Your Plant leaf structure images are ready in this website. Plant leaf structure are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Plant leaf structure files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for plant leaf structure images information linked to the plant leaf structure keyword, you have come to the ideal site. Our site always gives you suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Plant Leaf Structure. Browse more topics under anatomy of flowering plants plant tissues tissue system stem inflorescence Using their leaves, plants combine sunlight, carbon dioxide. Leaf structure varies to allow plants to survive and grow under diverse conditions. A leaf is made of many layers that are sandwiched between two layers of tough skin cells (called the epidermis).
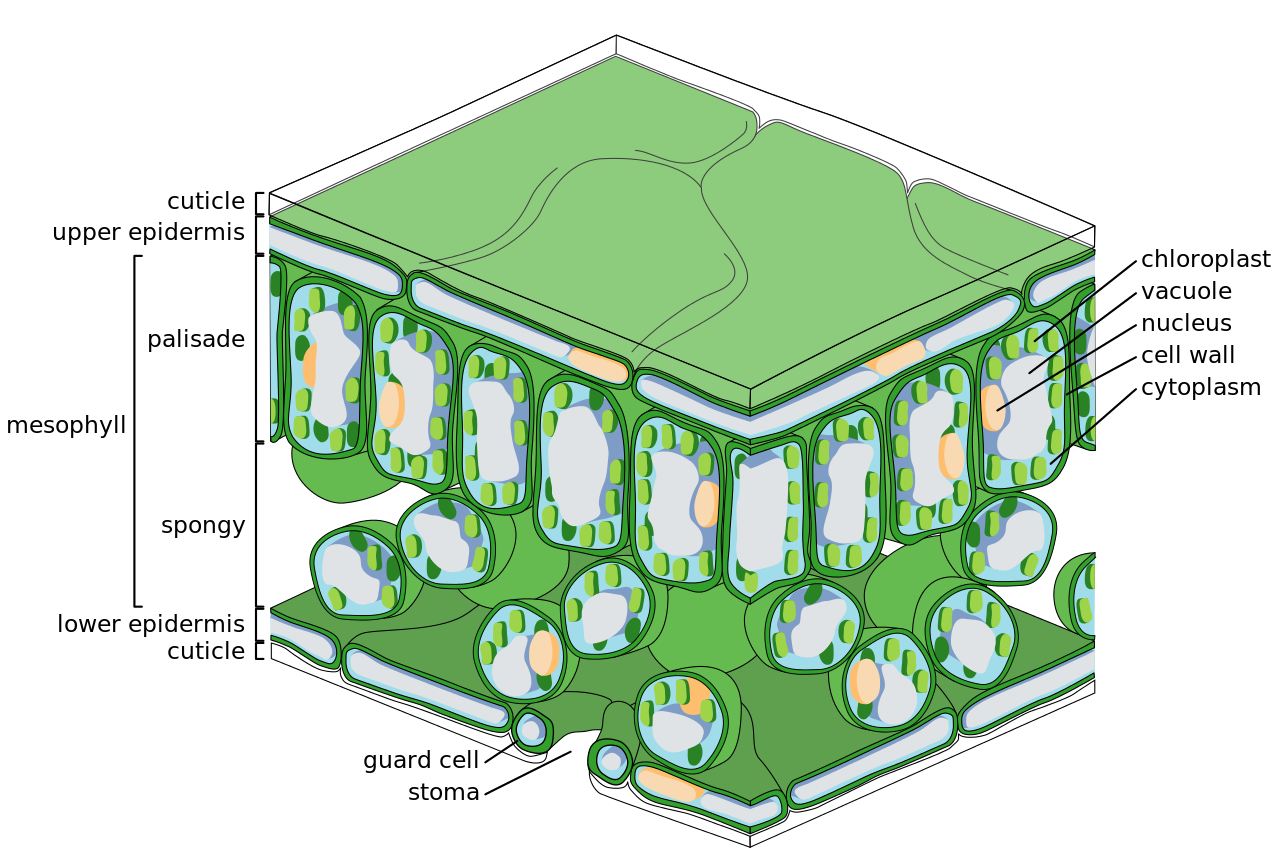 science 10 gladstone Looking at the leaf cross section From gladstonescience10.blogspot.com
science 10 gladstone Looking at the leaf cross section From gladstonescience10.blogspot.com
Using their leaves, plants combine sunlight, carbon dioxide. The veins pass through the petioles (leaf stalks) and are continuous with the rest of the vascular system of the plant. Leaves are vital to the survival of plants. Photosynthesis is the process where green plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to make food and oxygen. Leaf structure varies to allow plants to survive and grow under diverse conditions. It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating.
A structure at the sides originating and attached to the main plant body.
Using their leaves, plants combine sunlight, carbon dioxide. Apical dominance helps to maintain dormancy in most axillary buds; The xylem is responsible for the movement of water throughout the plant, while the phloem transports nutrients and. A leaf is the green, flat lateral outgrowth in plants. Running through the petiole are vascular bundles, which then form the veins in the leaf. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In angiosperms leaves commonly have a pair of structures known as stipules, which are located on each side of the leaf base and may resemble scales, spines, glands, or leaflike structures. They may range in length from a few millimeters to hundreds of meters, and also vary in diameter, depending on the plant type. It develops laterally at the node. Leaves can have different shapes and sizes. 4 rows the structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis.
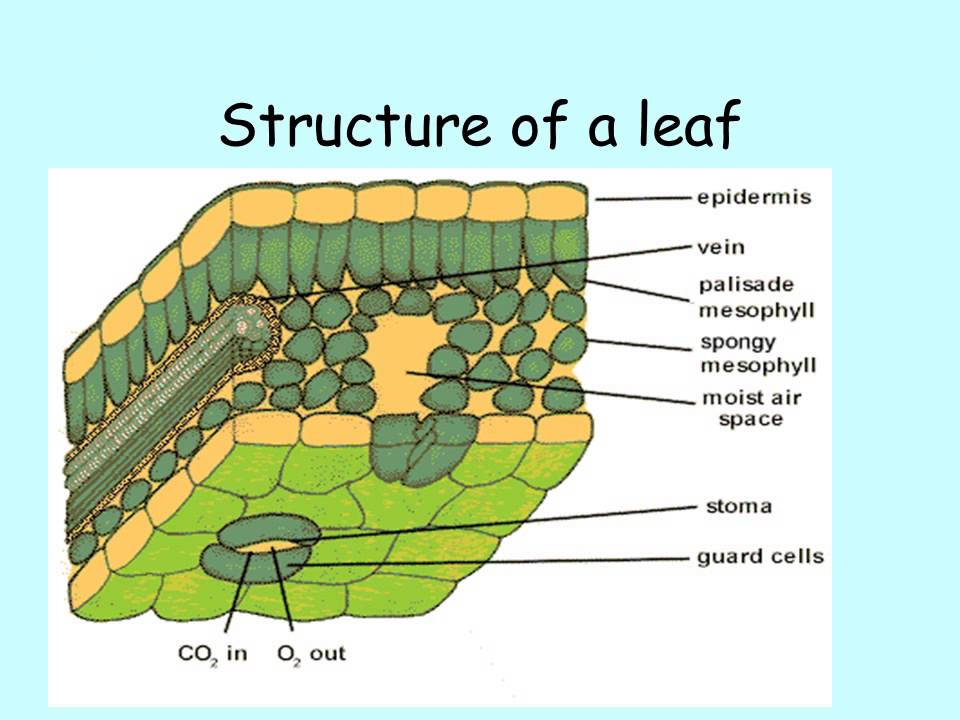 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The xylem is responsible for the movement of water throughout the plant, while the phloem transports nutrients and. The structure of the umbrella tree leaf is typical of leaves in general (above left photo). Practice leaf structure and function. Browse more topics under anatomy of flowering plants plant tissues tissue system stem inflorescence They may range in length from a few millimeters to hundreds of meters, and also vary in diameter, depending on the plant type.

The leaf consist of a broad, flat part called the lamina, which is joined to the rest of the plant by a leaf stalk or petiole. These layers protect the leaf from insects, bacteria, and other pests. Veins supply water and minerals to the leaf cells. A way to transport water to the leaf, and glucose to other parts of the. Although a leaf looks thin,.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating. Although a leaf looks thin,. The epidermis also secretes a waxy substance called the cuticle. It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating. Running through the petiole are vascular bundles, which then form the veins in the leaf.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In some plants, e.g., legumes, tamarind, mimosa (fig. In many plants the leaf base expands into a sheath which partially or wholly clasps the stem. An apical bud, or terminal bud, is located near the shoot tip and causes elongation of a young shoot; It develops laterally at the node. The xylem is responsible for the movement of water throughout the plant, while the phloem transports nutrients and.
 Source: gladstonescience10.blogspot.com
Source: gladstonescience10.blogspot.com
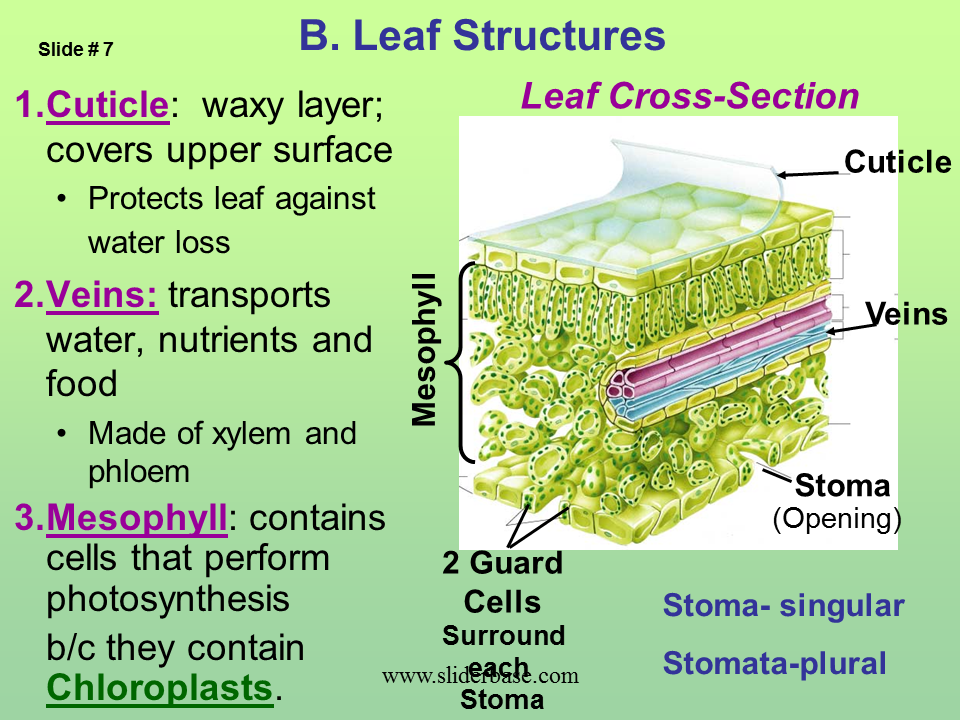
It is usually found above the ground forming part of the shoot along with the stem. It has a spongy layer, a palisade layer that consists of parenchyma cells and is where photosynthesis happens and an outer layer (the epidermis) with little holes (stomata) that could hold birthday candles. The leaf is arranged like a layered cake. Leaves are vital to the survival of plants. The petiole is the stalk connecting the leaf to the stem.
 Source: untpikapps.com
Source: untpikapps.com
The leaves just above the nodes arose from axillary buds. In some plants, e.g., legumes, tamarind, mimosa (fig. Although a leaf looks thin,. In many plants the leaf base expands into a sheath which partially or wholly clasps the stem. It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
Running through the petiole are vascular bundles, which then form the veins in the leaf. A leaf is the principal component of the plant as a lateral appendage i.e. The leaves just above the nodes arose from axillary buds. An apical bud, or terminal bud, is located near the shoot tip and causes elongation of a young shoot; Practice leaf structure and function.
 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
They are the main organ responsible for photosynthesis as they contain chlorophyll. For more detailed discussions of the evolution of leaves see steward and rothwell (1993) and taylor and taylor (1993). They help plants in a variety of ways, including producing food and. The epidermis also secretes a waxy substance called the cuticle. Browse more topics under anatomy of flowering plants plant tissues tissue system stem inflorescence
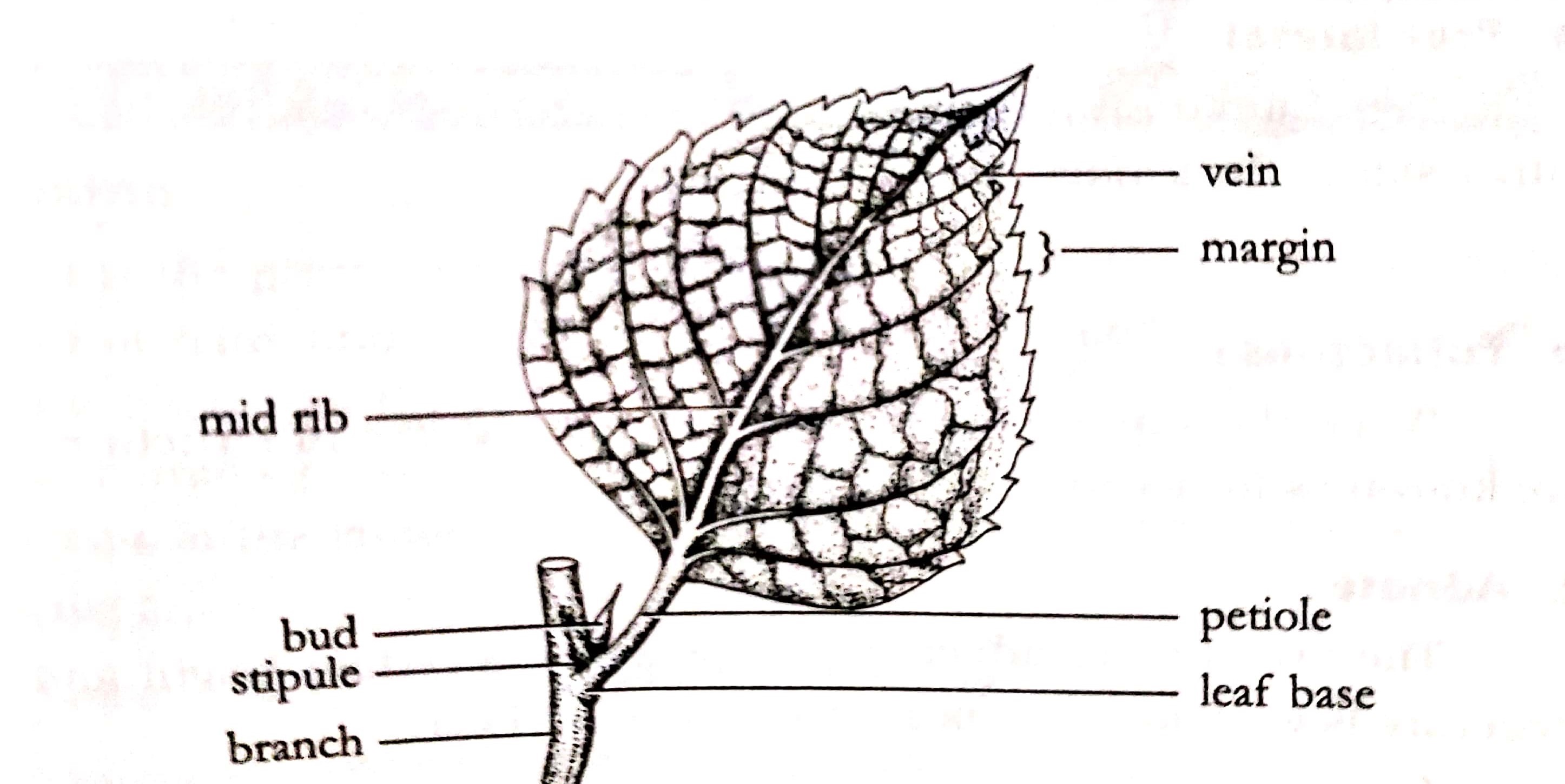 Source: onlinesciencenotes.com
Source: onlinesciencenotes.com
The leaf is arranged like a layered cake. It is an important part of the shoot system and it originates from shoot apical meristems. An apical bud, or terminal bud, is located near the shoot tip and causes elongation of a young shoot; Structure of the leaf | plant | biology | the fuseschoolplants make food through photosynthesis. The veins pass through the petioles (leaf stalks) and are continuous with the rest of the vascular system of the plant.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Browse more topics under anatomy of flowering plants plant tissues tissue system stem inflorescence Seed plant leaves which, on average, are much larger, and much more complex than those of lycophytes in both gross morphology and internal structure, are often referred to as megaphylls. Structure of a leaf leaves are thin, flat organs responsible for photosynthesis in the plants. It is usually found above the ground forming part of the shoot along with the stem. Many plants have modified stems (e.g., rhizomes, bulbs, stolons, tubers) leaves
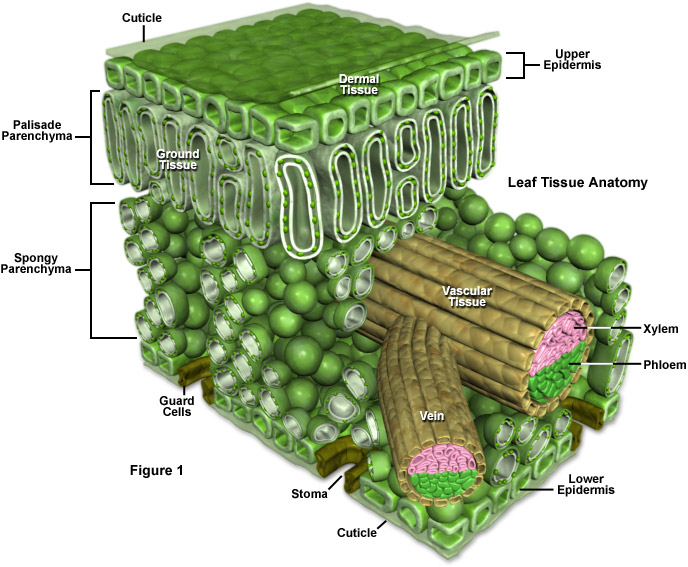 Source: micro.magnet.fsu.edu
Source: micro.magnet.fsu.edu
Running through the petiole are vascular bundles, which then form the veins in the leaf. Veins supply water and minerals to the leaf cells. The epidermis also secretes a waxy substance called the cuticle. Photosynthesis is the process where green plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to make food and oxygen. Typically, a leaf consists of a broad expanded blade (the lamina ), attached to the plant stem by a stalklike petiole.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
4 rows the structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis. Stems are a part of the shoot system of a plant. Photosynthesis is the process where green plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to make food and oxygen. Structure of the leaf | plant | biology | the fuseschoolplants make food through photosynthesis. It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If playback doesn�t begin shortly, try restarting your device. Typically, a leaf consists of a broad expanded blade (the lamina ), attached to the plant stem by a stalklike petiole. The epidermis of the undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores (stomata) which control the loss of water vapor (transpiration) and the. A structure at the sides originating and attached to the main plant body. In some plants, e.g., legumes, tamarind, mimosa (fig.
 Source: homestratosphere.com
Source: homestratosphere.com
Leaf structure varies to allow plants to survive and grow under diverse conditions. Internal structure of the dicot leaf 1. A leaf is made of many layers that are sandwiched between two layers of tough skin cells (called the epidermis). The leaves just above the nodes arose from axillary buds. Typically, a leaf consists of a broad expanded blade (the lamina ), attached to the plant stem by a stalklike petiole.
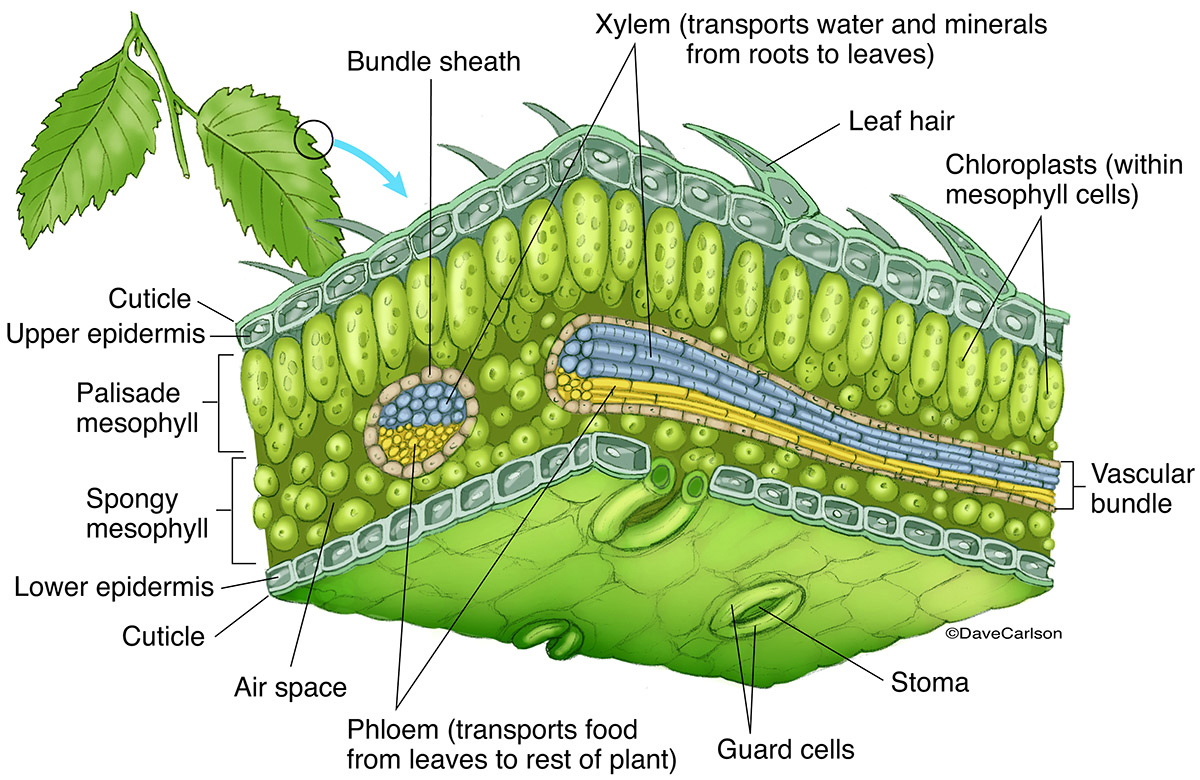 Source: carlsonstockart.com
Source: carlsonstockart.com
4 rows the structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis. A leaf is made of many layers that are sandwiched between two layers of tough skin cells (called the epidermis). Many plants have modified stems (e.g., rhizomes, bulbs, stolons, tubers) leaves Leaf structure the structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis effectively. Practice leaf structure and function.
The basic components of leaves in flowering plants (angiosperms) include the blade, the petiole, and the stipules. The epidermis of the undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores (stomata) which control the loss of water vapor (transpiration) and the. An axillary bud is a structure that has the potential to form a lateral shoot, or branch; It has a spongy layer, a palisade layer that consists of parenchyma cells and is where photosynthesis happens and an outer layer (the epidermis) with little holes (stomata) that could hold birthday candles. A leaf is the principal component of the plant as a lateral appendage i.e.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
Veins supply water and minerals to the leaf cells. If playback doesn�t begin shortly, try restarting your device. The basic components of leaves in flowering plants (angiosperms) include the blade, the petiole, and the stipules. The epidermis of the undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores (stomata) which control the loss of water vapor (transpiration) and the. Browse more topics under anatomy of flowering plants plant tissues tissue system stem inflorescence
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant leaf structure by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







