Your Plant meristems images are ready in this website. Plant meristems are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Plant meristems files here. Get all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for plant meristems images information linked to the plant meristems topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
Plant Meristems. In plants, the meristem is the tissue where development takes place. Apical meristematic cells in the roots and shoot contribute to the primary growth that results in the plant growing longer while the vascular cambium and cork cambium that make up the lateral meristems contribute to the secondary growth (making the plant wider). When activated, these laterally arranged meristems allow plants to shape the geometry of their architecture through secondary, tertiary, and higher order branching. There are two apical meristems that reside in the growing shoot and root tips of plants, and produce the aerial and subterranean parts of the plant body, respectively.

This is because primary tissues develop from primary meristems. All vascular plants undergo primary growth, which lengthens roots and shoots. These meristems occur in all plants and are responsible for growth in length. The zone where these cells exist is known as meristem. They contain stem cells, which remain undifferentiated, and supply new cells for growth and the formation of tissues. Apical meristematic cells in the roots and shoot contribute to the primary growth that results in the plant growing longer while the vascular cambium and cork cambium that make up the lateral meristems contribute to the secondary growth (making the plant wider).
Meristem is undifferentiated plant tissue found in areas of plant growth.
The functions of meristematic tissues are as follows: The apical meristem and three kinds of lateral—vascular cambium, cork cambium, and intercalary meristem. When activated, these laterally arranged meristems allow plants to shape the geometry of their architecture through secondary, tertiary, and higher order branching. Primary growth begins in apical meristems, located at the tips of stems and roots. It is responsible for growth in the length of the primary plant body. In general there are two types of meristems:
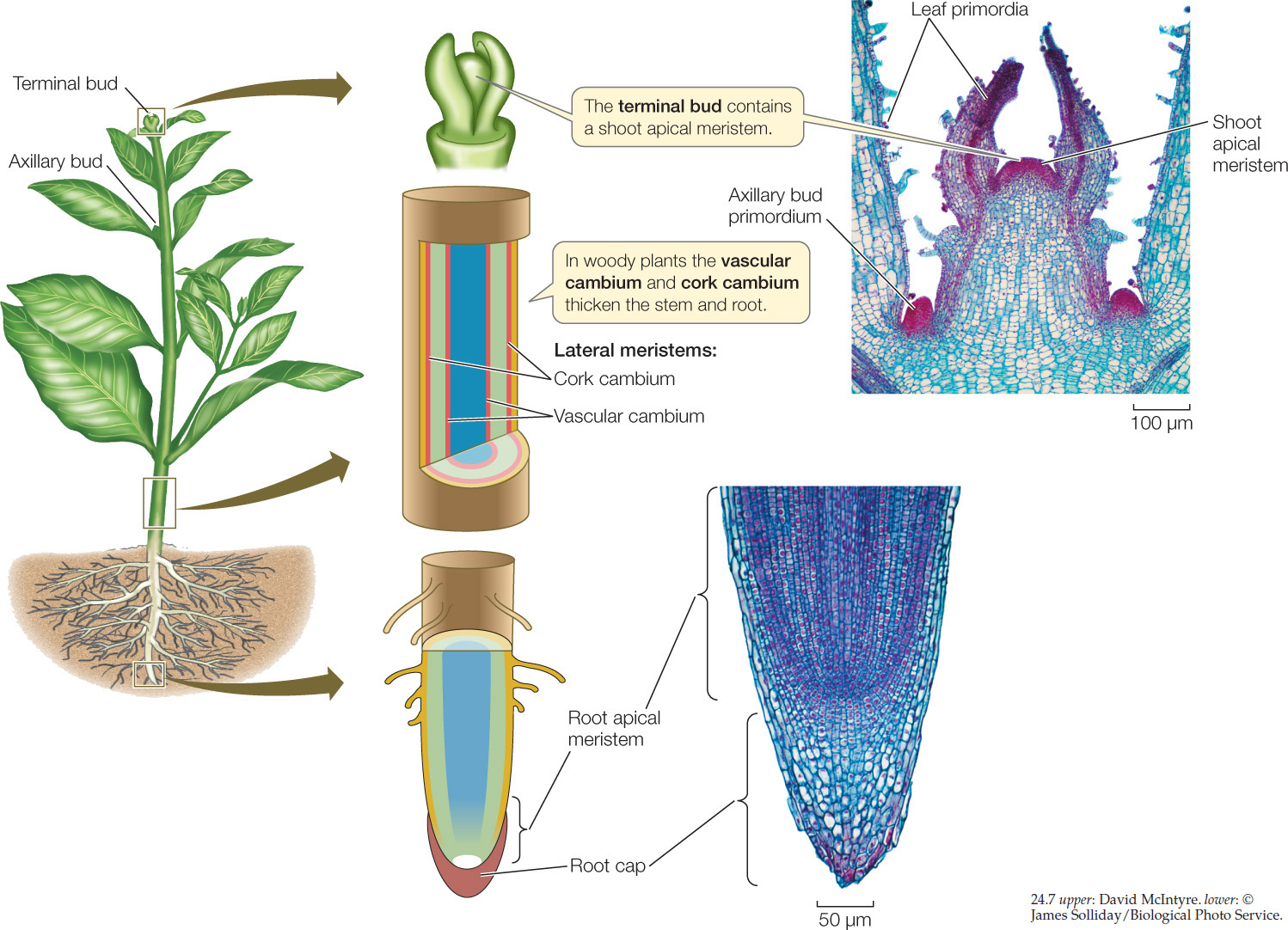 Source: webstreaming.com.br
Source: webstreaming.com.br
There are two apical meristems that reside in the growing shoot and root tips of plants, and produce the aerial and subterranean parts of the plant body, respectively. Meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in plants. Apical meristems are located at the tip (or apex) of the shoot and the root, as well as at the tips of their branches. This is because primary tissues develop from primary meristems. When activated, these laterally arranged meristems allow plants to shape the geometry of their architecture through secondary, tertiary, and higher order branching.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
It divides to form primary meristem. The sam produces all aerial parts of postembryonic organs, and the ram promotes the continuous growth of roots. Apical meristem is one of three types of meristem, or tissue which can differentiate into different cell types. They contain stem cells, which remain undifferentiated, and supply new cells for growth and the formation of tissues. Apical meristems are zones of cell division, made up of readily dividing cells, which are responsible for the increase in the height of the plant in both the shoot and root region.
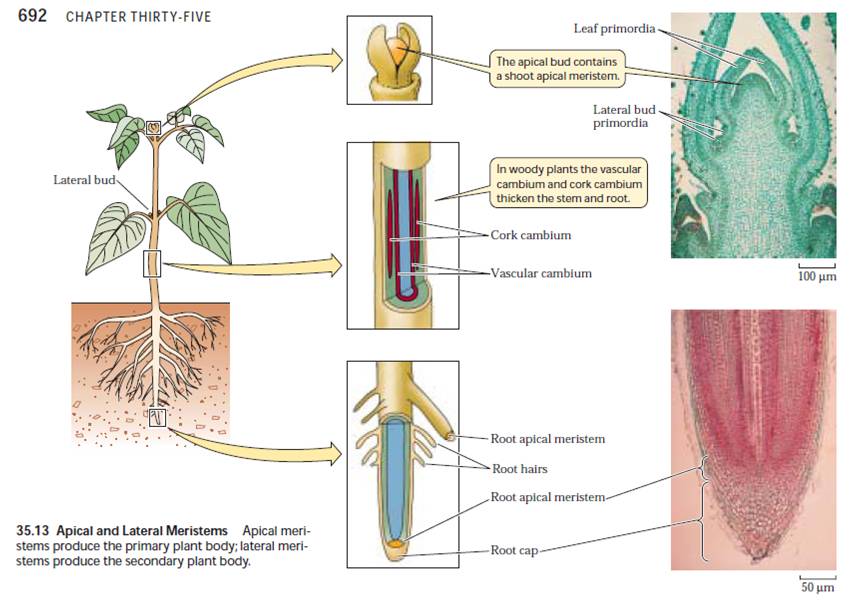 Source: biology4isc.weebly.com
Source: biology4isc.weebly.com
Meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork cambia), and intercalary (at internodes, or stem regions between the places at which leaves attach, and leaf bases, especially of certain monocotyledons—e.g., grasses). To fulfil this function, a meristem produces daughter cells that differentiate into. The functions of meristematic tissues are as follows: The meristem which is located at opposite ends of the plant axis in the tips of roots and shoots. In plants, the meristem is the tissue where development takes place.
 Source: biology-forums.com
Source: biology-forums.com
They are the actively and rapidly dividing tissues of the plant, resulting in their indefinite growth. Meristems in plants are the center of active mitotic cell division where plant growth occurs. Plant growth is facilitated by meristems, tissues containing undifferentiated cells that can perpetually divide—akin to animal stem cells. The period between the appearance of two successive leaf primordia is called plastochron (= plastochrone, fig. They possess a large nucleus devoid of the vacuole.
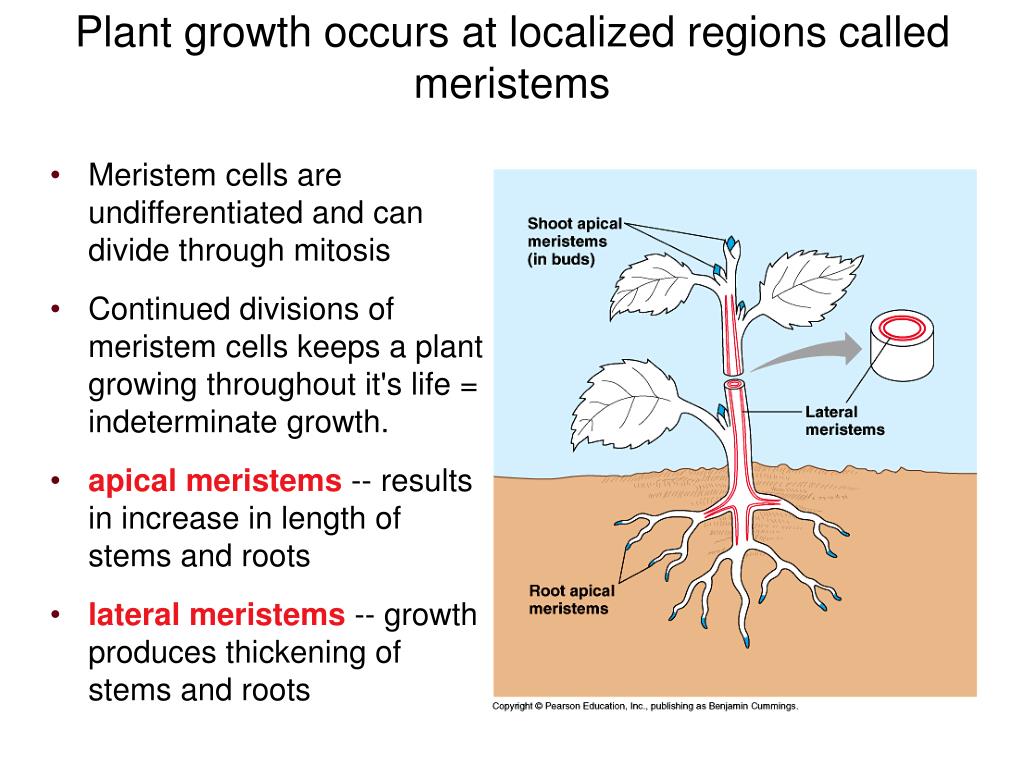 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
There are two apical meristems that reside in the growing shoot and root tips of plants, and produce the aerial and subterranean parts of the plant body, respectively. In plants, the meristem is the tissue where development takes place. A meristem is a site in the plant body where new cells of meristematic tissue form and the complex processes of growth and differentiation are initiated. When activated, these laterally arranged meristems allow plants to shape the geometry of their architecture through secondary, tertiary, and higher order branching. Meristems in plants are the center of active mitotic cell division where plant growth occurs.
 Source: education-portal.com
Source: education-portal.com
It is responsible for increase in the length of the plant, it is called as primary growth. The functions of meristematic tissues are as follows: Two meristem populations are established in the embryo, the sam (which gives rise to the aerial parts of the plant) and the ram (which gives rise to the root system). Meristems are regions of unspecialised cells in plants that are capable of cell division. All vascular plants undergo primary growth, which lengthens roots and shoots.
 Source: ricksci.com
Source: ricksci.com
To fulfil this function, a meristem produces daughter cells that differentiate into. Meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in plants. Active meristems are primarily maintained at the apices of shoots and roots. Meristem is the tissue in which growth occurs in plants. Primary meristems are responsible for the primary growth (elongation) of the plant.
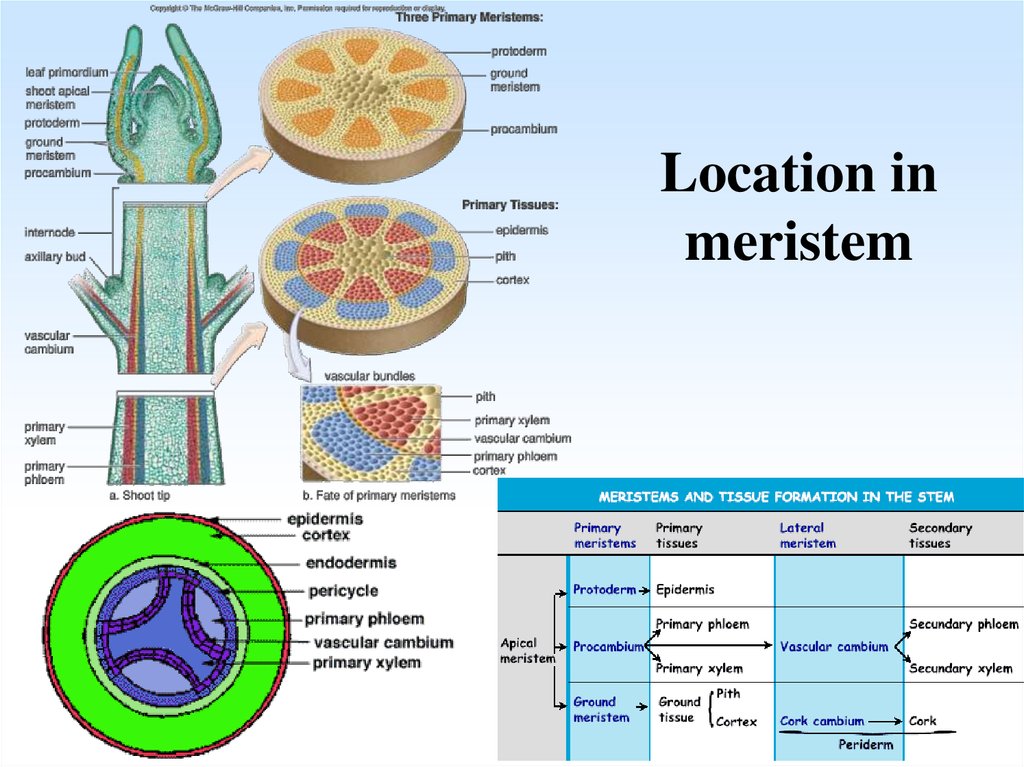 Source: en.ppt-online.org
Source: en.ppt-online.org
Plant meristems divide to produce cells that increase the height of plants, the length of roots and the girth of the stem. Primary plant meristems are the shoot and root meristems that are initiated at opposite poles of the plant embryo. Second, vertical transmission of viruses to the host progeny is often inefficient, thereby reducing the danger of viral transmission through seeds. These meristems occur in all plants and are responsible for growth in length. Apical meristematic cells in the roots and shoot contribute to the primary growth that results in the plant growing longer while the vascular cambium and cork cambium that make up the lateral meristems contribute to the secondary growth (making the plant wider).
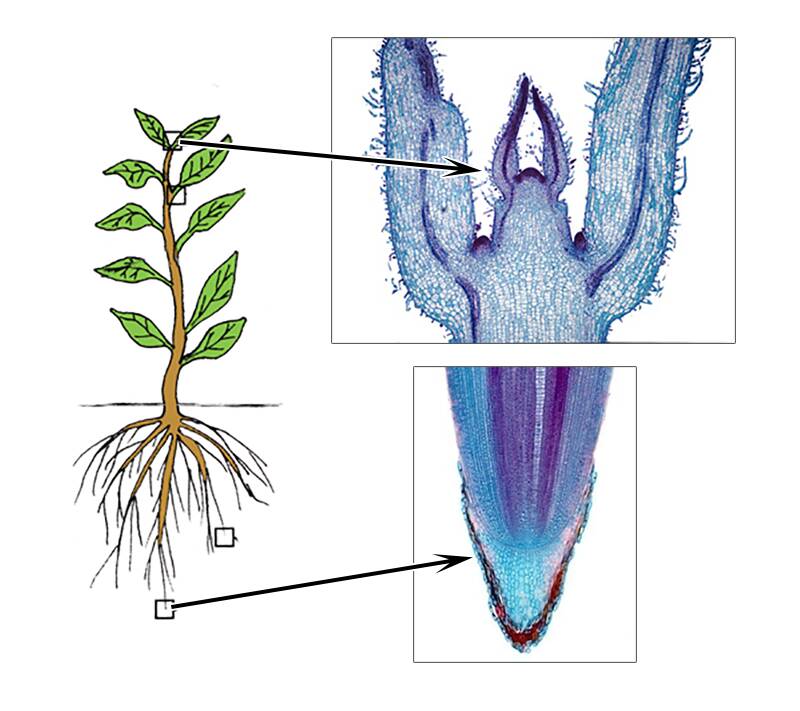 Source: propg.ifas.ufl.edu
Source: propg.ifas.ufl.edu
Meristems are regions of unspecialised cells in plants that are capable of cell division. The cells have no intercellular space. Is known as the apical meristem. Meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork cambia), and intercalary (at internodes, or stem regions between the places at which leaves attach, and leaf bases, especially of certain monocotyledons—e.g., grasses). In general there are two types of meristems:
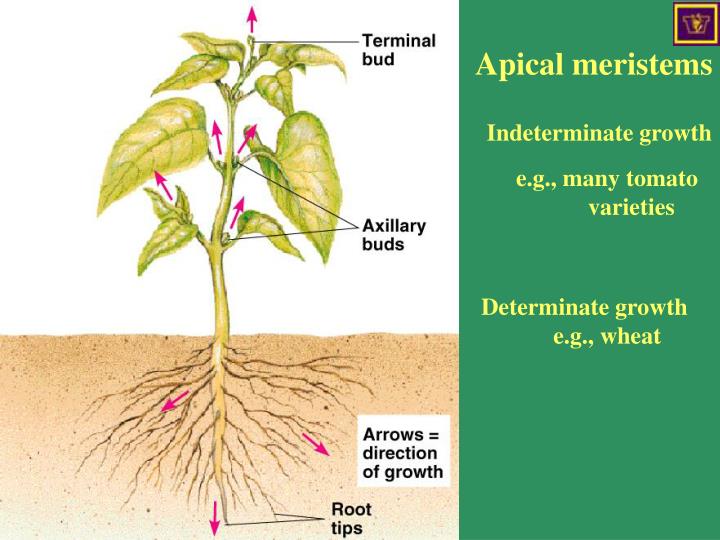 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The functions of meristematic tissues are as follows: They also produce cells that develop into leaves and flowers. Apical is a description of growth occurring at the tips. A plant has four kinds of meristems: Meristems are regions of active cell division within a plant.
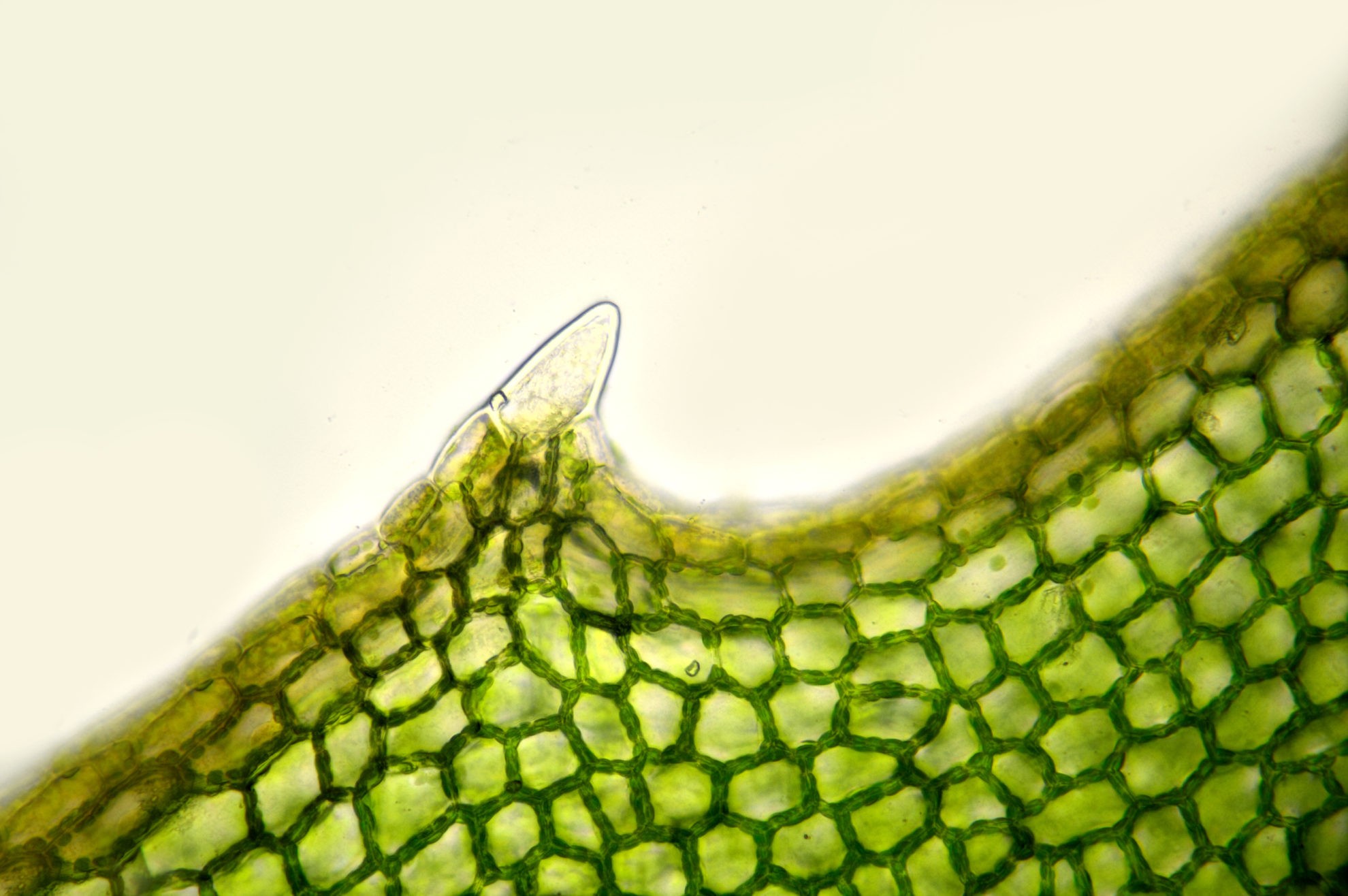 Source: biologyonline.com
Source: biologyonline.com
Meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in plants. Leaf primordia are produced periodically on the flanks. Is known as the apical meristem. Plant meristems divide to produce cells that increase the height of plants, the length of roots and the girth of the stem. The zone where these cells exist is known as meristem.
 Source: ibbiologyhelp.com
Source: ibbiologyhelp.com
Primary growth begins in apical meristems, located at the tips of stems and roots. They are the actively and rapidly dividing tissues of the plant, resulting in their indefinite growth. The meristem which is located at opposite ends of the plant axis in the tips of roots and shoots. Apical meristems are zones of cell division, made up of readily dividing cells, which are responsible for the increase in the height of the plant in both the shoot and root region. These tissues can be found in root tips, shoots, buds, and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
One of three types of meristems, or tissue that can divide into various cell types, is the apical meristem. All vascular plants undergo primary growth, which lengthens roots and shoots. Plant growth is facilitated by meristems, tissues containing undifferentiated cells that can perpetually divide—akin to animal stem cells. The apical meristem and three kinds of lateral—vascular cambium, cork cambium, and intercalary meristem. However, incipient meristems also typically form along the sides of shoots and roots (esau, 1965).

Search for other works by this author on: Apical meristem tissue is found in the tips of shoots and gives rise to leaves and flowers and is also found in the roots. The apical meristem and three kinds of lateral—vascular cambium, cork cambium, and intercalary meristem. This is because primary tissues develop from primary meristems. Apical meristems are zones of cell division, made up of readily dividing cells, which are responsible for the increase in the height of the plant in both the shoot and root region.
 Source: learnfatafat.com
Source: learnfatafat.com
A plant has four kinds of meristems: Present at the apices of the shoot and root tip. Apical meristems are located at the tip (or apex) of the shoot and the root, as well as at the tips of their branches. Plant meristems divide to produce cells that increase the height of plants, the length of roots and the girth of the stem. The meristems which are present universally at the apices of stem, branches and roots are called apical meristems.
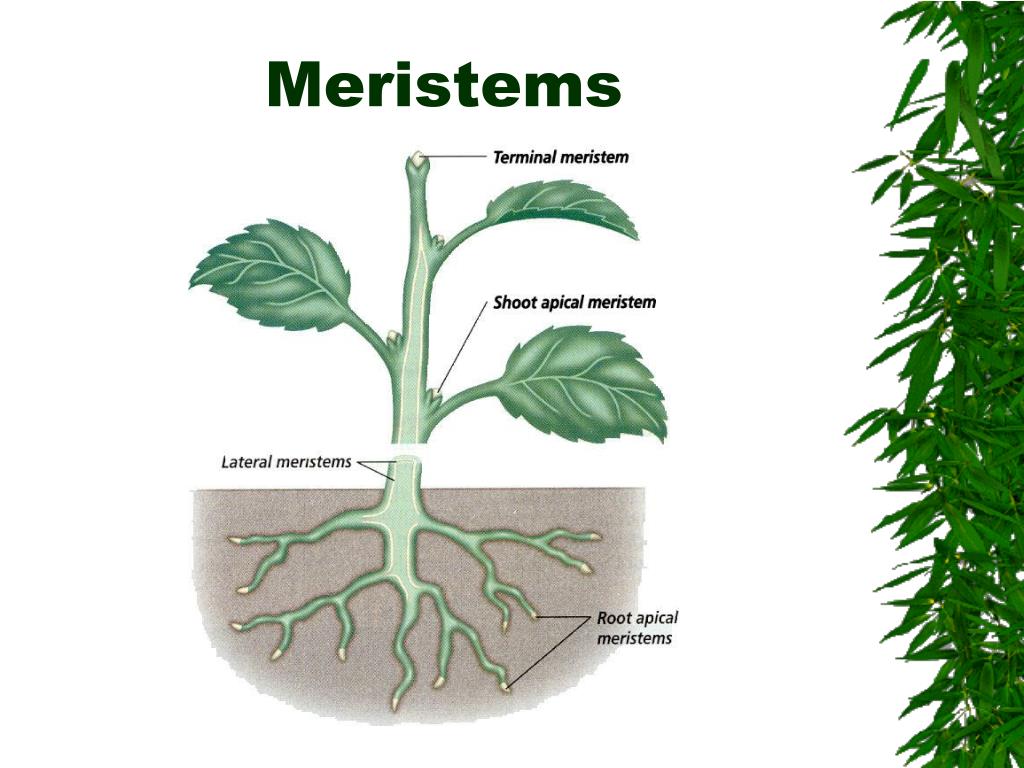 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
They divide to produce primary permanent tissue that forms the primary plant body. When activated, these laterally arranged meristems allow plants to shape the geometry of their architecture through secondary, tertiary, and higher order branching. All vascular plants undergo primary growth, which lengthens roots and shoots. Meristem is undifferentiated plant tissue found in areas of plant growth. Meristematic tissues, or simply meristems, are tissues in which the cells remain forever young and divide actively throughout the life of the plant.when a meristematic cell divides in two, the new cell that remains in the meristem is called an initial, the other the derivative.as new cells are added by repeated mitotic divisions of the initial cells, the derivatives are pushed farther away.
 Source: sakuhycizafek.janettravellmd.com
Source: sakuhycizafek.janettravellmd.com
Apical meristem is one of three types of meristem, or tissue which can differentiate into different cell types. Meristem is the tissue in which growth occurs in plants. A plant has four kinds of meristems: Meristems are regions of unspecialised cells in plants that are capable of cell division. Apical meristems and lateral meristems.
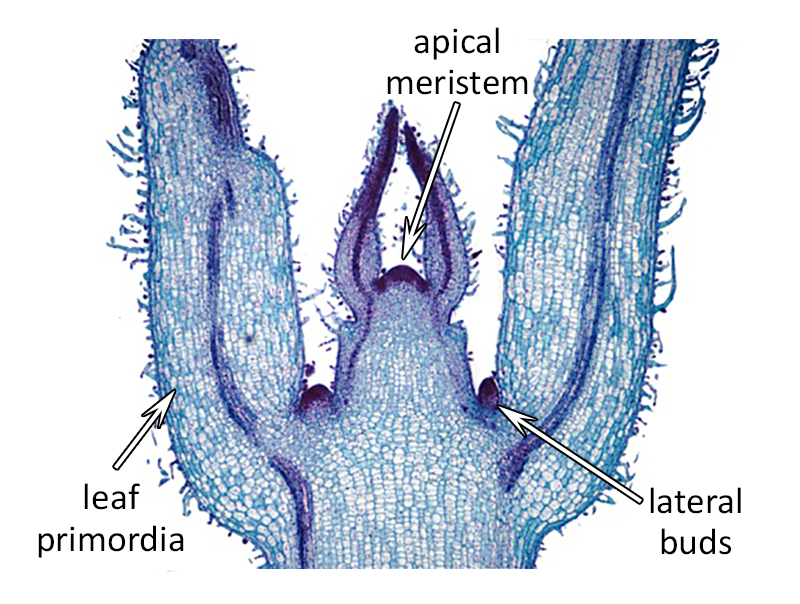 Source: microbenotes.com
Source: microbenotes.com
Meristem is undifferentiated plant tissue found in areas of plant growth. The zone where these cells exist is known as meristem. In general there are two types of meristems: Meristems are regions of active cell division within a plant. Growth means the irreversible increase in size that comes from both cell division and cell enlargement.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title plant meristems by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







