Your Plant cell in isotonic solution images are available. Plant cell in isotonic solution are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Plant cell in isotonic solution files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for plant cell in isotonic solution images information related to the plant cell in isotonic solution interest, you have come to the right site. Our site always gives you suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
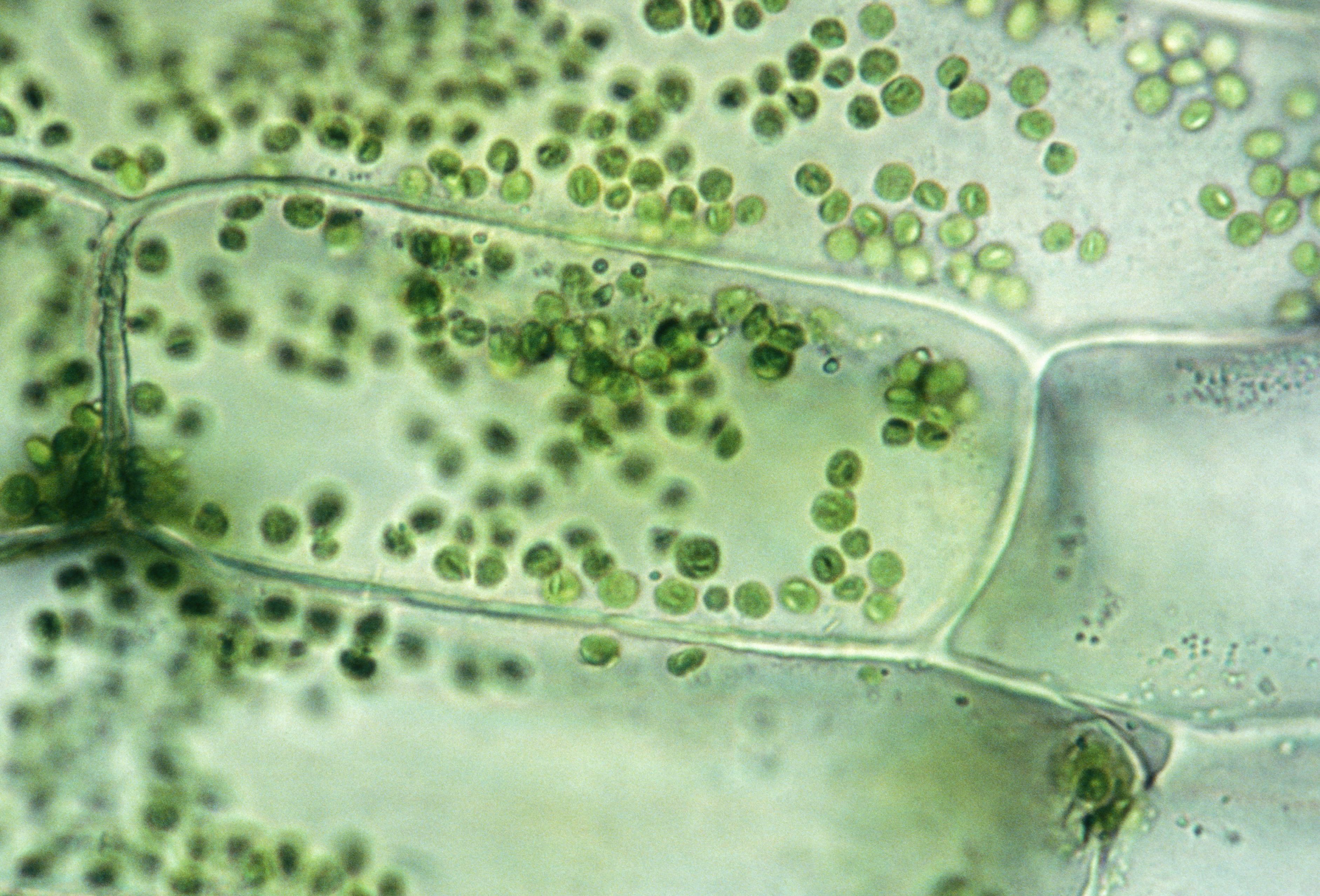
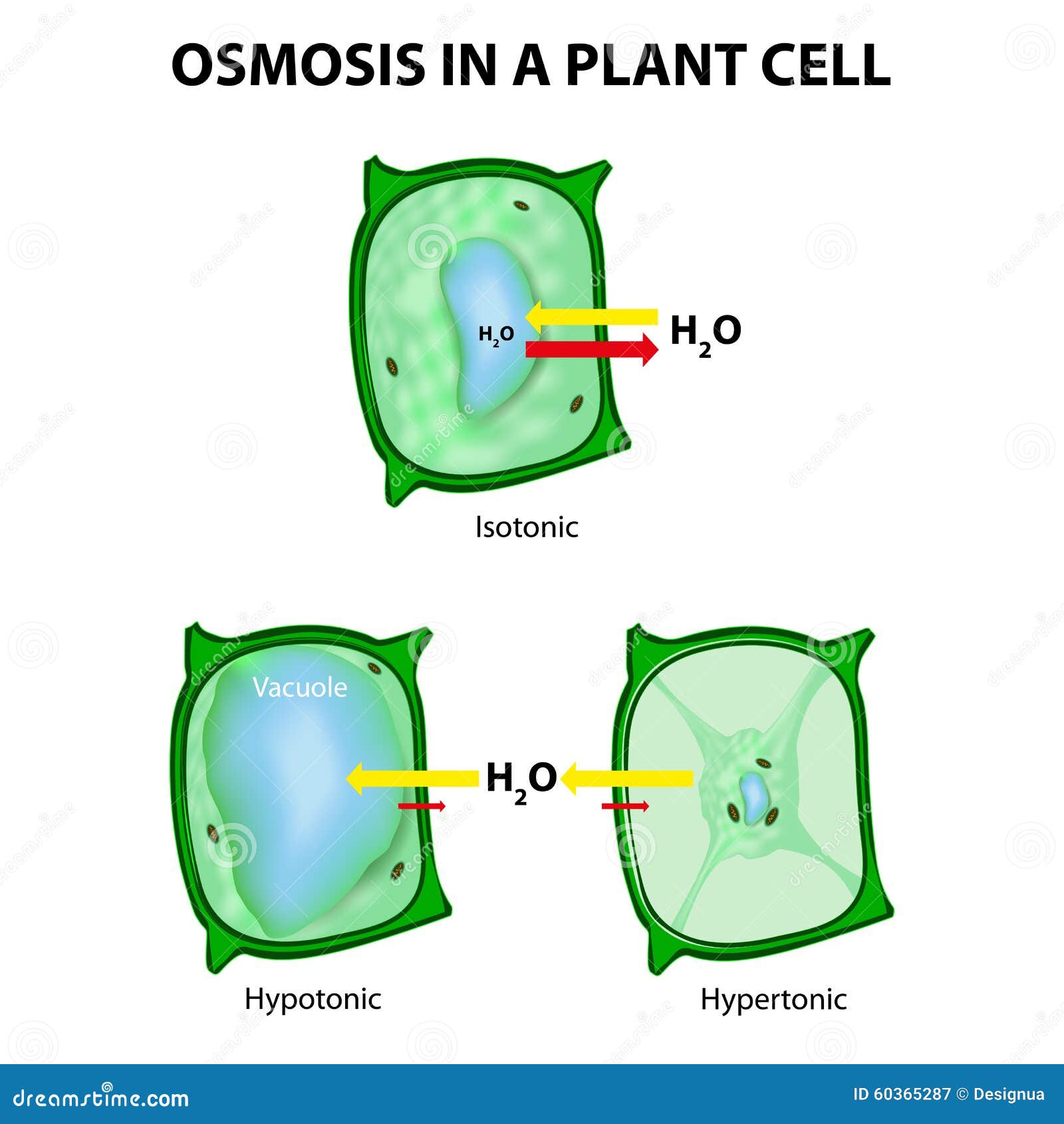
Plant Cell In Isotonic Solution. When water enters the plant cell, the cell swells up. As a result, the cell membrane is pushed towards the plant cell wall. When the flow of water into the cell and out of the cell exists in equilibrium then the plant cells are said to be flaccid. When the plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water towards the outside or inside.
 Learn About Plant Cell Types and Organelles From thoughtco.com
Learn About Plant Cell Types and Organelles From thoughtco.com
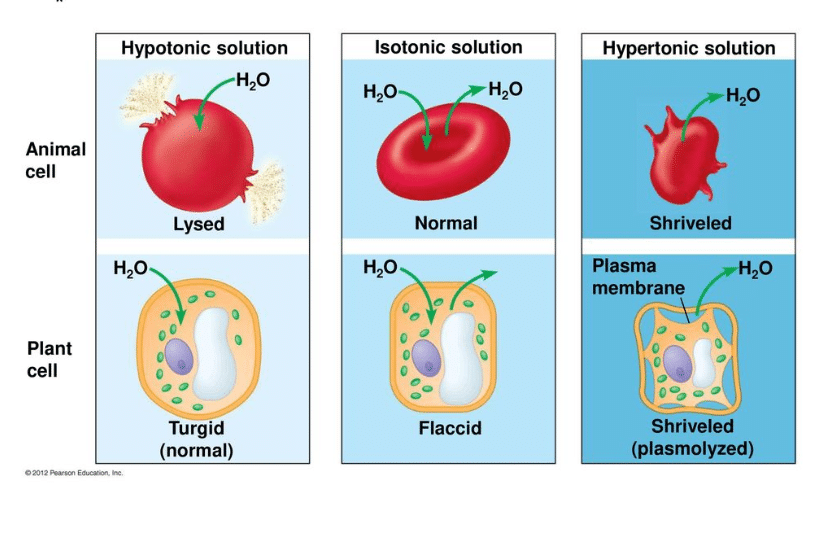
The cell retain their normal shape. This is because there is no net movement of water between the cell and the solution and thus. The red blood cell is said to have undrgone creanation. If you place an animal or a plant cell in a hypertonic solution, the cell shrinks, because it loses water ( water moves from a higher concentration inside the cell to a. When the plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, it. An isotonic solution refers to two solutions having the same osmotic pressure across a semipermeable membrane.
�incipient� means �about to be�.
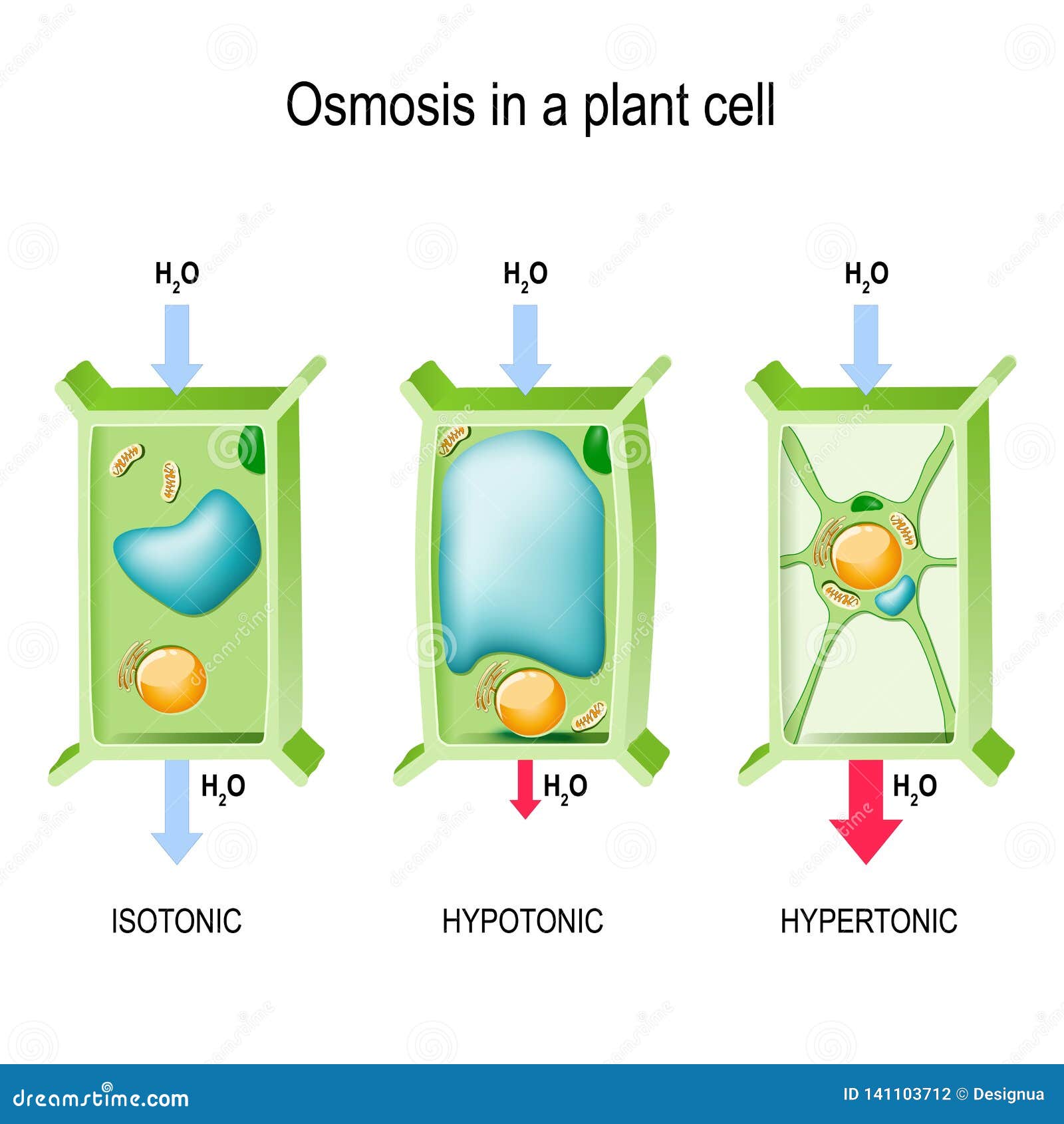
When cells are in isotonic solution, movement of water out of the cell is exactly balanced by movement of water into the cell. The solution is isotonic in relation to the cell. The cell wall can avoid the cell bursting. Though water diffuses in and out there is. When this happens, the green parts of the plant droop and are unable to hold the leaves up in the sunlight. Hypotonic conditions are ideal for plants, with osmotic pressure building turgor against the cell wall providing rigidity.
 Source: showme.com
Source: showme.com
Plant cells exposed to isotonic conditions will lose turgor pressure and become flaccid. Hypertonic solutions have less water ( and more solute such as salt or sugar ) than a cell. Secondly, what happens to a plant cell in a hypotonic solution? What happens when a plant cell is placed in isotonic solution? If you place an animal or a plant cell in a hypertonic solution, the cell shrinks, because it loses water ( water moves from a higher concentration inside the cell to a.
 Source: driverlayer.com
Source: driverlayer.com
When water enters the plant cell, the cell swells up. The external solution equals the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. When the flow of water into the cell and out of the cell exists in equilibrium then the plant cells are said to be flaccid. When the plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water towards the outside or inside. Hence, there will not be any change in cells.
 Source: slidedocnow.blogspot.com
Source: slidedocnow.blogspot.com
When kept in isotonic solutions, there is no change in the size. In this state there is no concentration gradient and therefore, no large movement of water in or out. What happens when you place a plant cell in a isotonic solution? An isotonic solution is defined as two solutions of equal concentrations of solutes and water separated by a semipermeable membrane to allow water to move freely in and out of a. If animal and plant cells are kept in isotonic solution then cells will not swell or shrink.
 Source: geteducationskills.com
Source: geteducationskills.com
�incipient� means �about to be�. The solution and solute percentage are the same inside the cell as it is in the solution outside of the cell. An isotonic solution is a solution, which contains the same concentration of solute as in a cell. The solution is isotonic in relation to the cell. A 0.9% solution of nacl (saline) is isotonic to animal cells.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
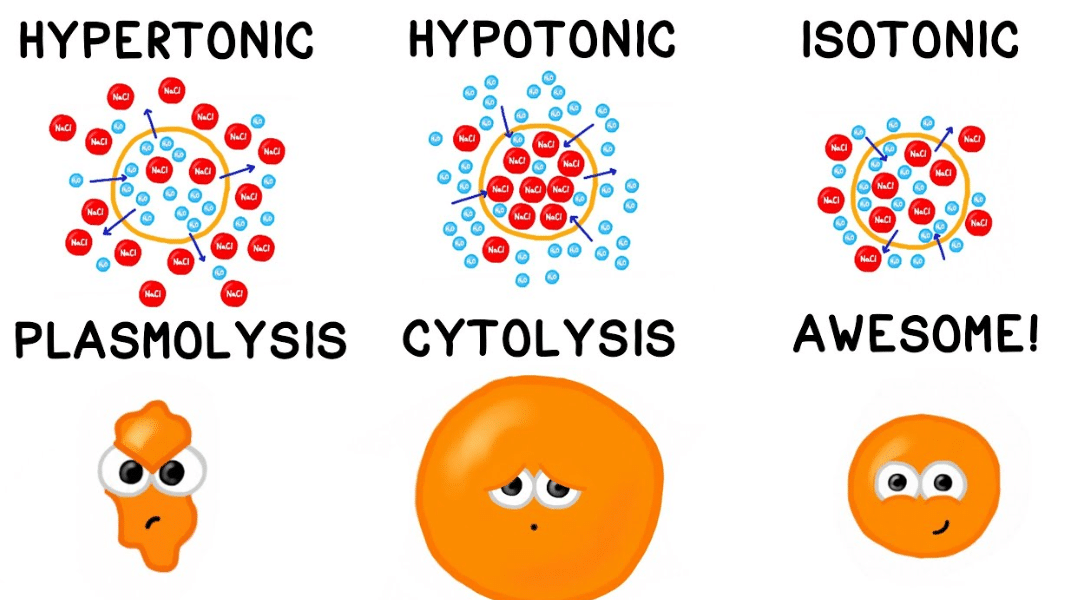
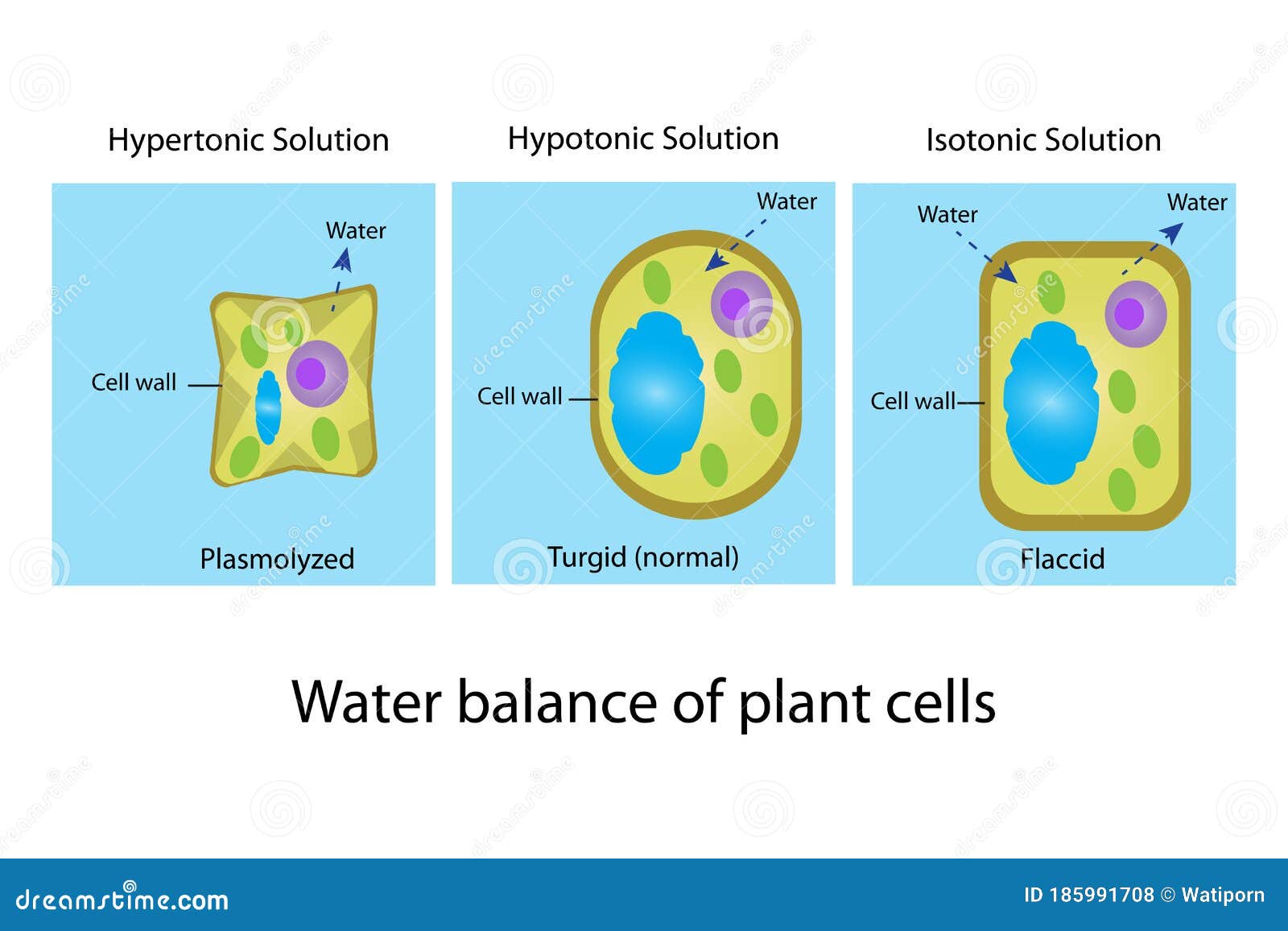
Terms in this set (13) isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic refer the effects of ___ on a cell. Hypotonic conditions are ideal for plants, with osmotic pressure building turgor against the cell wall providing rigidity. The solution and solute percentage are the same inside the cell as it is in the solution outside of the cell. There are observable changes in hypertonic and hypotonic solutions, however, if there is a sufficient difference in the osmotic gradient. If a plant cell is kept in a hypertonic solution then the plant cell loses water and becomes plasmolysed because of osmosis.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Plant cells exposed to isotonic conditions will lose turgor pressure and become flaccid. �incipient� means �about to be�. The external solution equals the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. When the plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water towards the outside or inside. Nothing happens to a plant cell in an isotonic solution.

During convex plasmolysis, the plasma membrane and the enclosed protoplast shrinks completely from the cell wall, with the plasma membrane’s ends in a symmetrically, spherically curved pattern. The external solution equals the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. The added water will make the solution hypertonic to the cell, and water will; Plant cells exposed to isotonic conditions will lose turgor pressure and become flaccid. The solution is isotonic in relation to the cell.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Why do plant cells shrink in hypertonic solution? The cytoplasm of the cell is more concentrated than the isotonic solvent outside of. When the plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water towards the outside or inside. During convex plasmolysis, the plasma membrane and the enclosed protoplast shrinks completely from the cell wall, with the plasma membrane’s ends in a symmetrically, spherically curved pattern. Thus, the cell remains the same size.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
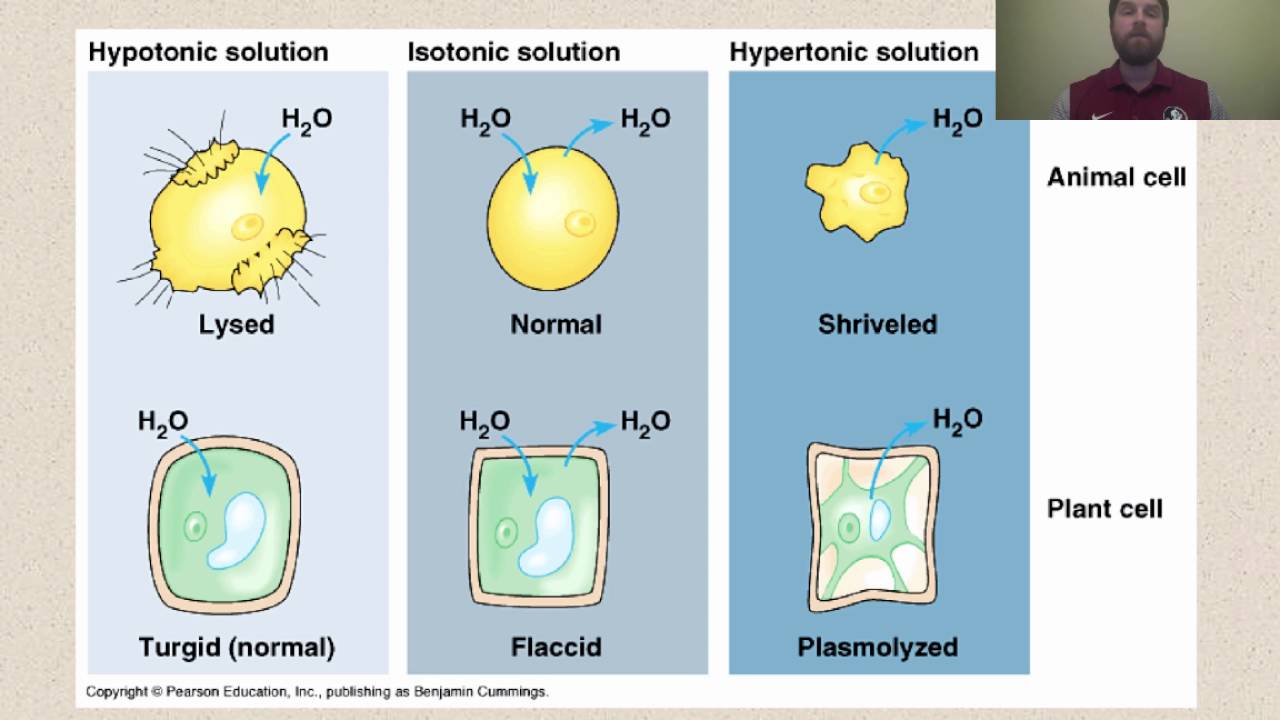
Thus, the cell remains the same size. Therefore the rate of diffusion of water into the cell is equal to the rate of diffusion of water out from the cell. Hypertonic solutions have less water ( and more solute such as salt or sugar ) than a cell. A cell placed in a hypotonic solution will swell up or gain water, and it can possibly rupture if the excess water inside the cell is not removed. This process is turgidity, or we call this swelled cell a “turgid cell”.
 Source: desertbruchid.net
Source: desertbruchid.net
During convex plasmolysis, the plasma membrane and the enclosed protoplast shrinks completely from the cell wall, with the plasma membrane’s ends in a symmetrically, spherically curved pattern. The added water will make the solution hypotonie to the cell, and water will leave the call by osmosis ob. Isotonic solution no net gain or loss of water. The red blood cell is said to have undrgone creanation. There are observable changes in hypertonic and hypotonic solutions, however, if there is a sufficient difference in the osmotic gradient.
 Source: cbse-notes.blogspot.com
Source: cbse-notes.blogspot.com
The effect of an isotonic solution is the same but not as obvious because of the rigid wall. The added water will make the solution hypertonic to the cell, and water will; Additional pure water is then added to the solution. As a result, the cell membrane is pushed towards the plant cell wall. Isotonic solutions are solutions that have the same concentration of solute.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
A 0.9% solution of nacl (saline) is isotonic to animal cells. If one of the solution is a cell, then water will diffuse both in and out of the cell, which causes no net effect on the cell. When a plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution solute concentration in the external solution is equal to the solute concentration i the cell sap. Animal and plant cell in an isotonic solution • isotonic solution is a solution in which the concentration of solutes is equal, so: When the plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water towards the outside or inside.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The red blood cell is said to have undrgone creanation. Plant cells have a cell wall surrounding the plasma membrane. Terms in this set (13) isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic refer the effects of ___ on a cell. The external solution equals the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. An isotonic solution is a solution, which contains the same concentration of solute as in a cell.
 Source: blog.justaquatic.com.au
Source: blog.justaquatic.com.au
Therefore, using the numbers above, a cell placed in a solution of water with 0.9% nacl is in equilibrium. A cell placed in a hypotonic solution will swell up or gain water, and it can possibly rupture if the excess water inside the cell is not removed. In this state there is no concentration gradient and therefore, no large movement of water in or out. The solution is isotonic in relation to the cell. When kept in isotonic solutions, there is no change in the size.
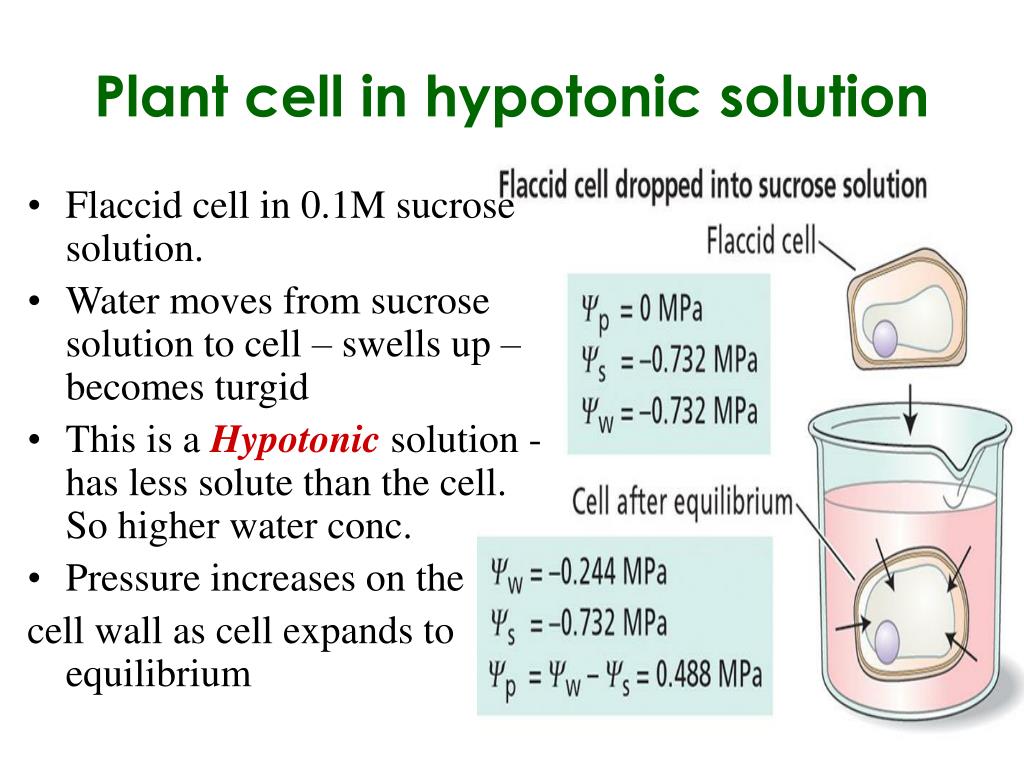 Source: colemanmagilied15111.blogspot.com
Source: colemanmagilied15111.blogspot.com
The solution is isotonic in relation to the cell. When water enters the plant cell, the cell swells up. Therefore, using the numbers above, a cell placed in a solution of water with 0.9% nacl is in equilibrium. If one of the solution is a cell, then water will diffuse both in and out of the cell, which causes no net effect on the cell. The red blood cell is said to have undrgone creanation.
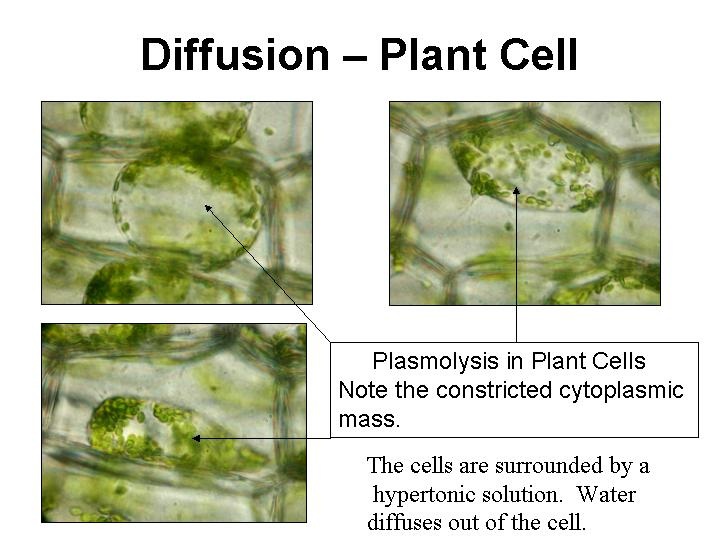 Source: maggiesscienceconnection.weebly.com
Source: maggiesscienceconnection.weebly.com
What happens when a plant cell is placed in isotonic solution? The cytoplasm of the cell is more concentrated than the isotonic solvent outside of. When the plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water towards the outside or inside. When this happens, the green parts of the plant droop and are unable to hold the leaves up in the sunlight. Nothing happens to a plant cell in an isotonic solution.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A plant cell in hypotonic solution will absorb water by endosmosis, so that the increased volume of water in the cell will increase pressure, making the protoplasm push against the cell wall, a condition known as turgor. This state allows for the free movement of water across the membrane without changing the concentration of solutes on either side. The external solution equals the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. If a plant cell is kept in a hypertonic solution then the plant cell loses water and becomes plasmolysed because of osmosis. The external solution equals the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm.
 Source: vectormine.com
Source: vectormine.com
In a plant cell the shrinking of protoplasm is called? When the plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water towards the outside or inside. When cells are in isotonic solution, movement of water out of the cell is exactly balanced by movement of water into the cell. When the flow of water into the cell and out of the cell exists in equilibrium then the plant cells are said to be flaccid. The osmolarity of both fluids is equal.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant cell in isotonic solution by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






