Your Plant nucleus images are available. Plant nucleus are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Plant nucleus files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for plant nucleus pictures information connected with to the plant nucleus keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Plant Nucleus. Example is (i) paramecium (mega and micronucleus) (ii) balantidium (iii) liver cells and cartilage cells. Until now, the nuclear response was mostly analyzed from the biochemical and transcriptional points of view. As in animals, the plant nucleus is delimited by a double membrane interrupted by nuclear pores, which allow exchanges with the cytoplasm. The nucleus of a plant cell is in the cytoplasm with the centre of the cell typically busy by the vacuole.
 Cell Nucleus From biology-questions-and-answers.com
Cell Nucleus From biology-questions-and-answers.com
An area via a cell might reveal the nucleus at the side, or it could show up in the centre of the cell if the area was of the “side” of a cell. The eukaryotic nucleus is enclosed by the nuclear envelope, which is perforated by the nuclear pores, the gateways of macromolecular exchange between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm. Plant cells can be defined as the eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out certain specific functions. The mechanical strength for the nucleus is provided by the nuclear matrix, a network of fibres and filaments which performs functions similar to the cytoskeleton. The most dramatic reorganization of this organelle occurs during mitosis and meiosis. Until now, the nuclear response was mostly analyzed from the biochemical and transcriptional points of view.
An eukaryotic cell’s nucleus directly or indirectly controls virtually all cellular physiological activities, including initiation, regulation, and termination of enzymatic events.
In an animal cell, the nucleus is typically located in the central region of the cell. The plant cell contains different components inside it, the cell wall, and these components have different functions. The nucleus is an organelle that consists of the genetic information for that organism. Both plant and animal cells contain nucleus along with similar organelles. All plant cells contain a nucleus, a structure that stores dna and acts as a cell�s command center. The nucleus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells and functions as the holder of a cell’s blueprint.
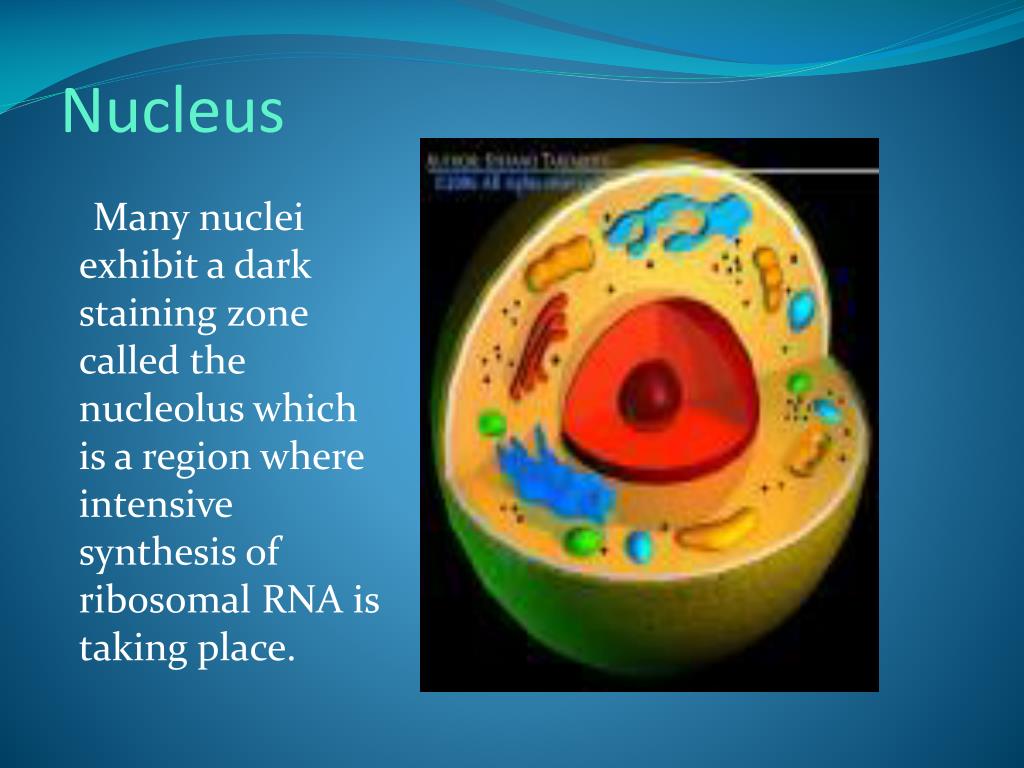 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
All plant cells contain a nucleus, a structure that stores dna and acts as a cell�s command center. Likewise, in the plant cell, the nucleus is located more on the periphery due to the large. It is surrounded by the nuclear envelope and is filled with nucleoplasm. The nucleus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells and functions as the holder of a cell’s blueprint. In an animal cell, the nucleus is located in the central region of the cell.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Other organelles found in a plant cell outside the nucleus are the vacuole, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, smooth endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. The nucleus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells and functions as the holder of a cell’s blueprint. An eukaryotic cell’s nucleus directly or indirectly controls virtually all cellular physiological activities, including initiation, regulation, and termination of enzymatic events. The most dramatic reorganization of this organelle occurs during mitosis and meiosis. Both plant and animal cells contain nucleus along with similar organelles.

If you had a swelling of dough and also hidden a pea in one side. Cell biology of the plant nucleus. Plants are multicellular organisms in which the plant cells act as the basic structural and functional units. In line with the established role of nuclear mechanics in animal development, plant development also relies on nuclear mechanotransduction. It stores the cell�s hereditary material, or dna, and it coordinates the cell�s activities, which include intermediary metabolism, growth, protein synthesis, and reproduction.
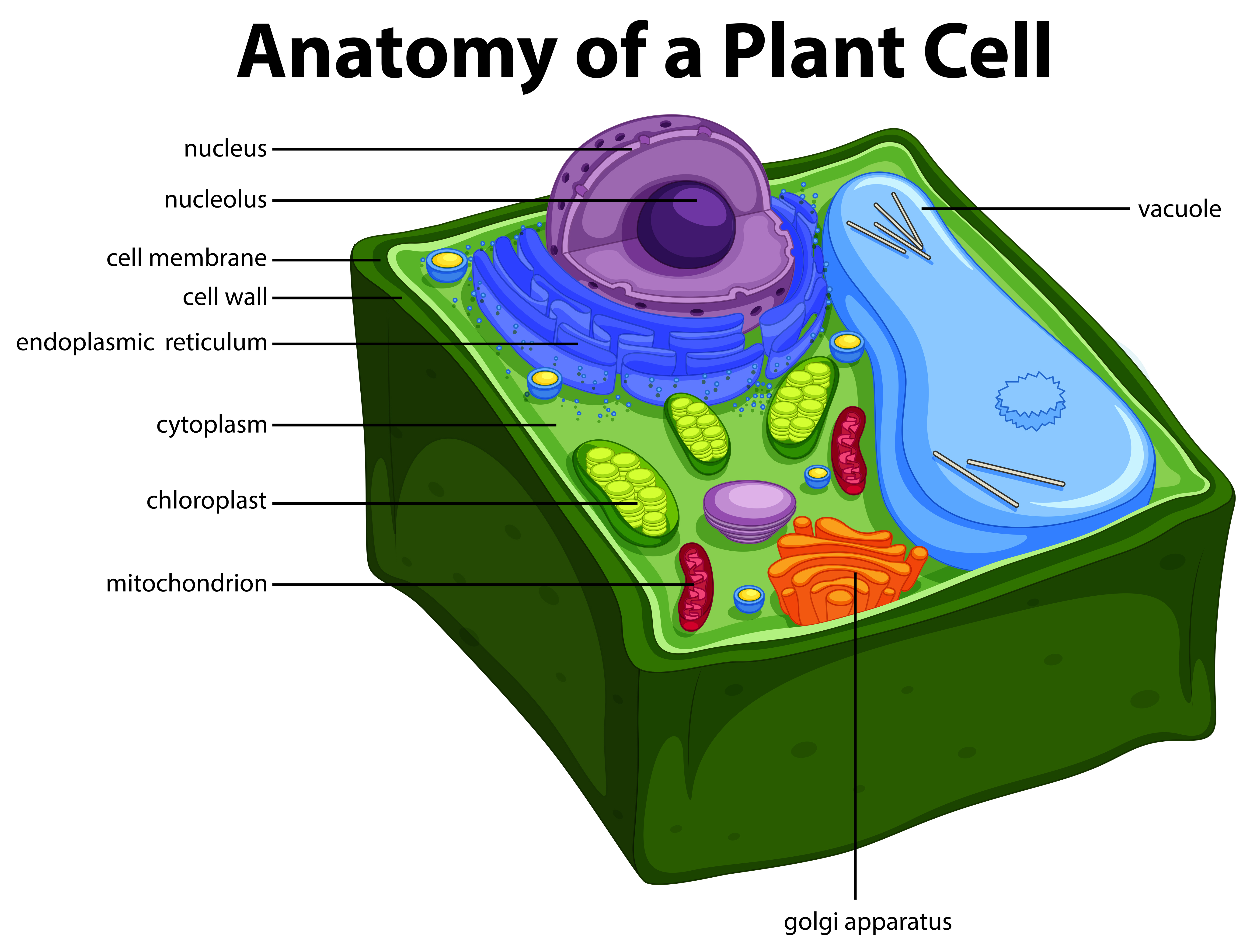 Source: vecteezy.com
Source: vecteezy.com
Plant cells can be defined as the eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out certain specific functions. One of the distinctive aspects of a plant cell is the presence of a cell. It is surrounded by the nuclear envelope and is filled with nucleoplasm. Plant nucleus movement is the movement of the cell nucleus in plants by the cytoskeleton. Notice how it has a rigid shape, due to the presence of a cell wall.
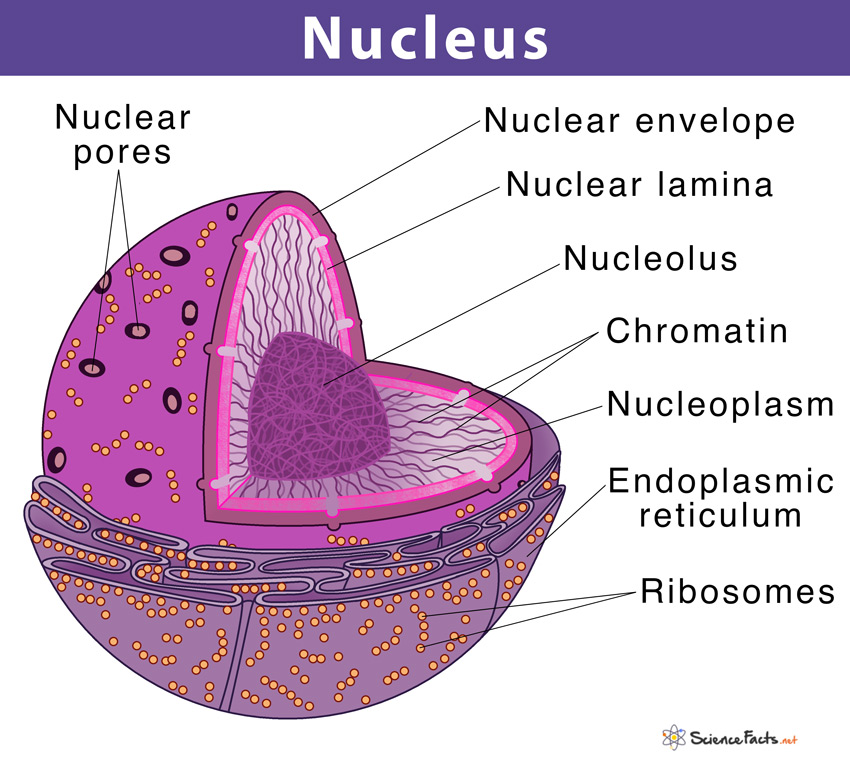 Source: sciencefacts.net
Source: sciencefacts.net
The nucleus is an organelle that consists of the genetic information for that organism. It is also the repository of genetic information (the genome), housing and protecting the chromosomes and the genes that they carry. The nuclear envelope contains nuclear pores which allow molecules with the appropriate nuclear import and export signals in and out of the nucleus. In line with the established role of nuclear mechanics in animal development, plant development also relies on nuclear mechanotransduction. In an animal cell, the nucleus is located in the central region of the cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The nucleus here is orange, shown with a chunk taken out to expose the interior. In an animal cell, the nucleus is located in the central region of the cell. The nucleolus is found within the nucleus, occupying 25% per cent of the volume. In an animal cell, the nucleus is typically located in the central region of the cell. Above is a generic plant cell.

The outer nuclear membrane (onm). A cell wall surrounds the plant cell and provides a shape to it. The reason the nucleus is referred to as the brain of the cell is that it controls the growth and reproduction of the cell. An important aspect of plant behavior includes responding to directional stimuli, which requires changes in the cellular signaling to control spatial elements. The spherical or ovoidal plant cell dna resides in a nucleus, occasionally when situation arises develops lobes, which increases its surface area.
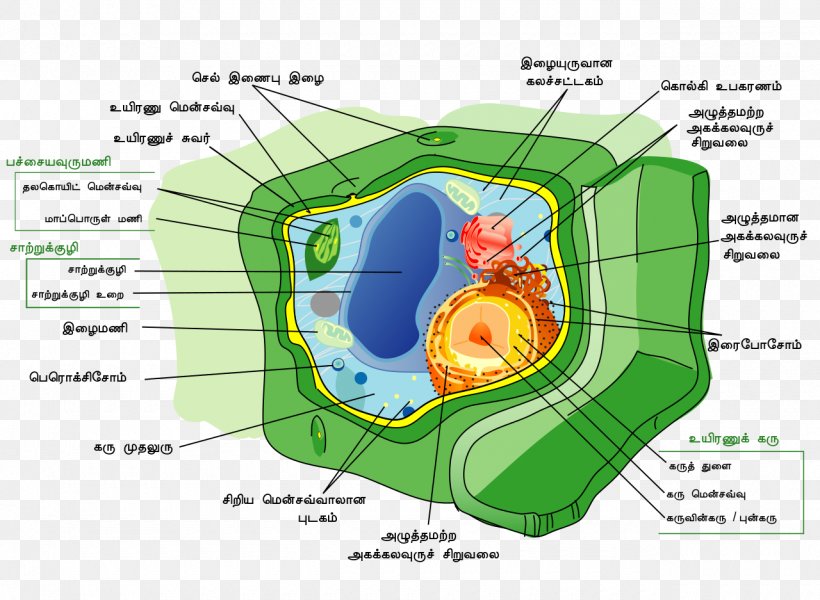 Source: favpng.com
Source: favpng.com
It is also the repository of genetic information (the genome), housing and protecting the chromosomes and the genes that they carry. In an animal cell, the nucleus is located in the central place of the cell. This organelle has two major functions. All plant cells contain a nucleus, a structure that stores dna and acts as a cell�s command center. An area via a cell might reveal the nucleus at the side, or it could show up in the centre of the cell if the area was of the “side” of a cell.
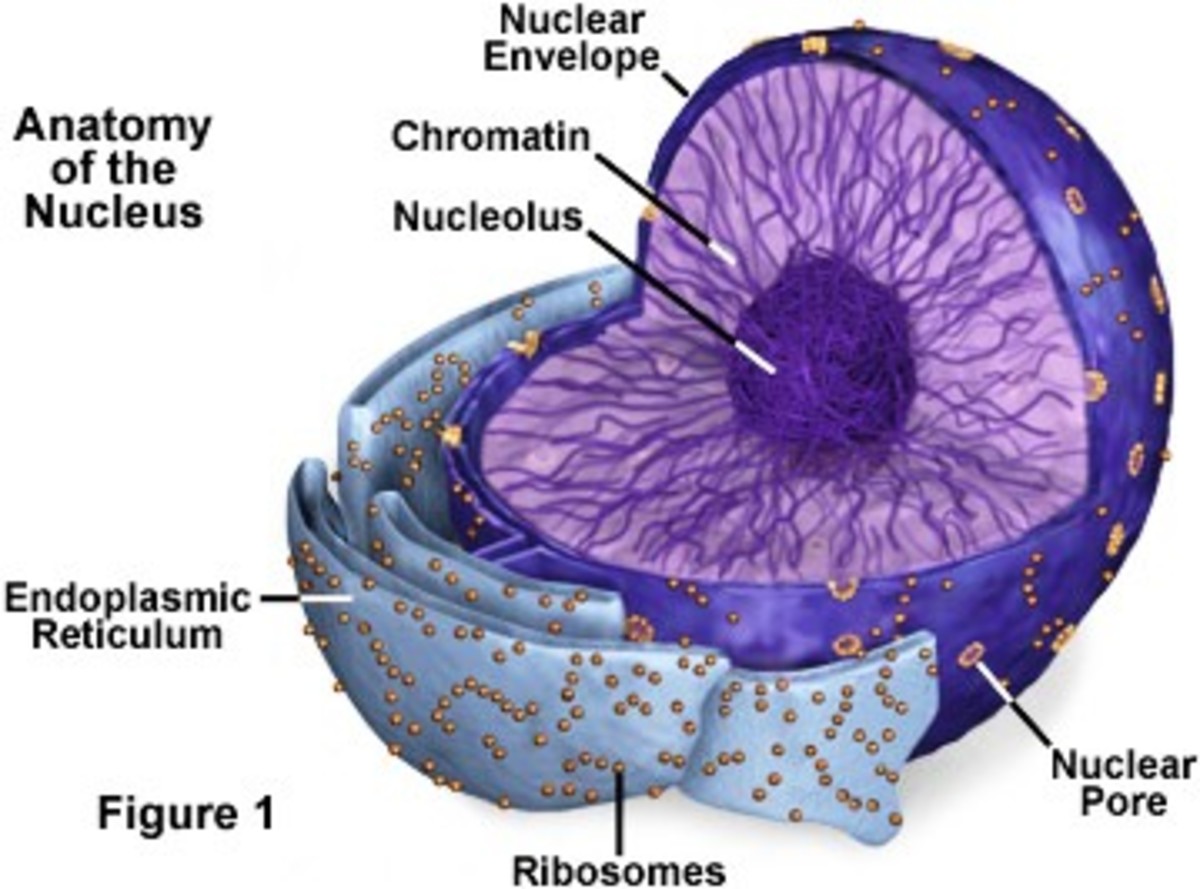 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
All plant cells contain a nucleus, a structure that stores dna and acts as a cell�s command center. One of the distinctive aspects of a plant cell is the presence of a cell. A cell wall surrounds the plant cell and provides a shape to it. All plant cells contain a nucleus, a structure that stores dna and acts as a cell�s command center. The nucleolus produces ribosomal rna while chromatin is a combination of dna, protein and rna.
Source: frederickirsteine02081.blogspot.com
In an animal cell, the nucleus is typically located in the central region of the cell. Example is (i) paramecium (mega and micronucleus) (ii) balantidium (iii) liver cells and cartilage cells. It is also the repository of genetic information (the genome), housing and protecting the chromosomes and the genes that they carry. The nucleus contains the nucleolus and chromatin. The nuclear envelope contains nuclear pores which allow molecules with the appropriate nuclear import and export signals in and out of the nucleus.
 Source: ibiologia.com
Source: ibiologia.com
The eukaryotic nucleus is enclosed by the nuclear envelope, which is perforated by the nuclear pores, the gateways of macromolecular exchange between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm. It is also referred to as monokaryotic cell, mostly plant cell which contain single nucleus. Other organelles found in a plant cell outside the nucleus are the vacuole, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, smooth endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. The outer nuclear membrane (onm). It stores the cell�s hereditary material, or dna, and it coordinates the cell�s activities, which include intermediary metabolism, growth, protein synthesis, and reproduction.
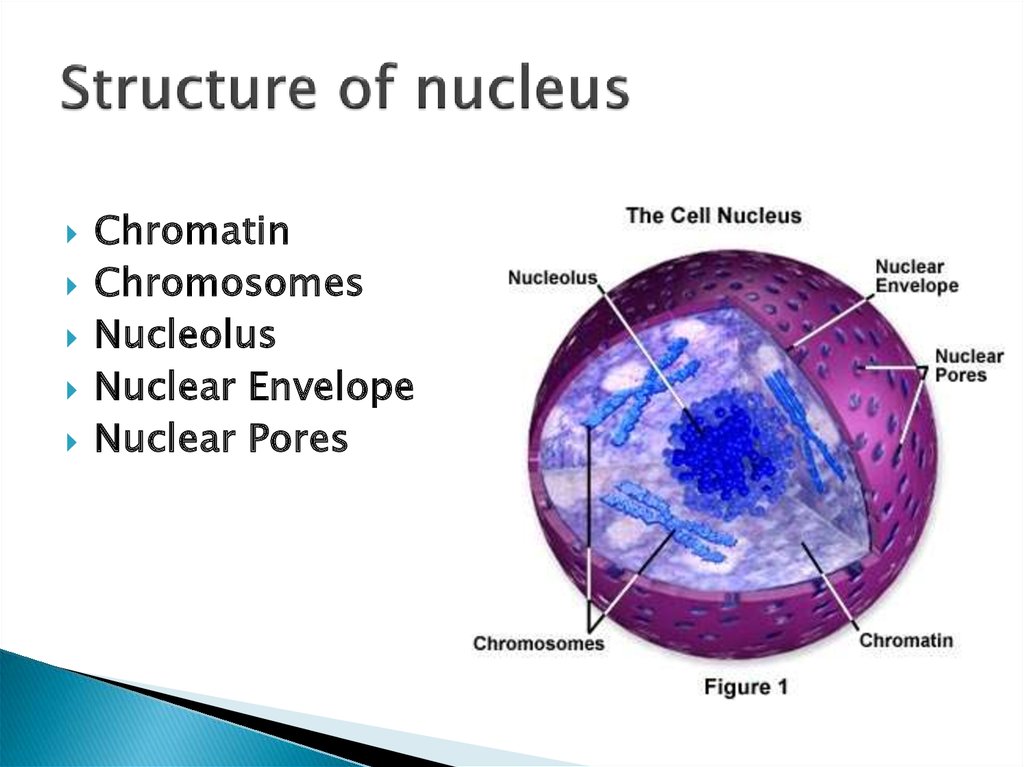 Source: en.ppt-online.org
Source: en.ppt-online.org
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that vary in several fundamental factors from other eukaryotic organisms. The eukaryotic nucleus is enclosed by the nuclear envelope, which is perforated by the nuclear pores, the gateways of macromolecular exchange between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm. Communication between the cytoplasm and the nucleus is a fundamental feature shared by both plant and animal cells. It stores the cell�s hereditary material, or dna, and it coordinates the cell�s activities, which include intermediary metabolism, growth, protein synthesis, and reproduction. It is also called as dikaryotic cell, which contains 2 nucleus at a time.
 Source: biology-questions-and-answers.com
Source: biology-questions-and-answers.com
The nucleolus is found within the nucleus, occupying 25% per cent of the volume. The nucleolus is found within the nucleus, occupying 25% per cent of the volume. Plant cells can be defined as the eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out certain specific functions. The nucleus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells and functions as the holder of a cell’s blueprint. The nucleus here is orange, shown with a chunk taken out to expose the interior.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
It is also the repository of genetic information (the genome), housing and protecting the chromosomes and the genes that they carry. The reason the nucleus is referred to as the brain of the cell is that it controls the growth and reproduction of the cell. Example is (i) paramecium (mega and micronucleus) (ii) balantidium (iii) liver cells and cartilage cells. The nucleus of a plant cell is in the cytoplasm with the centre of the cell typically busy by the vacuole. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum (spector 2001;
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Most of the cells have one nucleus; The eukaryotic nucleus is enclosed by the nuclear envelope, which is perforated by the nuclear pores, the gateways of macromolecular exchange between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm. The plant cell, like any eukaryotic cell, is able to perceive environmental signals and transduce them to the nucleus, which in turn modify the cell response (1). It is also called as dikaryotic cell, which contains 2 nucleus at a time. Further, a large central vacuole occupies the majority of the cell, pushing all the other constituents to the sides of the cell.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
Both plant and animal cells contain nucleus along with similar organelles. The nucleus is an organelle that consists of the genetic information for that organism. It is also called as dikaryotic cell, which contains 2 nucleus at a time. Until now, the nuclear response was mostly analyzed from the biochemical and transcriptional points of view. All plant cells contain a nucleus, a structure that stores dna and acts as a cell�s command center.
 Source: publiclearningcenter.com
Source: publiclearningcenter.com
Plant nucleus movement is the movement of the cell nucleus in plants by the cytoskeleton. The most dramatic reorganization of this organelle occurs during mitosis and meiosis. The nucleus is a highly specialized organelle that serves as the information and administrative center of the cell. Until now, the nuclear response was mostly analyzed from the biochemical and transcriptional points of view. In an animal cell, the nucleus is located in the central place of the cell.
 Source: walmart.com
Source: walmart.com
One of the distinctive aspects of a plant cell is the presence of a cell. The key step of our plant nucleus sequencing procedure consists of gentle but efficient isolation of plant nuclei. As in animals, the plant nucleus is delimited by a double membrane interrupted by nuclear pores, which allow exchanges with the cytoplasm. The nucleus is an organelle that consists of the genetic information for that organism. It stores the cell�s hereditary material, or dna, and it coordinates the cell�s activities, which include intermediary metabolism, growth, protein synthesis, and reproduction.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant nucleus by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







