Your Plant embryo images are available in this site. Plant embryo are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Plant embryo files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for plant embryo images information related to the plant embryo topic, you have visit the right blog. Our site always gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Plant Embryo. Somatic embryogenesis (se) is the most promising method for the quick propagation of desirable plant genotypes. Like animals, the initiation of plant embryogenesis is demarked by the fusion of the haploid sperm and egg cell, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote, which then undergoes a series of divisions to produce a fully developed embryo. In plant embryogenesis, the authors focus on the common developmental process and compile novel tools and methods designed specifically for studying plant embryogenesis. Double fertilisation in angiosperm was first explained by.
 Frontiers The Response of Picea abies Somatic Embryos to From frontiersin.org
Frontiers The Response of Picea abies Somatic Embryos to From frontiersin.org
Bolo, diamos, go, marquez, pilapil embryogenesis it describes the subsequent period of development (after the formation of zygote), during which the zygote undergoes a complex series of morphological and cellular changes resulting in the formation of a developmentally arrested mature embryo. (b) two sequential processes define plant embryogenesis: Plant embryogenesis starts at the fertilization of the egg cell encapsulated in the maternal tissue and leads to the establishment of a new organism capable of an autonomous life. Thereafter, rapid cell division provides the building. During embryogenesis the basic body plan of the plant is established, primary plant tissue types are differentiated, and. Because plants cannot move, their developmental strategies necessarily differ from those of animals.
The ovule in plants is a structure that encloses the reproductive cells in females which contains the nucleus, the integument and the female gametophyte.
Somatic embryogenesis (se) is the most promising method for the quick propagation of desirable plant genotypes. In this video we go over the stages of embryogenesis in plants. Recent technological advances, including novel genomics approaches, have provided insights into the function of the suspensor and the dna sequences that control suspensor. The plant embryo, sometimes called the seed embryo, is the part of a seed or bud that contains the earliest forms of a plant�s roots, stem and leaves. Polyembryony is the occurrence of more than two embryo in a seed. Apomixis is the type of reproduction that result in the development of.
 Source: matahariy.blogspot.com
Source: matahariy.blogspot.com
Se is the most important method for plant propagation in vitro, having both fundamental and applicative significance. The ovule in plants is a structure that encloses the reproductive cells in females which contains the nucleus, the integument and the female gametophyte. (c) embryos in land plants are diverse. Our hypothesis is that irrespective of embryo morphology there is a shared set of embryo. The fusion of egg and sperm produces the plant zygote, a totipotent cell that, through cell division and cell identity specification in early embryogenesis, establishes the major cell lineages and tissues of the adult plant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
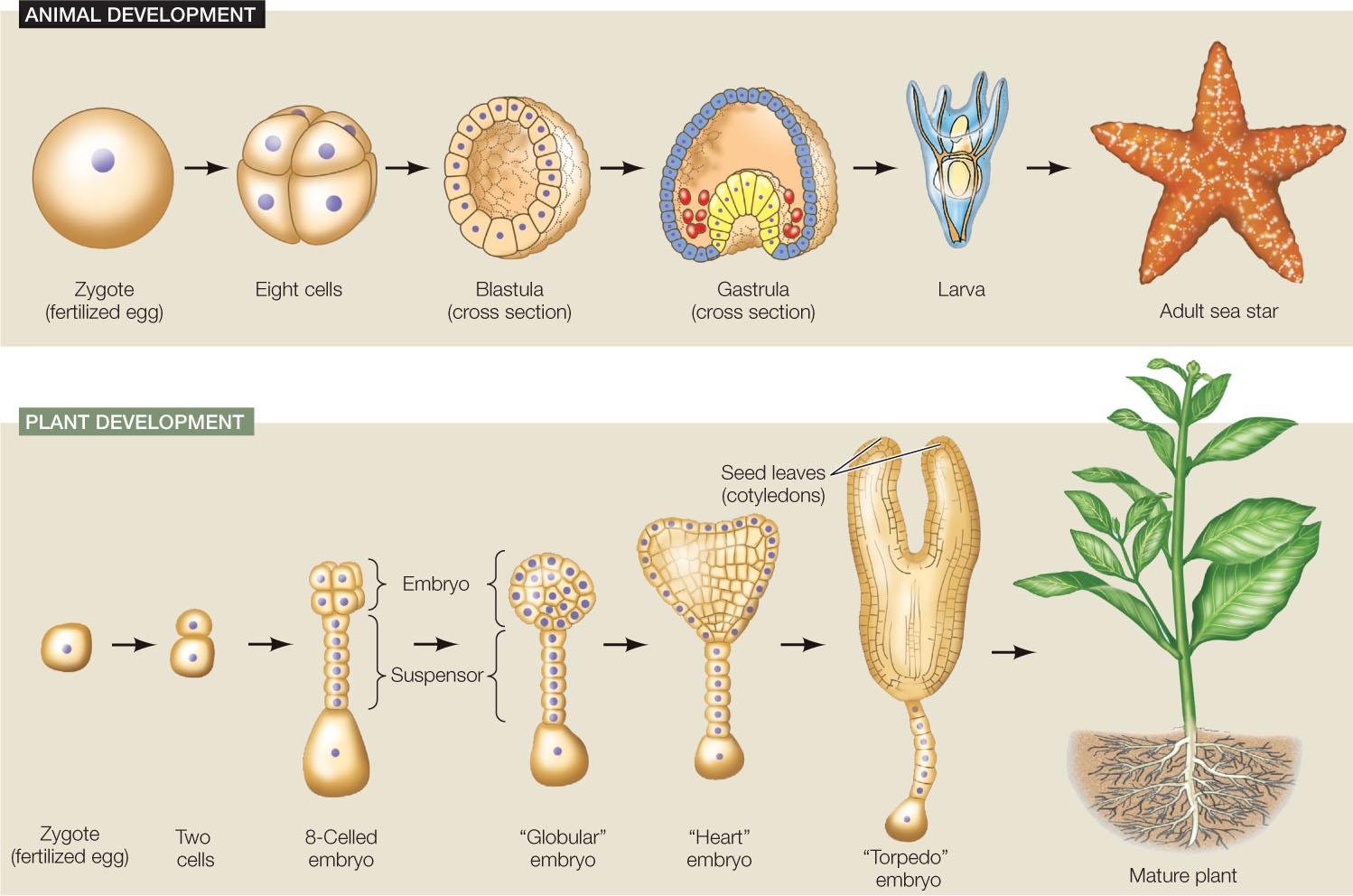
Each embryo starts development as a zygote, a single cell resulting from the fusion of. The fusion of egg and sperm produces the plant zygote, a totipotent cell that, through cell division and cell identity specification in early embryogenesis, establishes the major cell lineages and tissues of the adult plant. Each embryo starts development as a zygote, a single cell resulting from the fusion of. The zygote goes through various cellular differentiations and divisions in order to produce a mature embryo. Polyembryony is the occurrence of more than two embryo in a seed.
 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
Somatic embryogenesis (se) is the most promising method for the quick propagation of desirable plant genotypes. In plants, the embryonic stage ends with germination, when the plant begins to grow out of the seed. Somatic embryogenesis (se) is a developmental process during which plant somatic cells, under suitable conditions, produce embryogenic cells that develop into somatic embryos (se). Polyembryony was discovered by a v leeuwenhock in 1719 in the citrus plant. Somatic embryogenesis (se) is the most promising method for the quick propagation of desirable plant genotypes.
 Source: phys.org
Source: phys.org
In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization and continues through the formation of body structures, such as tissues and organs. The fusion of egg and sperm produces the plant zygote, a totipotent cell that, through cell division and cell identity specification in early embryogenesis, establishes the major cell lineages and tissues of the adult plant. The plant embryo and the endosperm which go on to develop into a seed. In plant embryogenesis, the authors focus on the common developmental process and compile novel tools and methods designed specifically for studying plant embryogenesis. These stem cell populations or ‘meristems’ are the.
 Source: dev.biologists.org
Source: dev.biologists.org
In plants, the embryonic stage ends with germination, when the plant begins to grow out of the seed. The zygote goes through various cellular differentiations and divisions in order to produce a mature embryo. Se is the most important method for plant propagation in vitro, having both fundamental and applicative significance. The uniqueness of plant embryogenesis resides on three characteristics that have tremendous implications for morphogenesis. Most of the time an embryo implants within the body of the uterus in a location that can support growth and development.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Embryo from an unfertilised egg is. The plant embryo, sometimes called the seed embryo, is the part of a seed or bud that contains the earliest forms of a plant�s roots, stem and leaves. Because plants cannot move, their developmental strategies necessarily differ from those of animals. Se is the most important method for plant propagation in vitro, having both fundamental and applicative significance. Plant embryogenesis is the process by which plant embryos form and develop.
Source: learning.uonbi.ac.ke
However, in addition to embryos. Bolo, diamos, go, marquez, pilapil embryogenesis it describes the subsequent period of development (after the formation of zygote), during which the zygote undergoes a complex series of morphological and cellular changes resulting in the formation of a developmentally arrested mature embryo. An embryo is the early stage of development of a multicellular organism. Our hypothesis is that irrespective of embryo morphology there is a shared set of embryo. What is the site of embryonic development?
 Source: maghsci.blogspot.com
Source: maghsci.blogspot.com
Se is the most important method for plant propagation in vitro, having both fundamental and applicative significance. What is the site of embryonic development? In this video we go over the stages of embryogenesis in plants. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization and continues through the formation of body structures, such as tissues and organs. The uniqueness of plant embryogenesis resides on three characteristics that have tremendous implications for morphogenesis.
 Source: sciencelearn.org.nz
Source: sciencelearn.org.nz
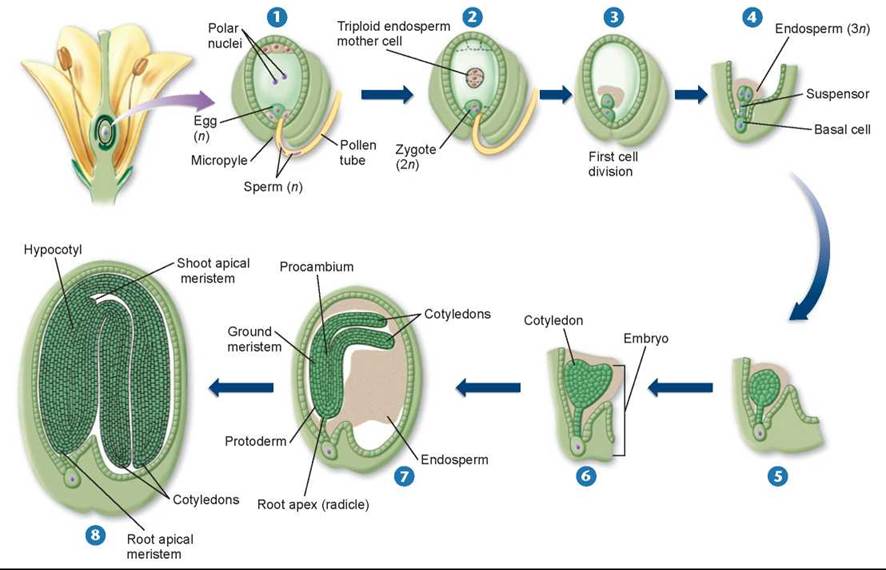
In the embryo‐proper, two functionally distinct meristems form at each pole, through the localized expression of key genes. In vascular plants embryo formation, or embryogenesis, usually occurs within a few hours after fertilization, with the first cell division that cleaves the zygote, or fertilized egg, into two daughter cells. Se is the most important method for plant propagation in vitro, having both fundamental and applicative significance. (botany) a young, developing plant, such as the rudimentary plant inside the seed of higher plants or that inside the archegonium of mosses and ferns. Land plants are called �embryophytes� and thus, their collective name is defined by their ability to form embryos.
 Source: snaplant.com
Source: snaplant.com
In vascular plants embryo formation, or embryogenesis, usually occurs within a few hours after fertilization, with the first cell division that cleaves the zygote, or fertilized egg, into two daughter cells. The number of chromosomes in its endosperm will be. Polyembryony is the occurrence of more than two embryo in a seed. A plant has 25 chromosomes in ‘ microspore mother cell ‘. Embryogenesis occurs naturally as a result of single, or double fertilization, of the ovule, giving rise to two distinct structures:
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Because plants cannot move, their developmental strategies necessarily differ from those of animals. Land plants are called �embryophytes� and thus, their collective name is defined by their ability to form embryos. Most of the time an embryo implants within the body of the uterus in a location that can support growth and development. Plants,however, only pattern a basic body plan during embryogenesis, with their adult body forms bearing very little resemblance to the embryo. Whereas animals generally have all of their organs formed during embryogenesis, plant embryos can be thought of as two sets of stem cells, one that will form the aerial tissues and the other that will form the roots (figure 20.1).
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The uniqueness of plant embryogenesis resides on three characteristics that have tremendous implications for morphogenesis. A plant has 25 chromosomes in ‘ microspore mother cell ‘. The fusion of egg and sperm produces the plant zygote, a totipotent cell that, through cell division and cell identity specification in early embryogenesis, establishes the major cell lineages and tissues of the adult plant. Land plants are called �embryophytes� and thus, their collective name is defined by their ability to form embryos. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization and continues through the formation of body structures, such as tissues and organs.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Like animals, the initiation of plant embryogenesis is demarked by the fusion of the haploid sperm and egg cell, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote, which then undergoes a series of divisions to produce a fully developed embryo. Each embryo starts development as a zygote, a single cell resulting from the fusion of. The fusion of egg and sperm produces the plant zygote, a totipotent cell that, through cell division and cell identity specification in early embryogenesis, establishes the major cell lineages and tissues of the adult plant. Se is the most important method for plant propagation in vitro, having both fundamental and applicative significance. The plant embryo and the endosperm which go on to develop into a seed.
 Source: ibiologia.com
Source: ibiologia.com
The plant embryo and the endosperm which go on to develop into a seed. In this video we go over the stages of embryogenesis in plants. Polyembryony is the occurrence of more than two embryo in a seed. Embryonic development represents an important reproductive phase of sexually reproducing plant species. Polyembryony was discovered by a v leeuwenhock in 1719 in the citrus plant.
 Source: kimonodasukke.blogspot.com
Source: kimonodasukke.blogspot.com
The zygote goes through various cellular differentiations and divisions in order to produce a mature embryo. Indeed, embryogenesis is a widespread phenomenon in plants, and much of our diet is composed of embryos (just think of grains, beans or nuts; Plant embryogenesis starts at the fertilization of the egg cell encapsulated in the maternal tissue and leads to the establishment of a new organism capable of an autonomous life. In the embryo‐proper, two functionally distinct meristems form at each pole, through the localized expression of key genes. However, in addition to embryos.
 Source: philschatz.com
Source: philschatz.com
In the embryo‐proper, two functionally distinct meristems form at each pole, through the localized expression of key genes. However, in addition to embryos. Plants,however, only pattern a basic body plan during embryogenesis, with their adult body forms bearing very little resemblance to the embryo. In the embryo‐proper, two functionally distinct meristems form at each pole, through the localized expression of key genes. (botany) a young, developing plant, such as the rudimentary plant inside the seed of higher plants or that inside the archegonium of mosses and ferns.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Bolo, diamos, go, marquez, pilapil embryogenesis it describes the subsequent period of development (after the formation of zygote), during which the zygote undergoes a complex series of morphological and cellular changes resulting in the formation of a developmentally arrested mature embryo. An embryo is the early stage of development of a multicellular organism. Somatic embryogenesis (se) is a developmental process during which plant somatic cells, under suitable conditions, produce embryogenic cells that develop into somatic embryos (se). Given this diversity in postembryonic development, it is remarkable that plant embryos from a wide range of species go through very similar stages of development, many with stereotyped, almost invariant cell. Embryonic development proceeds within the.
 Source: plantcell.org
Source: plantcell.org
Plant embryogenesis starts at the fertilization of the egg cell encapsulated in the maternal tissue and leads to the establishment of a new organism capable of an autonomous life. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization and continues through the formation of body structures, such as tissues and organs. Plants,however, only pattern a basic body plan during embryogenesis, with their adult body forms bearing very little resemblance to the embryo. The embryo develops after a fertilized adult plant flowers, and is generally contained within a seed or bud. The fusion of egg and sperm produces the plant zygote, a totipotent cell that, through cell division and cell identity specification in early embryogenesis, establishes the major cell lineages and tissues of the adult plant.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title plant embryo by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







