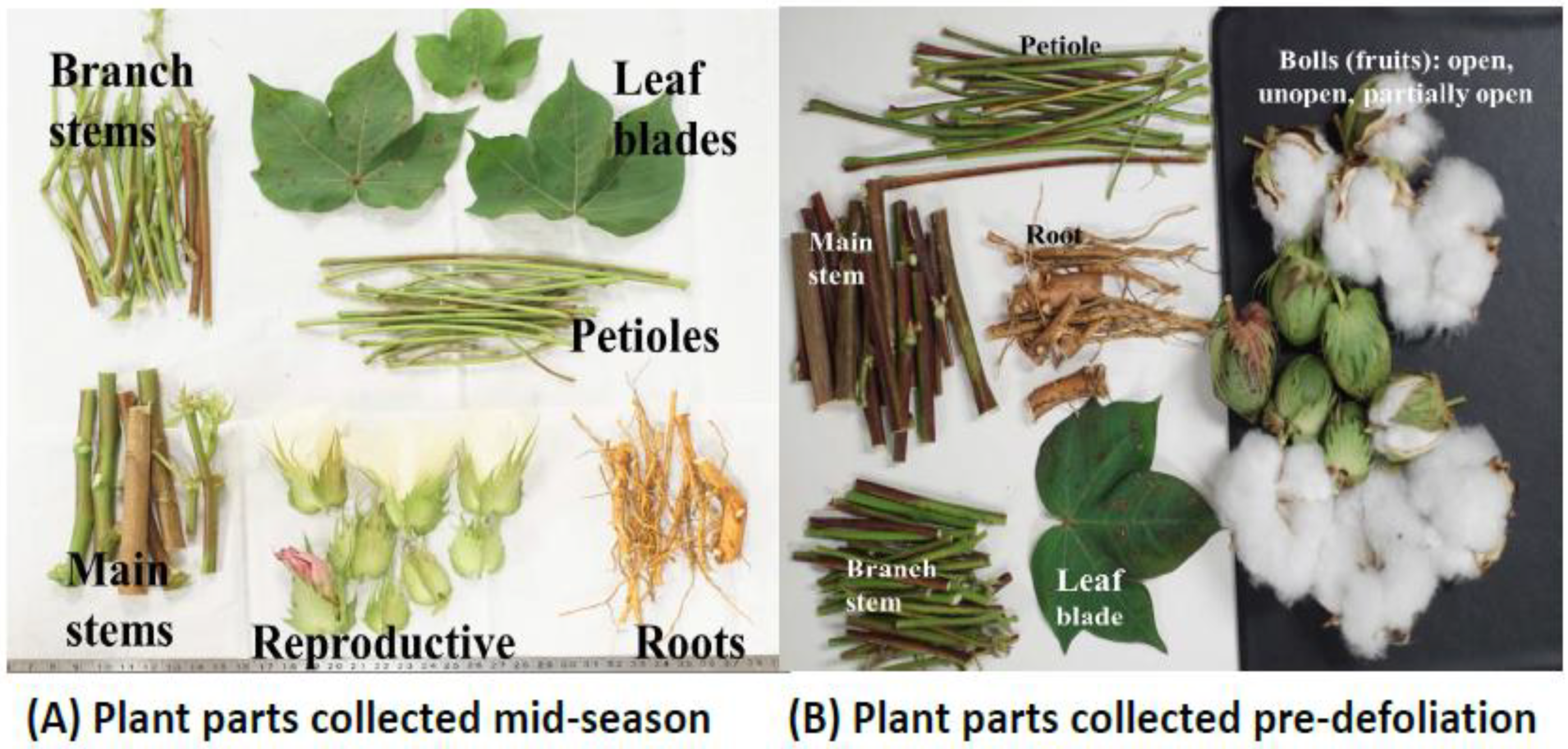
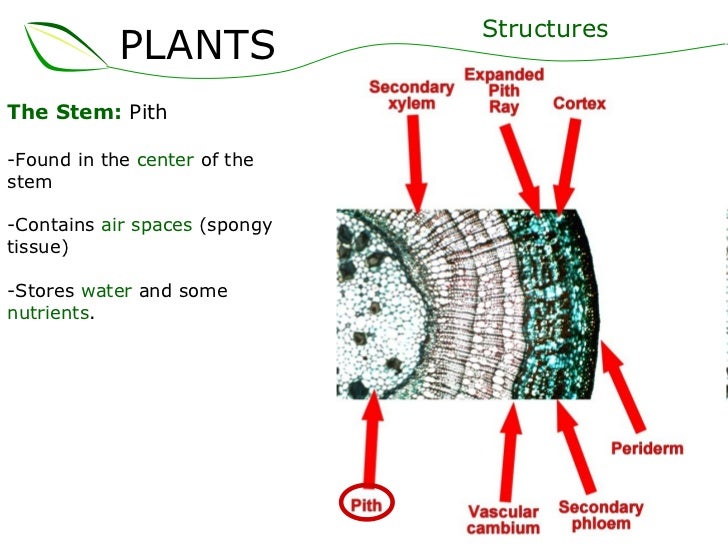
Pith In Plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. Pits are characteristic of cell walls with secondary layers. In monocots, it extends also into flowering stems and roots. It is mainly present in young growth;
 Pith The soft spongy and fibrous tissue in the stems of From plant-phytography.blogspot.com
Pith The soft spongy and fibrous tissue in the stems of From plant-phytography.blogspot.com
In monocotyledons, it extends also into flowering stems and roots. Pith definition, the soft, spongy central cylinder of parenchymatous tissue in the stems of dicotyledonous plants. Soft or spongy tissue in plants or animals, in particular: Answered by lifeeasy authors ask related question ← prev question next question → Another name for this tissue is the medulla. A usually continuous central strand of spongy tissue in the stems of most vascular plants that probably functions chiefly in storage…
A soft white substance that fills the stems of some plants examples from the corpus pith • small wonder that doctors are calling for the return of the parasol and.
The primary function of phloem is to transport sugar and amino acids to the plant. In monocotyledons, it extends also into flowering stems and roots. Our central hypothesis concerning the aetiology of pith autolysis states that the carbon from the pith is transported to the growth regions of the plant and used at times when the plant cannot meet its. It is mainly present in young growth; Pith /pɪθ/ noun [ uncountable] 1. This is particularly noticeable inside sunflower stems and their central cores, or steles.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Pith asked in stems by lifeeasy biology 1 answer 0 votes the important functions of pith are that it serves as a region of storag e of different substances such as the fatty substances, starch, mucilage and tannin etc. A white substance just under the outside skin of oranges and similar fruit peel the oranges with a sharp knife to remove all pith. A usually continuous central strand of spongy tissue in the stems of most vascular plants that probably functions chiefly in storage… Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Most of the higher vascular plants exhibit steles with pith in the centre.
 Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
A soft white substance that fills the stems of some plants examples from the corpus pith • small wonder that doctors are calling for the return of the parasol and. A soft white substance that fills the stems of some plants examples from the corpus pith • small wonder that doctors are calling for the return of the parasol and. Pith (pĭth) the soft, spongy tissue in the center of the stems of most flowering plants. Pits are characteristic of cell walls with secondary layers. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant.
 Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Pith is the innermost almost a cylindrical ground tissue; What is the function of the pith in a plant? Pits are characteristic of cell walls with secondary layers. The pith of young stem contains chloroplast whereas the mature stems possess abundant leucoplast. The pith cavity is similar to the cortex.
 Source: plant-phytography.blogspot.com
Source: plant-phytography.blogspot.com
Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. This is particularly noticeable inside sunflower stems and their central cores, or steles. It forms the central core of the stem.the cells are isodiametrical in shape. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. The pith of young stem contains chloroplast whereas the mature stems possess abundant leucoplast.
 Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Pith /pɪθ/ noun [ uncountable] 1. Definition of pith spongy tissue in animals and plants examples of pith in a sentence the heart of a watermelon is the best part because he pith tastes the best. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. In monocotyledons, it extends also into flowering stems and roots. Pith is a tissue present in the center of the stem of vascular plants.
 Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Pith is composed of parenchyma cells. Pits are characteristic of cell walls with secondary layers. How to use pith in a sentence. Pith (pĭth) the soft, spongy tissue in the center of the stems of most flowering plants. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem.
 Source: ohioplants.org
Source: ohioplants.org
Most of the higher vascular plants exhibit steles with pith in the centre. The cells of the stems differ from those of many seed plants in lacking collenchyma (modified parenchyma cells with expanded primary walls) and… Composed of parenchyma cells, the pith is gradually compressed by the inward growth of the vascular tissue known as xylem. Another name for this tissue is the medulla. The primary function of phloem is to transport sugar and amino acids to the plant.
 Source: cropprotectionnetwork.org
Source: cropprotectionnetwork.org
Soft or spongy tissue in plants or animals, in particular: Pith occupies the centre of stele and is composed of parenchyma cells. The meaning of pith is a usually continuous central strand of spongy tissue in the stems of most vascular plants that probably functions chiefly in storage. What is the function of the pith in a plant? In botany, pith is a term used to refer to a spongy, usually soft, substance that is found in the middle of the stems and roots of many plants.
 Source: u.osu.edu
Source: u.osu.edu
Definition of pith spongy tissue in animals and plants examples of pith in a sentence the heart of a watermelon is the best part because he pith tastes the best. These complementary pits are called pit pairs. In eudicots, pith is located in the center of the stem. Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. The pith cavity is similar to the cortex.
 Source: hgic.clemson.edu
Source: hgic.clemson.edu
Our central hypothesis concerning the aetiology of pith autolysis states that the carbon from the pith is transported to the growth regions of the plant and used at times when the plant cannot meet its. In monocotyledons, it extends also into flowering stems and roots. Pits are characteristic of cell walls with secondary layers. What is the function of the pith in a plant? In monocots, it extends also into flowering stems and roots.
 Source: www2.palomar.edu
Source: www2.palomar.edu
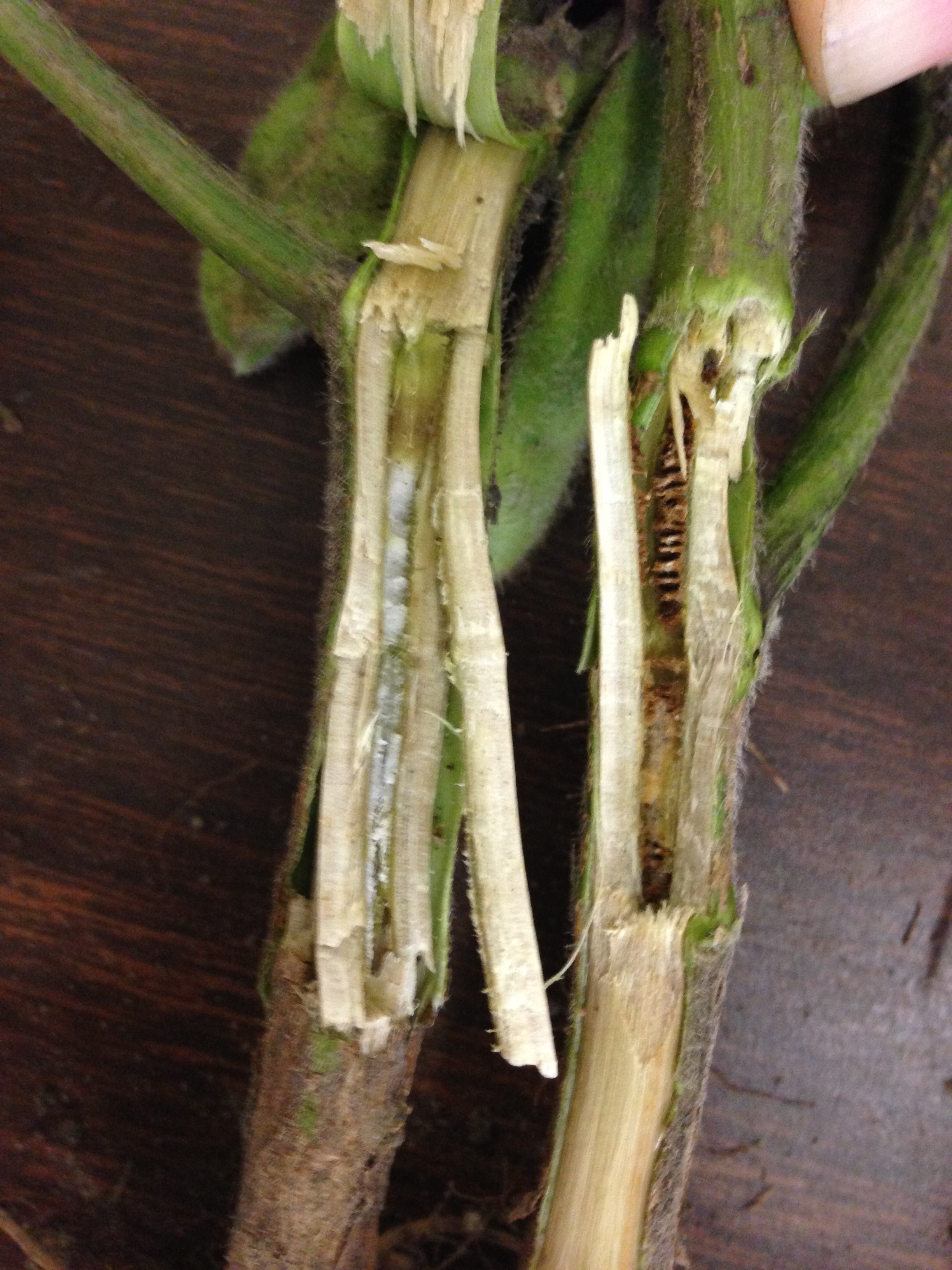
What is pith in plants? Pith autolysis, a condition in which dicotyledonous herbaceous plants have a hollow stem, results from the autolysis of a plant�s storage pith. Stem pith in the very center of many stems, you can see a spongy area. What is the function of the pith in a plant? Composed of parenchyma cells, the pith is gradually compressed by the inward growth of the vascular tissue known as xylem.
 Source: minnesotawildflowers.info
Source: minnesotawildflowers.info
It is made up of distinctive parenchyma cells. Answered by lifeeasy authors ask related question ← prev question next question → These complementary pits are called pit pairs. Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. It is made up of.
Source: indianahightunnels.blogspot.com
Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. Pith is composed of parenchyma cells. A usually continuous central strand of spongy tissue in the stems of most vascular plants that probably functions chiefly in storage… These complementary pits are called pit pairs.
 Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Source: plantpath.ifas.ufl.edu
Pith definition, the soft, spongy central cylinder of parenchymatous tissue in the stems of dicotyledonous plants. What is pith in plants? A white substance just under the outside skin of oranges and similar fruit peel the oranges with a sharp knife to remove all pith. Pith (pĭth) the soft, spongy tissue in the center of the stems of most flowering plants. Because the center of the meat is raw, make sure the pith isn’t bloody when served.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Pith is the innermost almost a cylindrical ground tissue; Pits are characteristic of cell walls with secondary layers. Most of the higher vascular plants exhibit steles with pith in the centre. Soft or spongy tissue in plants or animals, in particular: In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Pith remains surrounded by xylem that in turn is surrounded by phloem on the peripheral side (ectophloic siphonostele) only or on both outside and inside (amphiphloic siphonostele). Pith (pĭth) the soft, spongy tissue in the center of the stems of most flowering plants. Pith asked in stems by lifeeasy biology 1 answer 0 votes the important functions of pith are that it serves as a region of storag e of different substances such as the fatty substances, starch, mucilage and tannin etc. Pith is composed of parenchyma cells. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem.
 Source: novascotiavegetableblog.com
Source: novascotiavegetableblog.com
It is soft and spongy. What is the function of the pith in a plant? Pith remains surrounded by xylem that in turn is surrounded by phloem on the peripheral side (ectophloic siphonostele) only or on both outside and inside (amphiphloic siphonostele). The medulla tissue is made up of a particular type of plant cell, called parenchyma cells, which tend to be relatively large, with thin cell walls. Soft or spongy tissue in plants or animals, in particular:
 Source: biolib.cz
Source: biolib.cz
Composed of parenchyma cells, the pith is gradually compressed by the inward growth of the vascular tissue known as xylem. The pith of young stem contains chloroplast whereas the mature stems possess abundant leucoplast. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. A white substance just under the outside skin of oranges and similar fruit peel the oranges with a sharp knife to remove all pith. Pith asked in stems by lifeeasy biology 1 answer 0 votes the important functions of pith are that it serves as a region of storag e of different substances such as the fatty substances, starch, mucilage and tannin etc.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title pith in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.