Your Plant defenses against herbivores images are available. Plant defenses against herbivores are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Plant defenses against herbivores files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for plant defenses against herbivores pictures information related to the plant defenses against herbivores topic, you have visit the right site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Plant Defenses Against Herbivores. Plants may effectively tailor defenses by recognizing their attackers and reprogramming their physiology. Both protect plants against herbivores. An enormous diversity of plant (bio)chemicals are toxic, repellent, or antinutritive for herbivores of all types. Hard silicon particles make the grass leaves abrasive.
 PPT Plant Defenses Against Herbivory Structural Defenses From slideserve.com
PPT Plant Defenses Against Herbivory Structural Defenses From slideserve.com
To guard against herbivorous insects, some plants use a layer of plant hairs, or trichomes (figure 3d). Grasses, like maize (corn), rice, and wheat, take up the element silicon from the soil. Other adaptations against herbivores include hard shells, thorns (modified branches), and spines (modified leaves). Both protect plants against herbivores. This special issue belongs to the section molecular plant sciences . Defenses against pathogens and herbivores.
Plants defend themselves against herbivores using a complex array of resistance traits.
A plant will then use compounds such as toxins and enzymes that discourage herbivores. Defenses against pathogens and herbivores. Plant defense strategies against herbivores evolve under the complexity of multiherbivore attack but have been largely studied in isolation over the past decades. A plant will then use compounds such as toxins and enzymes that discourage herbivores. These bioactive specialized plant defense compounds may repel or intoxicate insects, while defense proteins often interfere with their digestion. Studies on dual herbivore attack identified that defense against one attacker may.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Grasses, like maize (corn), rice, and wheat, take up the element silicon from the soil. Defenses against pathogens and herbivores. Plants may effectively tailor defenses by recognizing their attackers and reprogramming their physiology. Benzoxazinoids constitute a class of activated plant defenses that function against a wide range of insect herbivores and other target organisms. Plants defend themselves against herbivores using a complex array of resistance traits.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Plants may effectively tailor defenses by recognizing their attackers and reprogramming their physiology. Persimmon, genus diospyros, has a high tannin content which gives immature fruit, seen above, an. Many morphological and chemical features of plants are classified as plant defenses against herbivores. Sclerophylly refers to the hardened leaves, and plays an active role in plant defense against herbivores by reducing the palatability and digestibility of the tissues, thereby, reducing the herbivore damage. A plant will then use compounds such as toxins and enzymes that discourage herbivores.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Other adaptations against herbivores include hard shells, thorns (modified branches), and spines (modified leaves). Plants have evolved a plethora of different chemical defenses covering nearly all classes of (secondary) metabolites that represent a major barrier. Grasses, like maize (corn), rice, and wheat, take up the element silicon from the soil. The prickles on the stem of this raspberry plant, serve as a mechanical defense against herbivory. Volatiles are released upon herbivory to repel herbivores, attract predators or for communication between leaves or plants, and to induce defense responses.
 Source: embopress.org
Source: embopress.org
These compounds are known as secondary metabolites. A plant will then use compounds such as toxins and enzymes that discourage herbivores. Plants may effectively tailor defenses by recognizing their attackers and reprogramming their physiology. These bioactive specialized plant defense compounds may repel or intoxicate insects, while defense proteins often interfere with their digestion. Other adaptations against herbivores include hard shells, thorns (modified branches), and spines (modified leaves).
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Many morphological and chemical features of plants are classified as plant defenses against herbivores. Some plants mimic the presence. Early research on the evolution of plant defense focused on the role of plant secondary metabolites (stahl, 1888; Because of this disparity, there exist large gaps in our knowledge about the. There are many classes of idioblasts including pigmented cells, sclereids, crystalliferous cells,.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Volatiles are released upon herbivory to repel herbivores, attract predators or for communication between leaves or plants, and to induce defense responses. Because of this disparity, there exist large gaps in our knowledge about the. Hard silicon particles make the grass leaves abrasive. Both protect plants against herbivores. Idioblasts (“crazy cells”) help protect plants against herbivory because they contain toxic chemicals or sharp crystals that tear the mouthparts of insects and mammals as they feed.
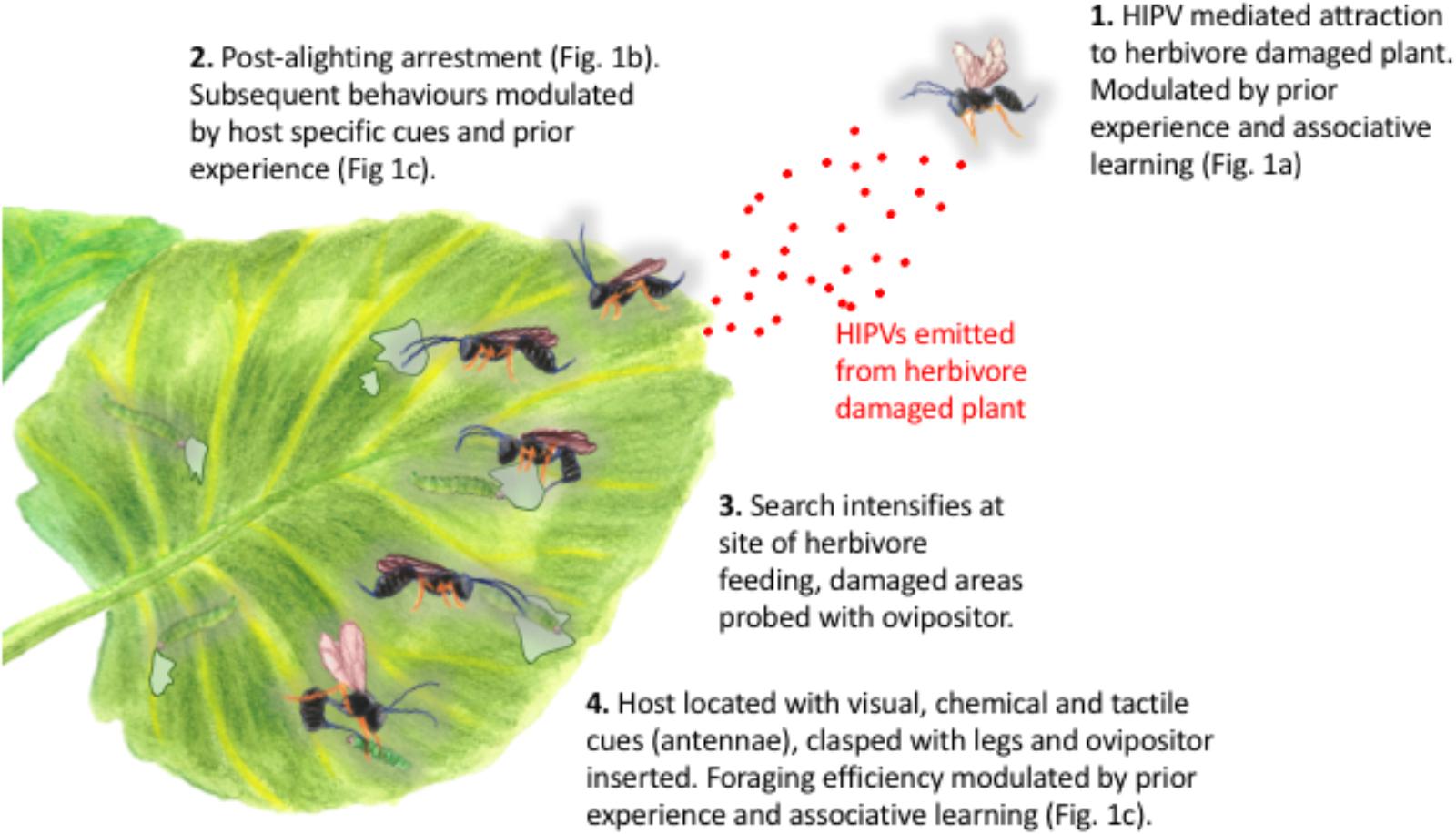 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Plants have evolved specific defense mechanisms to recognize and respond to herbivorous pest/insect attacks which include physical barriers such as waxy cuticle, trichomes (often toxic),. Trichomes are extensions of the epidermis that can prevent insect eggs from sticking to a. Others are macromolecules and comprise latex or proteinase inhibitors. These compounds are known as secondary metabolites. Other adaptations against herbivores include hard shells, thorns (modified branches), and spines (modified leaves).
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Both protect plants against herbivores. Studies on dual herbivore attack identified that defense against one attacker may. Examples include cyanogenic glycosides, glucosinolates, alkaloids, and terpenoids; An enormous diversity of plant (bio)chemicals are toxic, repellent, or antinutritive for herbivores of all types. There are many classes of idioblasts including pigmented cells, sclereids, crystalliferous cells,.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Both protect plants against herbivores. Volatiles are released upon herbivory to repel herbivores, attract predators or for communication between leaves or plants, and to induce defense responses. Some plants mimic the presence. This defense works by wearing down the teeth of large grazing mammals and mandibles of grasshoppers. Although various phytohormones are involved in plant defense against herbivores, ja is the most important phytohormone linked to plant defense against herbivores and activates the expression of both direct and indirect defenses.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Early research on the evolution of plant defense focused on the role of plant secondary metabolites (stahl, 1888; This special issue belongs to the section molecular plant sciences . Although most plants are under attack by a large diversity of herbivores, surprisingly little is known about the physiological capabilities of plants to deal with attack by multiple herbivores. As immobile organisms, plants have little choice but to defend themselves against both pathogens and herbivores by mounting a variety of. Examples include cyanogenic glycosides, glucosinolates, alkaloids, and terpenoids;
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
There are many classes of idioblasts including pigmented cells, sclereids, crystalliferous cells,. Plants may effectively tailor defenses by recognizing their attackers and reprogramming their physiology. In this review, we have seen that the effects of bxds on different guilds of insect herbivores are strongly influenced by the specific distributions of the compounds themselves and their activating β. Plants have evolved a plethora of different chemical defenses covering nearly all classes of (secondary) metabolites that represent a major barrier. Volatiles are released upon herbivory to repel herbivores, attract predators or for communication between leaves or plants, and to induce defense responses.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Some plants mimic the presence. These bioactive specialized plant defense compounds may repel or intoxicate insects, while defense proteins often interfere with their digestion. These physical defenses hurt the herbivores and stop them from eating plants’ stems or leaves. Studies on dual herbivore attack identified that defense against one attacker may. 4, 5, 125 ja is derived from linolenic acid through octadecanoid pathway and accumulates upon wounding and herbivory in plant.
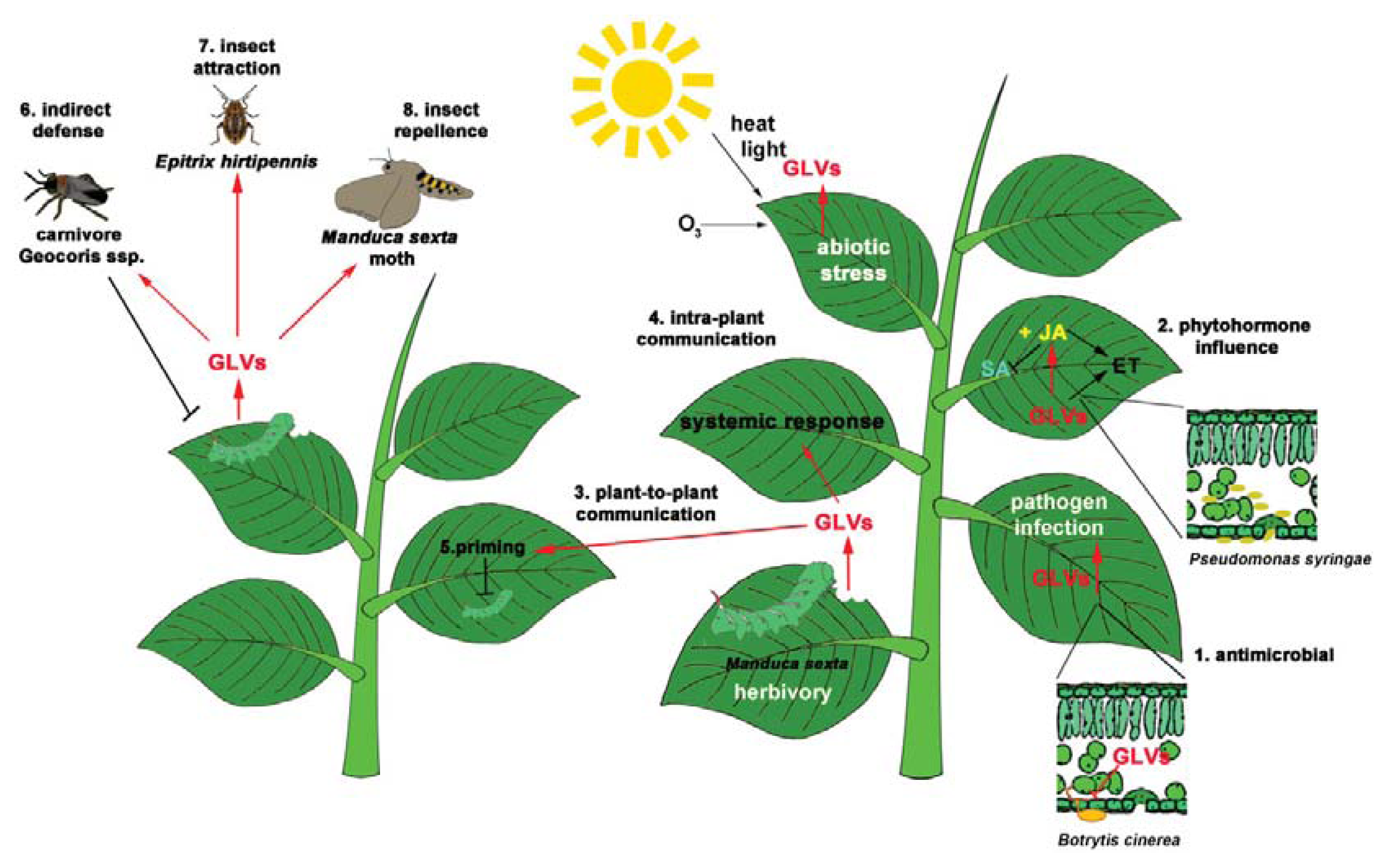 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Many morphological and chemical features of plants are classified as plant defenses against herbivores. Plant defense strategies against herbivores evolve under the complexity of multiherbivore attack but have been largely studied in isolation over the past decades. Although various phytohormones are involved in plant defense against herbivores, ja is the most important phytohormone linked to plant defense against herbivores and activates the expression of both direct and indirect defenses. The first line of defense in plants is an intact and impenetrable barrier composed of bark and a waxy cuticle. Plants may effectively tailor defenses by recognizing their attackers and reprogramming their physiology.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Both protect plants against herbivores. Idioblasts (“crazy cells”) help protect plants against herbivory because they contain toxic chemicals or sharp crystals that tear the mouthparts of insects and mammals as they feed. To guard against herbivorous insects, some plants use a layer of plant hairs, or trichomes (figure 3d). Plants defend themselves against herbivores using a complex array of resistance traits. Plants have evolved a plethora of different chemical defenses covering nearly all classes of (secondary) metabolites that represent a major barrier.
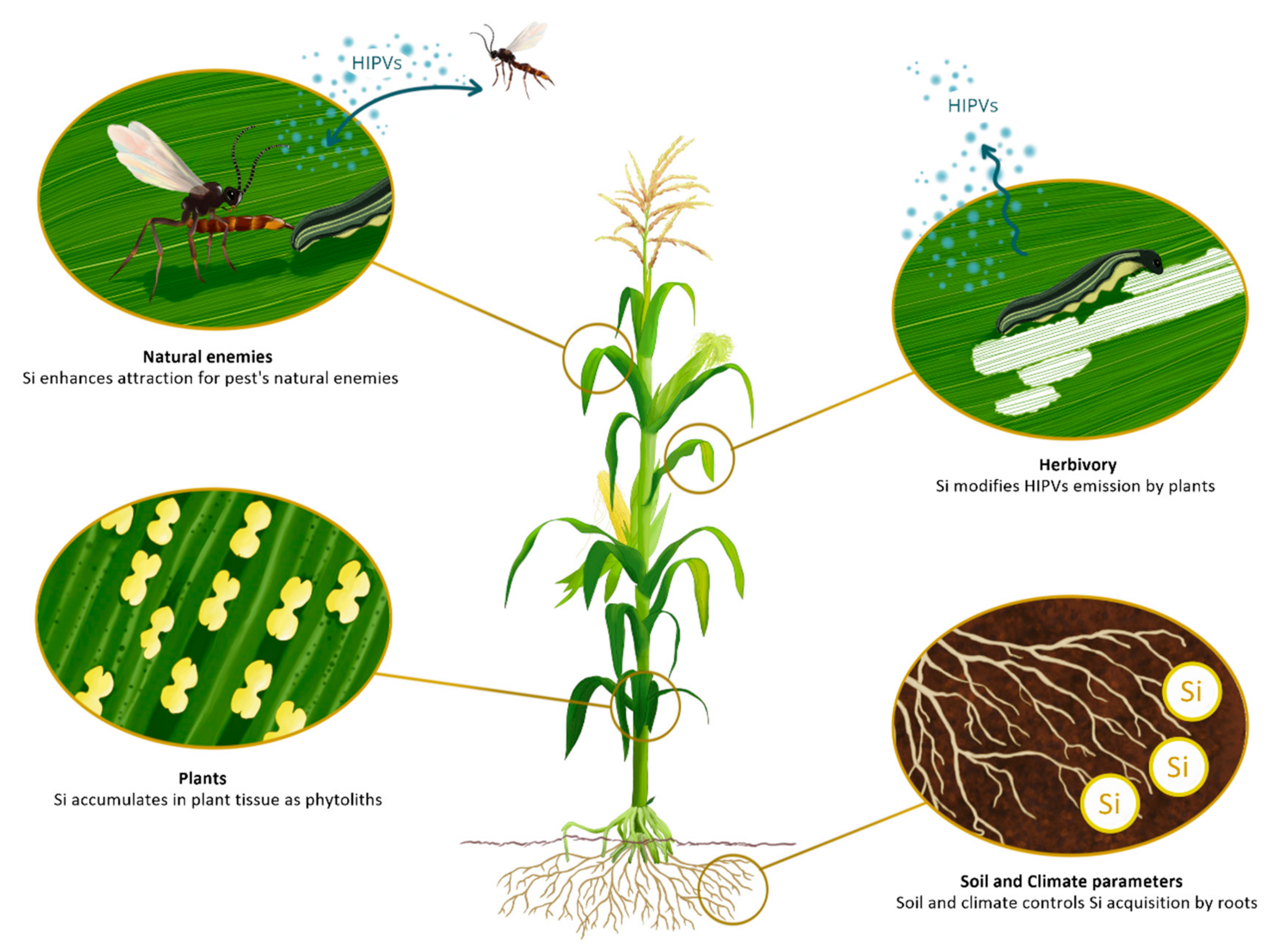 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Although most plants are under attack by a large diversity of herbivores, surprisingly little is known about the physiological capabilities of plants to deal with attack by multiple herbivores. Volatiles are released upon herbivory to repel herbivores, attract predators or for communication between leaves or plants, and to induce defense responses. There are many classes of idioblasts including pigmented cells, sclereids, crystalliferous cells,. Plants have evolved a plethora of different chemical defenses covering nearly all classes of (secondary) metabolites that represent a major barrier. Although various phytohormones are involved in plant defense against herbivores, ja is the most important phytohormone linked to plant defense against herbivores and activates the expression of both direct and indirect defenses.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Other adaptations against herbivores include hard shells, thorns (modified branches), and spines (modified leaves). Examples include cyanogenic glycosides, glucosinolates, alkaloids, and terpenoids; Summary plant species vary greatly in defenses against herbivores, but existing theory has struggled to explain this variation. Plants present a rich source of nutrients for many organisms, making it a target for herbivores and infectious agents. 4, 5, 125 ja is derived from linolenic acid through octadecanoid pathway and accumulates upon wounding and herbivory in plant.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
Idioblasts (“crazy cells”) help protect plants against herbivory because they contain toxic chemicals or sharp crystals that tear the mouthparts of insects and mammals as they feed. Hard silicon particles make the grass leaves abrasive. 4, 5, 125 ja is derived from linolenic acid through octadecanoid pathway and accumulates upon wounding and herbivory in plant. The defensive metabolites are bioactive specialized compounds used to protect plant against herbivores, and these compounds can use as target systems unique to herbivores, such as the nervous, digestive, and endocrine organs, may act as repellents for generalist herbivores, while specialists are forced to invest resources in detoxification. These physical defenses hurt the herbivores and stop them from eating plants’ stems or leaves.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Volatiles are released upon herbivory to repel herbivores, attract predators or for communication between leaves or plants, and to induce defense responses. Others are macromolecules and comprise latex or proteinase inhibitors. The first line of defense in plants is an intact and impenetrable barrier composed of bark and a waxy cuticle. In this review, we have seen that the effects of bxds on different guilds of insect herbivores are strongly influenced by the specific distributions of the compounds themselves and their activating β. Sclerophylly refers to the hardened leaves, and plays an active role in plant defense against herbivores by reducing the palatability and digestibility of the tissues, thereby, reducing the herbivore damage.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title plant defenses against herbivores by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







