Your Plant microbiome images are ready. Plant microbiome are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Plant microbiome files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for plant microbiome pictures information linked to the plant microbiome topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Plant Microbiome. The core plant microbiome is thought to comprise keystone microbial taxa that are important for plant fitness and established through evolutionary mechanisms of selection and enrichment of microbial taxa containing essential functions. Studying the distribution of microbial taxa and genes across plant habitats has revealed the importance of various ecological and evolutionary forces shaping plant microbiota. A large body of research has shown that the interactions between plants and their microbiomes are highly complex and dynamic in nature (abhilash et al., 2016; Plant microbiome structure and functions are shaped by several factors, including host genotype and developmental stage, the presence or absence of diseases, and environmental conditions.
 Embracing Community Ecology in Plant Microbiome Research From cell.com
Embracing Community Ecology in Plant Microbiome Research From cell.com
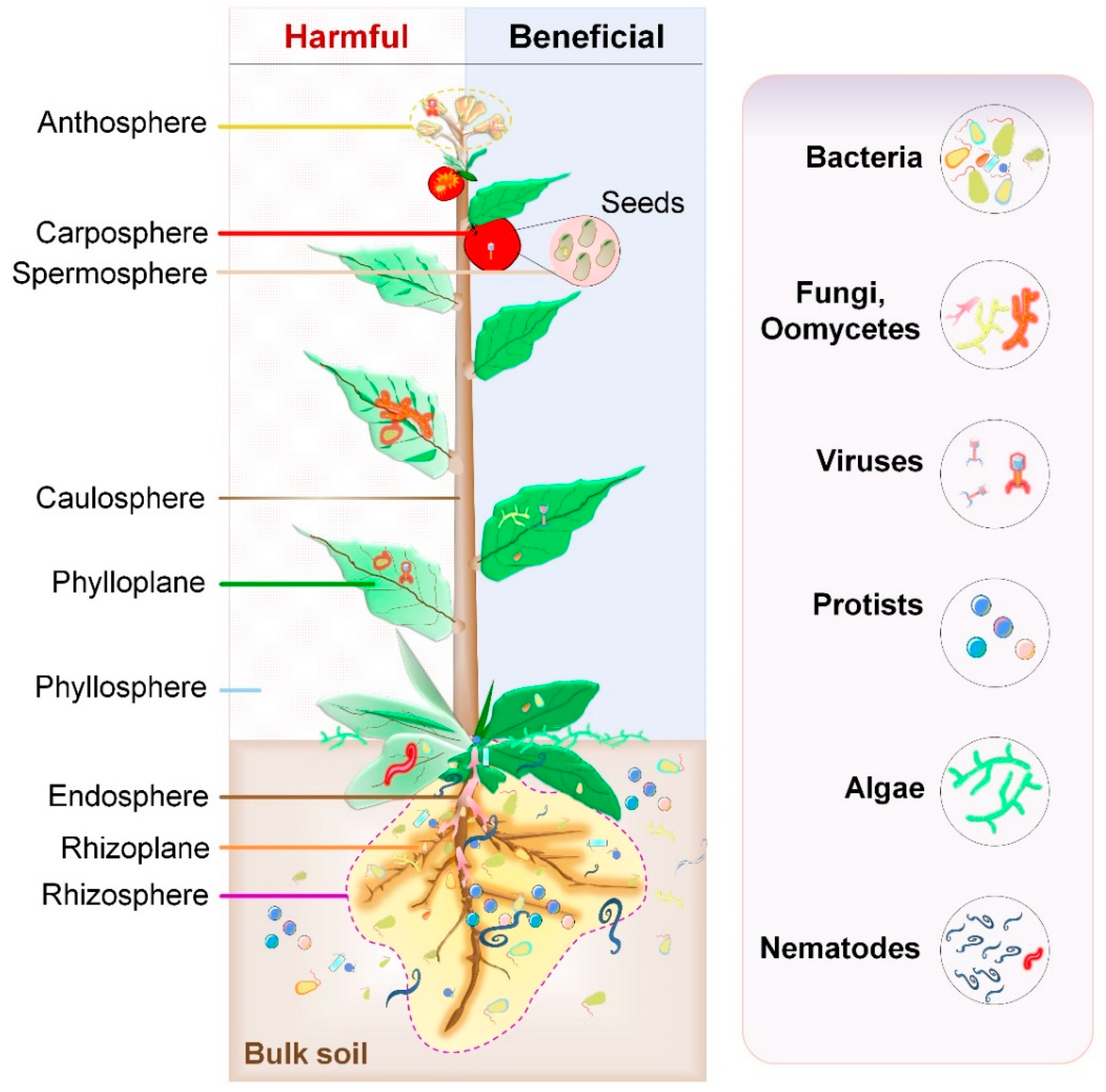
In particular, selection imposed by plant habitats strongly shapes the diversity and composition of microbiota and leads to microbial adaptation associated with navigating the plant immune system and. Plants and their microbiomes have evolved adaptation strategies over time. These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere. Plant genomes contribute to the structure and function of the plant microbiome, a key determinant of plant health and productivity. In this review, we explore how plant microbiome research has unravelled the complex network of genetic, biochemical, physical and metabolic interactions among the plant, the associated microbial communities and the environment. The plant microbiome extends the functional system of plants by participating in a variety of processes, including nutrient absorption, growth promotion, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
Manipulating the plant holobiont by microbiome engineering is an emerging biotechnological.
Understanding the plant microbiome interactions could provide an opportunity to develop strategies for sustainable agricultural. The microbiome is intricately involved in plant health and serves as a reservoir of additional genes that plants can access when needed. Microbes that form specialized structures with the help of plants, and live in a mutually beneficial partnership with plants, are known as. Plants are intimately associated with diverse, taxonomically structured communities of microorganisms. The core plant microbiome is thought to comprise keystone microbial taxa that are important for plant fitness and established through evolutionary mechanisms of selection and enrichment of microbial taxa containing essential functions. Over the last few years, research into plant microbiota (i.e.
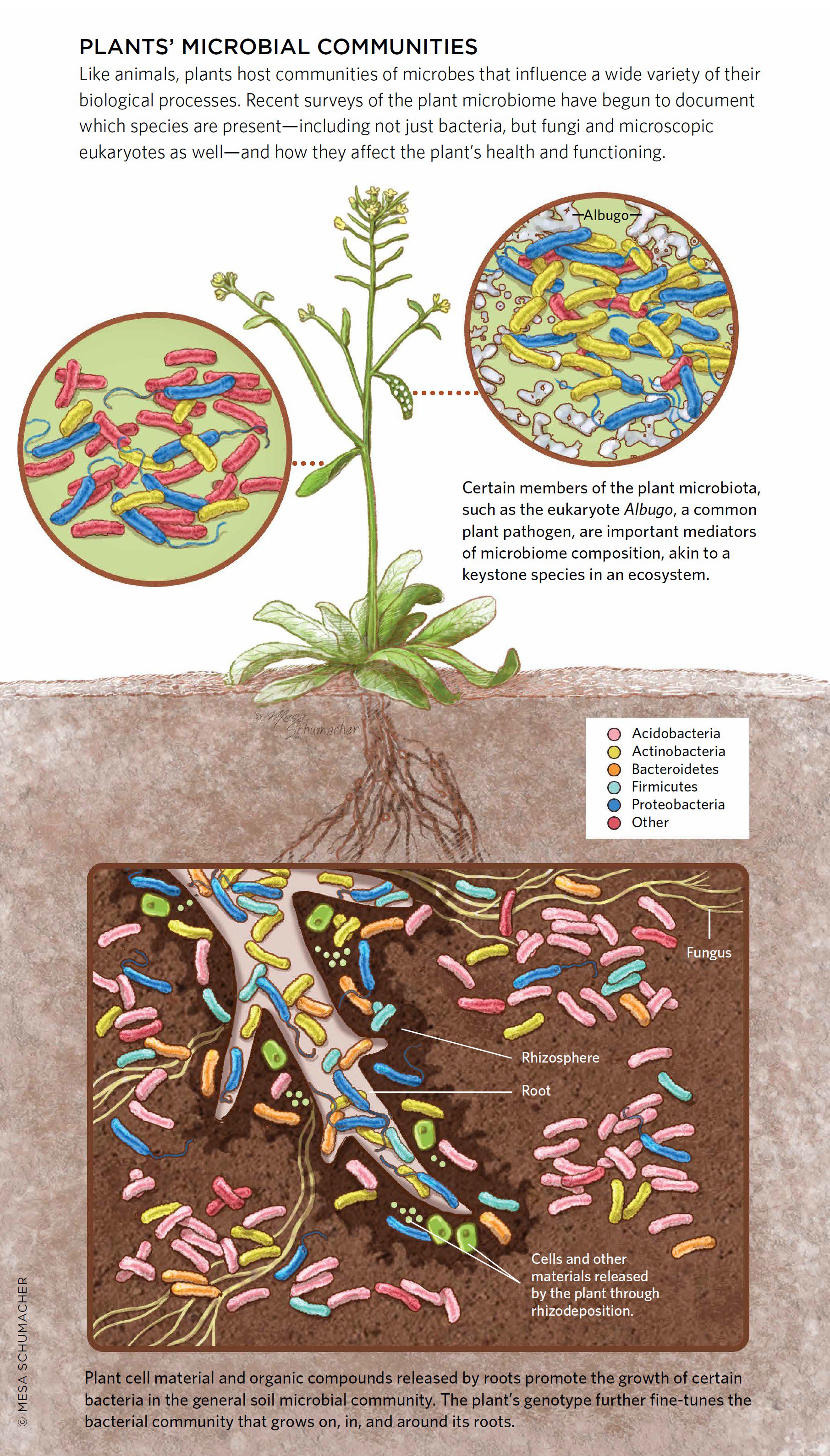
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants.microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere. Understanding the plant microbiome interactions could provide an opportunity to develop strategies for sustainable agricultural. Manuscripts submitted to the plant microbiome section should advance our knowledge on the microbiota of agricultural and wild plants and their surrounding soil. Plants share their habitat with a variety of microbes that include bacteria, oomycetes, fungi, archaea, and a poorly explored universe of viruses (reviewed in agler et al., 2016, berendsen et al., 2012, buée et al., 2009, swanson et al., 2009).
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
In particular, selection imposed by plant habitats strongly shapes the diversity and composition of microbiota and leads to microbial adaptation associated with navigating the plant immune system and. Studying the distribution of microbial taxa and genes across plant habitats has revealed the importance of various ecological and evolutionary forces shaping plant microbiota. Regardless of their physiological purpose, lignin and tannins represent a significant portion of terrestrial carbon. Over the last few years, research into plant microbiota (i.e. Microbes that form specialized structures with the help of plants, and live in a mutually beneficial partnership with plants, are known as.
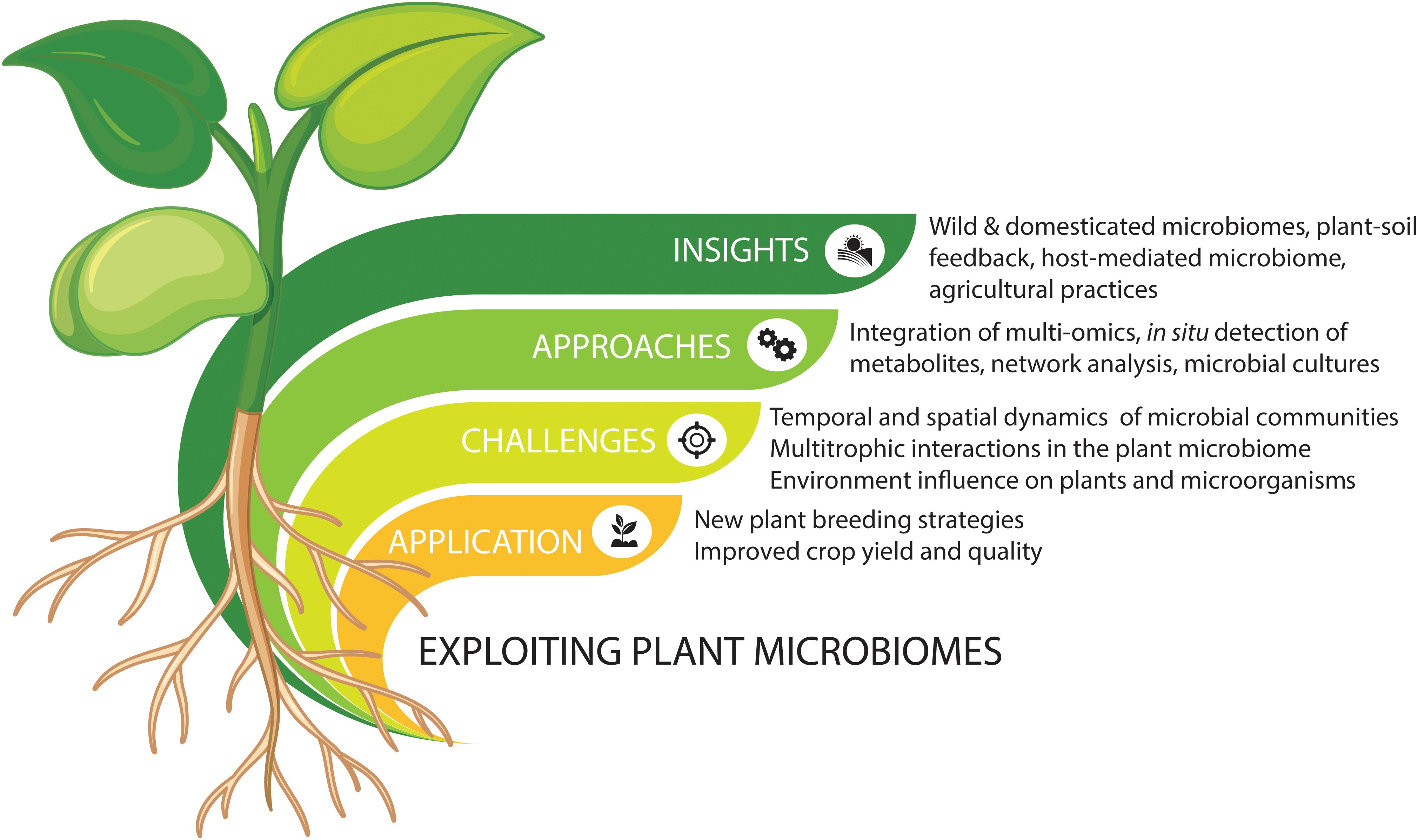 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Plants produce polyphenols for a variety of purposes. Importantly, the microbiome is strongly influenced by the plant genome and may be considered as an. The core plant microbiome is thought to comprise keystone microbial taxa that are important for plant fitness and established through evolutionary mechanisms of selection and enrichment of microbial taxa containing essential functions. The microbiome (microbiota and their genomes) inhabiting the soil, rhizosphere, roots and other plant tissues establishes. Plant genomes contribute to the structure and function of the plant microbiome, a key determinant of plant health and productivity.
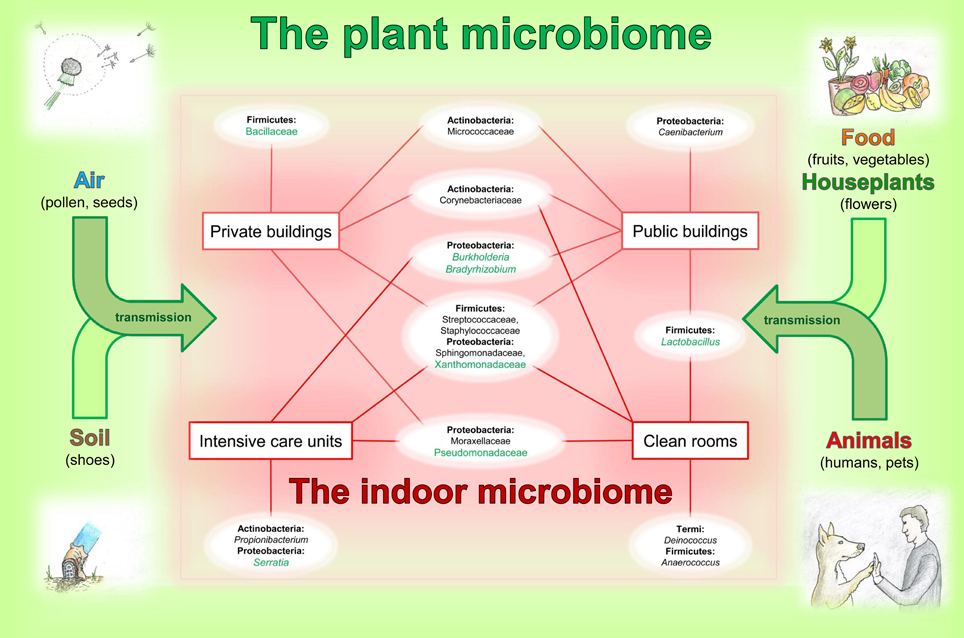 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants.microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. Microbes that form specialized structures with the help of plants, and live in a mutually beneficial partnership with plants, are known as. Methodological advances over the past two decades have propelled plant microbiome research, allowing the field to comprehensively test ideas proposed over a century ago and generate many new hypotheses. The core plant microbiome is thought to comprise keystone microbial taxa that are important for plant fitness and established through evolutionary mechanisms of selection and enrichment of microbial taxa containing essential functions. Manipulating the plant holobiont by microbiome engineering is an emerging biotechnological.
 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
In particular, selection imposed by plant habitats strongly shapes the diversity and composition of microbiota and leads to microbial adaptation associated with navigating the plant immune system and. Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants.microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The plant microbiota includes bacteria, fungi, protists, nematodes and viruses that colonize all accessible plant tissues (trivedi et al., 2020). The microbiome is intricately involved in plant health and serves as a reservoir of additional genes that plants can access when needed. These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
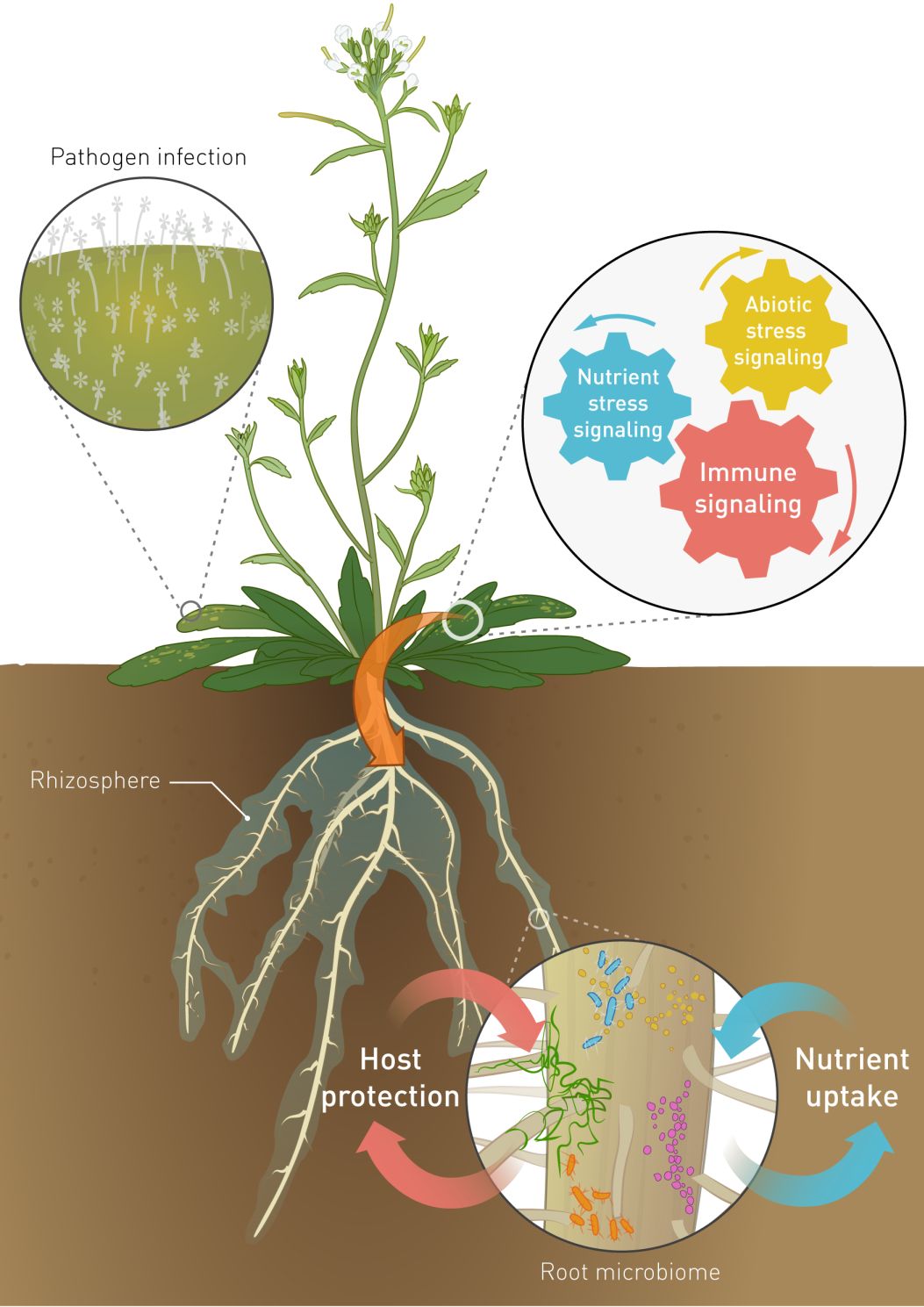
These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere. The symbiotic microbiota of plants are involved in everything from nutrient acquisition to escalation of defense systems during periods of biotic and abiotic stresses. The core plant microbiome is thought to comprise keystone microbial taxa that are important for plant fitness and established through evolutionary mechanisms of selection and enrichment of microbial taxa containing essential functions. Understanding the plant microbiome interactions could provide an opportunity to develop strategies for sustainable agricultural. Regardless of their physiological purpose, lignin and tannins represent a significant portion of terrestrial carbon.
 Source: plantae.org
Source: plantae.org
Plant microbiomes have remarkably robust composition in comparison to the complex and dynamic microbial environments from which they form, suggesting finely tuned discrimination by the plant host. The symbiotic microbiota of plants are involved in everything from nutrient acquisition to escalation of defense systems during periods of biotic and abiotic stresses. The un general assembly proclaimed that 2020 is the international year of plant health to recognize and protect plant health, and to raise awareness of the crucial role of. Plants share their habitat with a variety of microbes that include bacteria, oomycetes, fungi, archaea, and a poorly explored universe of viruses (reviewed in agler et al., 2016, berendsen et al., 2012, buée et al., 2009, swanson et al., 2009). Changes in the rhizosphere microbiome and/or epigenetic changes.
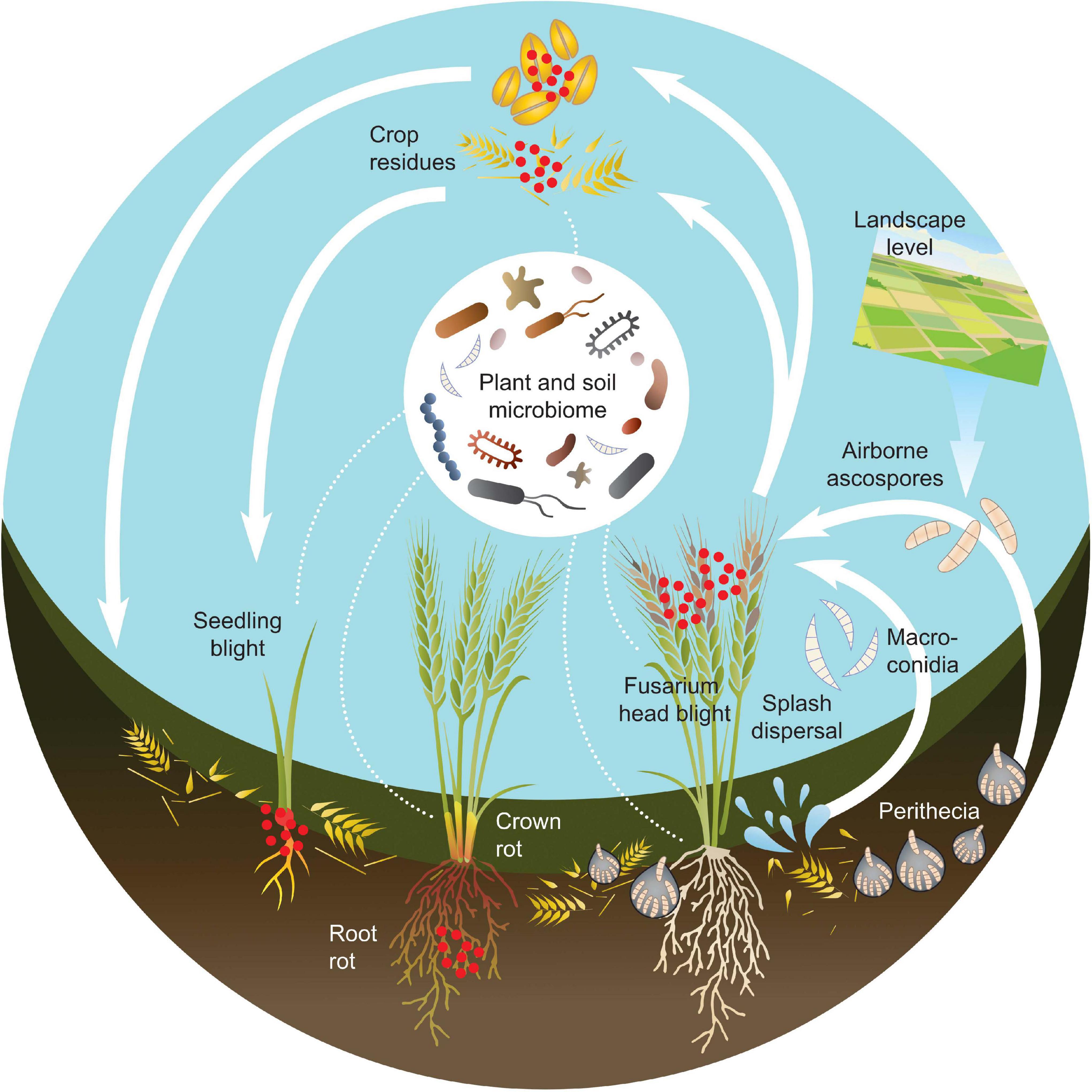 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Importantly, the microbiome is strongly influenced by the plant genome and may be considered as an. Plants produce polyphenols for a variety of purposes. Analysis of the plant microbiome involves linking microbial ecology and the plant host�s biology and functioning, and viewing microorganisms as a reservoir of additional genes and functions. Plant microbiome structure and functions are shaped by several factors, including host genotype and developmental stage, the presence or absence of diseases, and environmental conditions. Microbes that form specialized structures with the help of plants, and live in a mutually beneficial partnership with plants, are known as.
Source: researchgate.net
Microbes that form specialized structures with the help of plants, and live in a mutually beneficial partnership with plants, are known as. Manuscripts submitted to the plant microbiome section should advance our knowledge on the microbiota of agricultural and wild plants and their surrounding soil. Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants.microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. Several studies have shown that bacterial communities are dynamically shaped by environmental factors such as soil, season, daytime, as well as host factors such as species, developmental stage, and compartment. The plant microbiota includes bacteria, fungi, protists, nematodes and viruses that colonize all accessible plant tissues (trivedi et al., 2020).
 Source: microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com
Source: microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com
These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere. Plant microbiome structure and functions are shaped by several factors, including host genotype and developmental stage, the presence or absence of diseases, and environmental conditions. These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere. Studying the distribution of microbial taxa and genes across plant habitats has revealed the importance of various ecological and evolutionary forces shaping plant microbiota. Regardless of their physiological purpose, lignin and tannins represent a significant portion of terrestrial carbon.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Plants are intimately associated with diverse, taxonomically structured communities of microorganisms. Regardless of their physiological purpose, lignin and tannins represent a significant portion of terrestrial carbon. These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere. The microbiome (microbiota and their genomes) inhabiting the soil, rhizosphere, roots and other plant tissues establishes. Lignin, the most abundant polyphenols, are a part of the plant cell wall, whereas the second most abundant type of polyphenol, tannins, serve defensive roles in plants.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Methodological advances over the past two decades have propelled plant microbiome research, allowing the field to comprehensively test ideas proposed over a century ago and generate many new hypotheses. Studying the distribution of microbial taxa and genes across plant habitats has revealed the importance of various ecological and evolutionary forces shaping plant. The microbiome is intricately involved in plant health and serves as a reservoir of additional genes that plants can access when needed. Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants.microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The symbiotic microbiota of plants are involved in everything from nutrient acquisition to escalation of defense systems during periods of biotic and abiotic stresses.
 Source: cegsb.icrisat.org
Source: cegsb.icrisat.org
The term microbiome describes either the collective. Understanding the plant microbiome interactions could provide an opportunity to develop strategies for sustainable agricultural. Plants share their habitat with a variety of microbes that include bacteria, oomycetes, fungi, archaea, and a poorly explored universe of viruses (reviewed in agler et al., 2016, berendsen et al., 2012, buée et al., 2009, swanson et al., 2009). Changes in the rhizosphere microbiome and/or epigenetic changes. Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants.microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host.
 Source: uu.nl
Source: uu.nl
Lignin, the most abundant polyphenols, are a part of the plant cell wall, whereas the second most abundant type of polyphenol, tannins, serve defensive roles in plants. Studies directed to microbial interactions in plant. Lignin, the most abundant polyphenols, are a part of the plant cell wall, whereas the second most abundant type of polyphenol, tannins, serve defensive roles in plants. Regardless of their physiological purpose, lignin and tannins represent a significant portion of terrestrial carbon. The un general assembly proclaimed that 2020 is the international year of plant health to recognize and protect plant health, and to raise awareness of the crucial role of.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
These factors may lead to distinct microbial communities in the rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllosphere. The microbiome is intricately involved in plant health and serves as a reservoir of additional genes that plants can access when needed. Manipulating the plant holobiont by microbiome engineering is an emerging biotechnological. Importantly, the microbiome is strongly influenced by the plant genome and may be considered as an. The plant microbiota includes bacteria, fungi, protists, nematodes and viruses that colonize all accessible plant tissues (trivedi et al., 2020).
 Source: theaustralianagronomist.com
Source: theaustralianagronomist.com
Importantly, the microbiome is strongly influenced by the plant genome and may be considered as an. Importantly, the microbiome is strongly influenced by the plant genome and may be considered as an. Plant microbiomes have remarkably robust composition in comparison to the complex and dynamic microbial environments from which they form, suggesting finely tuned discrimination by the plant host. Over the last few years, research into plant microbiota (i.e. Regardless of their physiological purpose, lignin and tannins represent a significant portion of terrestrial carbon.
 Source: microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com
Source: microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com
Plant microbiomes have remarkably robust composition in comparison to the complex and dynamic microbial environments from which they form, suggesting finely tuned discrimination by the plant host. Studies directed to microbial interactions in plant. The core plant microbiome is thought to comprise keystone microbial taxa that are important for plant fitness and established through evolutionary mechanisms of selection and enrichment of microbial taxa containing essential functions. Manuscripts submitted to the plant microbiome section should advance our knowledge on the microbiota of agricultural and wild plants and their surrounding soil. The plant microbiome extends the functional system of plants by participating in a variety of processes, including nutrient absorption, growth promotion, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
 Source: eurekalert.org
Source: eurekalert.org
The microbiome (microbiota and their genomes) inhabiting the soil, rhizosphere, roots and other plant tissues establishes. Plants produce polyphenols for a variety of purposes. Importantly, the microbiome is strongly influenced by the plant genome and may be considered as an. Manipulating the plant holobiont by microbiome engineering is an emerging biotechnological. Microbes that form specialized structures with the help of plants, and live in a mutually beneficial partnership with plants, are known as.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant microbiome by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







