Your Plant chemical defense images are ready. Plant chemical defense are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Plant chemical defense files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for plant chemical defense images information connected with to the plant chemical defense interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
Plant Chemical Defense. The chemical defenses of plants can be induced or constitutive (constant) (baldwin 1998, sirvent and gibson 2002, agrawal 1998). All plants produce a diverse group of chemicals whose main function is to protect the plant against herbivores and diseases; In rosenthal da, janzen dh (eds) herbivores their interaction with secondary plant metabolites. (eds) biochemical interaction between plants and insects.
 Plant Defense Priming against Herbivores Getting Ready From plantphysiol.org
Plant Defense Priming against Herbivores Getting Ready From plantphysiol.org
Primary metabolites are substances produced by all plant cells that are directly involved in growth, development, or reproduction. Examples include sugars, proteins, amino acids, and nucleic acids. Induced responses are changes in a plant following 1. On planet earth, the green plants (autotrophs) constitute the only Plants are often attacked by multiple enemies, including pathogens and herbivores. Roots anchor them to the soil, so plants can’t run away.
Structural defense mechanism the surface of the plant or host is first line of defense against the pathogen.
On planet earth, the green plants (autotrophs) constitute the only In this opinion article, we examine how the costs of plant chemical defense can be offset by multifunctional biosynthesis and the optimization of primary metabolism. While many plant secondary metabolites show specific effects toward either pathogens or herbivores, some can affect the performance of both these groups of natural enemies and are considered to be generalized defense compounds. The dieffenbachia, a common houseplant, contains idioblasts that fire barbed calcium oxalate crystals into the mouths of predators and then release an enzyme analogous to reptilian venom. These defenses make it difficult for. Many of these compounds seem to have no role in such core plant functions as growth and reproduction, and they are synthesized in unique pathways in the plant.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A chemical defence mechanism is an inbuilt characteristic of a plant that is activated by a specific event such as touch or movement. Adaptation to certain plant chemicals whereby. The chemical defenses of plants constitute a major obstacle to herbivore feeding. Physical defenses are a first line of protection for many plants. Plants diseases or phytopathogens affects plants right from the planting stage up to the harvesting and storage of the produce.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
The pathogen must adhere to the surface and penetrate, if it is to cause infection. The role of plant secondary compounds w. Primary metabolites and secondary metabolites. Plants have evolved a plethora of different chemical defenses covering nearly all classes of (secondary) metabolites that represent a major barrier to herbivory: Herbivory or infection that lower the preference, performance, or pathogenicity of the attacker on
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Plants are often attacked by multiple enemies, including pathogens and herbivores. Plants diseases or phytopathogens affects plants right from the planting stage up to the harvesting and storage of the produce. When activated, these cells release chemicals that are either distasteful, harmful or poisonous to the offender. All plants produce a diverse group of chemicals whose main function is to protect the plant against herbivores and diseases; The costs of plant chemical defense can be offset by multifunctional biosynthesis and the optimization of primary metabolism.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
This is due to an evolutionary. Plant chemical defense is highly complex. In this opinion article, we examine how the costs of plant chemical defense can be offset by multifunctional biosynthesis and the optimization of primary metabolism. These strategies either act independently or in conjunction with each other. Chemical defenses plant chemicals can be divided into two major categories:
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
The chemical defenses of plants can be induced or constitutive (constant) (baldwin 1998, sirvent and gibson 2002, agrawal 1998). While many plant secondary metabolites show specific effects toward either pathogens or herbivores, some can affect the performance of both these groups of natural enemies and are considered to be “generalized defense compounds”. While many plant secondary metabolites show specific effects toward either pathogens or herbivores, some can affect the performance of both these groups of natural enemies and are considered to be generalized defense compounds. The pathogen must adhere to the surface and penetrate, if it is to cause infection. (1976) plant apparency and chemical defense.
 Source: gels.okayama-u.ac.jp
Source: gels.okayama-u.ac.jp
Induced responses are changes in a plant following 1. While many plant secondary metabolites show specific effects toward either pathogens or herbivores, some can affect the performance of both these groups of natural enemies and are considered to be “generalized defense compounds”. In rosenthal da, janzen dh (eds) herbivores their interaction with secondary plant metabolites. Physical defenses are a first line of protection for many plants. Volatiles which can alert neighbor plants or tissues to potential attacks are promoted by herbivory and are a complex blend.
![[PDF] Plant defense against herbivores chemical aspects [PDF] Plant defense against herbivores chemical aspects](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/25e5a1dc02db90ee0158f2d604b4409ea3aba3fe/9-Figure5-1.png) Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
If the first line of defense is breached, the plant must resort to a different set of defense mechanisms, such as toxins and enzymes. All plants produce a diverse group of chemicals whose main function is to protect the plant against herbivores and diseases; Recent advances in phytochemistry, vol 10. The pathogen must adhere to the surface and penetrate, if it is to cause infection. Chemical defenses of the host plant than are.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
While many plant secondary metabolites show specific effects toward either pathogens or herbivores, some can affect the performance of both these groups of natural enemies and are considered to be generalized defense compounds. Volatiles which can alert neighbor plants or tissues to potential attacks are promoted by herbivory and are a complex blend. The costs of plant chemical defense can be offset by multifunctional biosynthesis and the optimization of primary metabolism. While many plant secondary metabolites show specific effects toward either pathogens or herbivores, some can affect the performance of both these groups of natural enemies and are considered to be generalized defense compounds. Physical defenses are a first line of protection for many plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Others are induced after attack. (eds) biochemical interaction between plants and insects. Primary metabolites are substances produced by all plant cells that are directly involved in growth, development, or reproduction. On planet earth, the green plants (autotrophs) constitute the only Chemical defense is a life history strategy employed by many organisms to avoid consumption by producing toxic or repellent metabolites.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
In rosenthal da, janzen dh (eds) herbivores their interaction with secondary plant metabolites. The chemical defenses of plants constitute a major obstacle to herbivore feeding. The role of plant secondary compounds w. In this opinion article, we examine how the costs of plant chemical defense can be offset by multifunctional biosynthesis and the optimization of primary metabolism. A chemical defence mechanism is an inbuilt characteristic of a plant that is activated by a specific event such as touch or movement.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
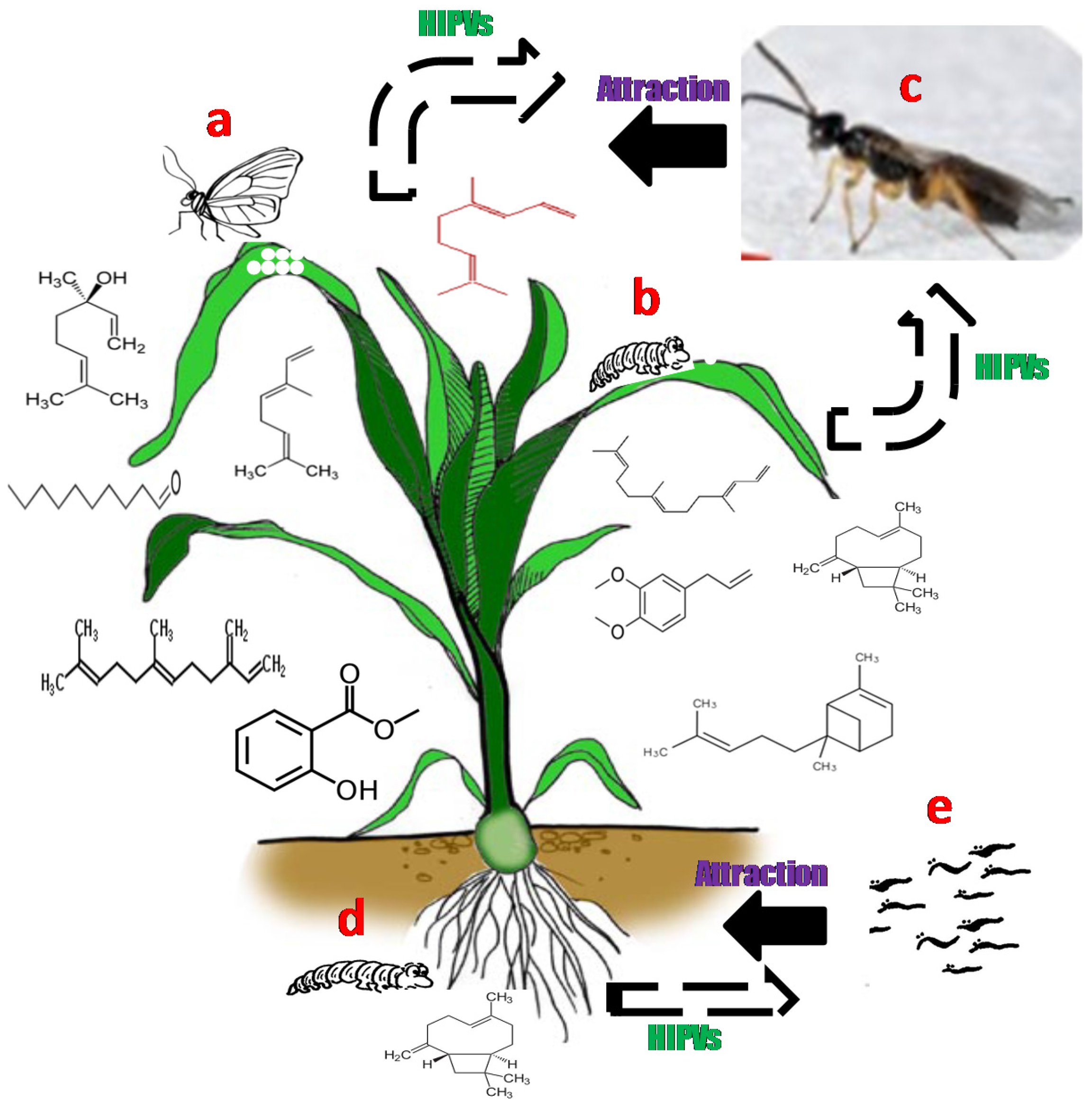
Plants have evolved a plethora of different chemical defenses covering nearly all classes of (secondary) metabolites that represent a major barrier to herbivory: In addition, plants also release volatile organic compounds that attract the natural enemies of the herbivores. Volatiles which can alert neighbor plants or tissues to potential attacks are promoted by herbivory and are a complex blend. All plants produce a diverse group of chemicals whose main function is to protect the plant against herbivores and diseases; (eds) biochemical interaction between plants and insects.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Induced responses are changes in a plant following 1. Plants are often attacked by multiple enemies, including pathogens and herbivores. A case is made for plant phenolics as defensive substances by considering their structural diversity, concentration, alteration upon infection, and mode of action. The dieffenbachia, a common houseplant, contains idioblasts that fire barbed calcium oxalate crystals into the mouths of predators and then release an enzyme analogous to reptilian venom. The chemical defenses of plants can be induced or constitutive (constant) (baldwin 1998, sirvent and gibson 2002, agrawal 1998).
 Source: plantphysiologyblog.com
Source: plantphysiologyblog.com
Many of these compounds seem to have no role in such core plant functions as growth and reproduction, and they are synthesized in unique pathways in the plant. Plants diseases or phytopathogens affects plants right from the planting stage up to the harvesting and storage of the produce. Roots anchor them to the soil, so plants can’t run away. When activated, these cells release chemicals that are either distasteful, harmful or poisonous to the offender. The defensive compounds are either produced constitutively or in response to plant damage, and affect feeding, growth, and survival of herbivores.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Herbivory or infection that lower the preference, performance, or pathogenicity of the attacker on Chemical defenses of the host plant than are. Plant chemical defense is highly complex. Plants have evolved a plethora of different chemical defenses covering nearly all classes of (secondary) metabolites that represent a major barrier to herbivory: This is due to an evolutionary.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Induced responses are changes in a plant following 1. Publisher name springer, boston, ma Induced responses are changes in a plant following 1. These defense mechanisms in plants are termed as “basal resistance”. Structural defense mechanism the surface of the plant or host is first line of defense against the pathogen.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Plants chemical defenses rhoades df (1979) evolution of plant chemical defense against herbivores. Compounds that contain n include cyanogenic glucosides, alkaloids, and nonprotein amino acids. Publisher name springer, boston, ma Defensive compounds without n include tannins, terpenes, phytoalexins, steroids, and phenolic acids. Recent advances in phytochemistry, vol 10.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
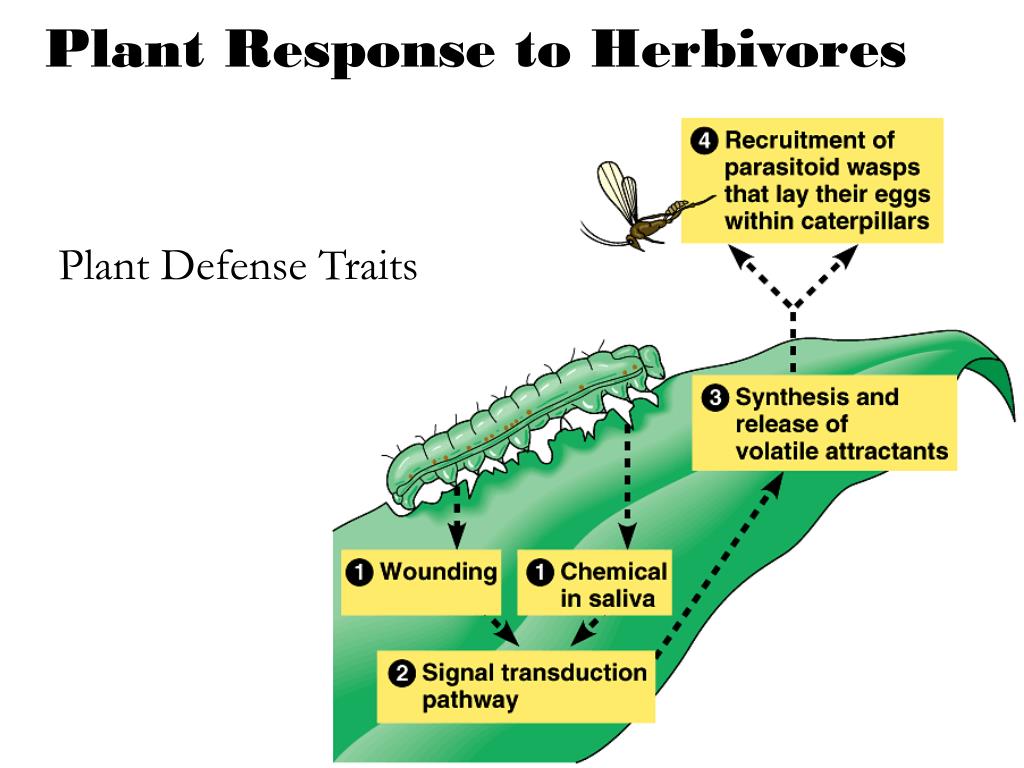
The pathogen must adhere to the surface and penetrate, if it is to cause infection. In addition, plants also release volatile organic compounds that attract the natural enemies of the herbivores. The dieffenbachia, a common houseplant, contains idioblasts that fire barbed calcium oxalate crystals into the mouths of predators and then release an enzyme analogous to reptilian venom. Herbivory & chemical defense •overview • theory of plant defense • types of defenses • data on defense •herbivore mechanisms whitebark pine ghost forest Many of these compounds seem to have no role in such core plant functions as growth and reproduction, and they are synthesized in unique pathways in the plant.
 Source: embopress.org
Source: embopress.org
These defense mechanisms in plants are termed as “basal resistance”. While many plant secondary metabolites show specific effects toward either pathogens or herbivores, some can affect the performance of both these groups of natural enemies and are considered to be “generalized defense compounds”. A chemical defence mechanism is an inbuilt characteristic of a plant that is activated by a specific event such as touch or movement. Janzen environmental science the american naturalist 1974 tldr For example, bitter almonds and apple pips both release hydrogen cyanide when crushed.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant chemical defense by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






