Your Plant parasitic nematodes images are available in this site. Plant parasitic nematodes are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Plant parasitic nematodes files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for plant parasitic nematodes images information connected with to the plant parasitic nematodes topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Plant Parasitic Nematodes. Infection by plant nematodes damages the plant and causes a reduction in water uptake, leaf expansion, and. Plant parasitic nematode species and their distribution. Defence priming involves the release in the apoplast of toxic molecules derived from reactive species or secondary metabolism. The life cycle of a nematode includes eggs, juveniles and adults, and they can overwinter at any of these stages.
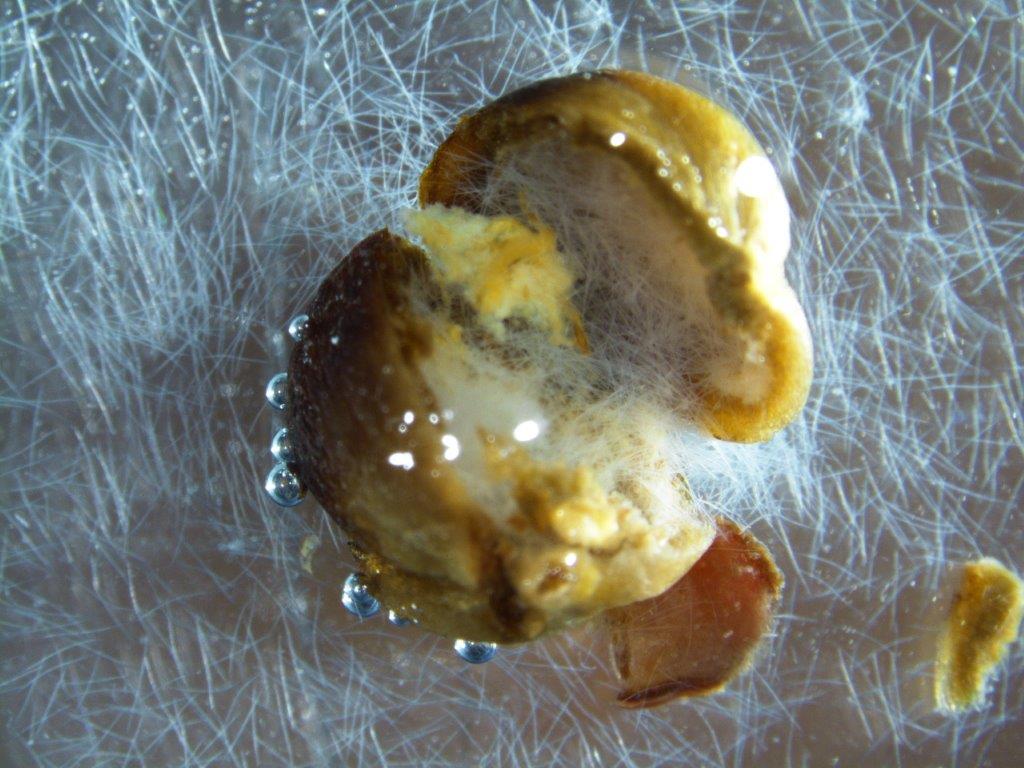 Plantparasitic nematodes in seed (including stem nematode) From fera.co.uk
Plantparasitic nematodes in seed (including stem nematode) From fera.co.uk
Plant parasitic nematodes in subtropical and tropical agriculture, edited by richard sikora, danny coyne, johannes hallman and patricia timper, is available now from the cabi bookshop. This structure has been homologized in tylenchida with the stoma of other nematodes and is used as a piercing organ through which nematodes acquire food. Nematodes that feed on plant parts are called plant parasitic nematodes (ppn) and are ubiquitous in agricultural soils. The immature stage of the nematode called as juvenile. Any such list will not be definitive as economic importance will vary depending on the region o. The duration of the different juvenile stages is highly variable.
They are parasites that infect plant roots and form feeding sites known as root knots to reproduce.
In the uk alone, it is estimated that the cyst nematodes globodera rostochiensis and globodera pallida are responsible for approximately 9% of the total uk potato production losses []. Nematodes that feed on plant parts are called plant parasitic nematodes (ppn) and are ubiquitous in agricultural soils. Of the hundreds of different kinds of nematodes that infect plants, only a dozen or so species. In plant parasitic nematodes, there are four juvenile stages and an adult stage. They are parasites that infect plant roots and form feeding sites known as root knots to reproduce. This means that if the host dies, the nematodes will disperse to search for other plants.
 Source: fera.co.uk
Source: fera.co.uk
Plant parasitic nematodes feed on living plant tissues, using an oral stylet, a spearing device somewhat like a hypodermic needle, to puncture host cells. Plant parasitic nematodes feed on living plant tissues, using an oral stylet, a spearing device somewhat like a hypodermic needle, to puncture host cells. This is the main characteristic that suggests that the nematode is a plant parasite. Herbivore nematodes are found in the orders rhabditida, dorylaimida, and triplonchida. In the uk alone, it is estimated that the cyst nematodes globodera rostochiensis and globodera pallida are responsible for approximately 9% of the total uk potato production losses [].
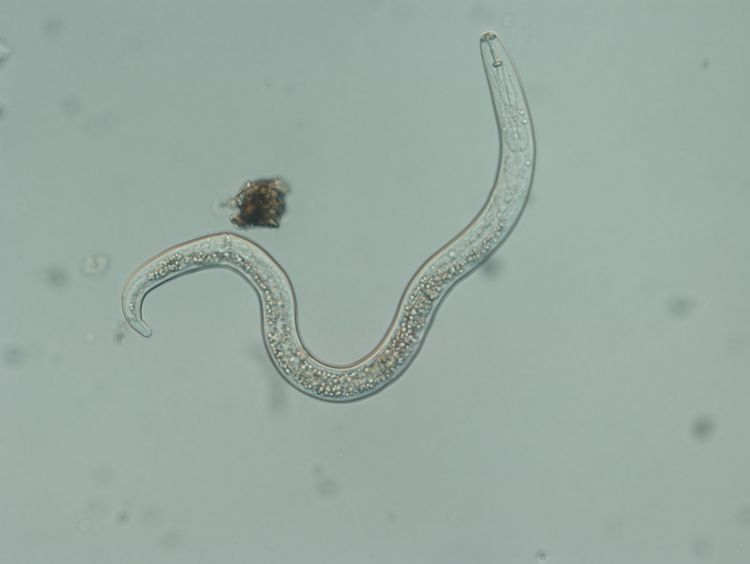
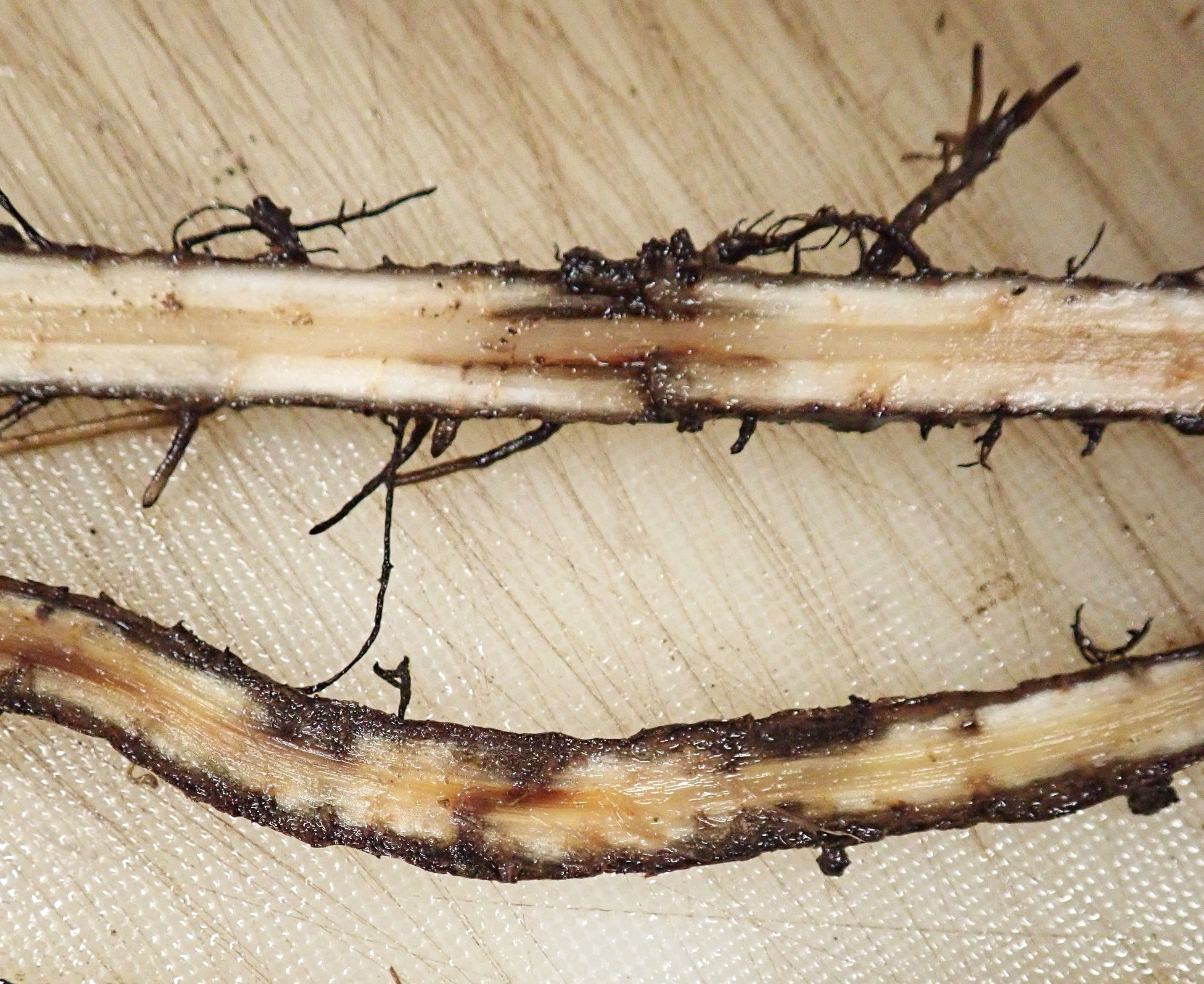
Chemical nematicides have been employed with varying degrees of success, but their implementation can be cumbersome, and furthe. Nematodes damaging to potatoes occur in both of these groupings: These remain in the soil and feed from root cells, moving Although worldwide recognition of nematodes as important cause of plant. Any such list will not be definitive as economic importance will vary depending on the region o.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It has been found that nematodes, alone or in combination with other soil microorganisms, infect almost every part of the plant, including roots, stems, leaves, fruits and seeds. Chemical nematicides have been employed with varying degrees of success, but their implementation can be cumbersome, and furthe. Infection by plant nematodes damages the plant and causes a reduction in water uptake, leaf expansion, and. Plant parasitic nematode species and their distribution. Gheysen & mitchum, 2019), endomycorrhizal fungi (le marquer et al., 2019), and other fungi and bacteria (ronald & joe, 2018) have been shown to secrete molecules mimicking plant
 Source: lsuagcenter.com
The duration of the different juvenile stages is highly variable. Although worldwide recognition of nematodes as important cause of plant. Infection by plant nematodes damages the plant and causes a reduction in water uptake, leaf expansion, and. These dangerous nematodes feed on plant roots, which ultimately damages the plant and severely impacts plant growth. Nematodes that damage plant roots are often called parasites.
 Source: abgc.org.au
Source: abgc.org.au
Gheysen & mitchum, 2019), endomycorrhizal fungi (le marquer et al., 2019), and other fungi and bacteria (ronald & joe, 2018) have been shown to secrete molecules mimicking plant Many, probably all, plant nematodes inject enzymes into a host cell before feeding to partially digest the cell contents before they are sucked into the gut. Infection by plant nematodes damages the plant and causes a reduction in water uptake, leaf expansion, and. Nematodes that feed on plant parts are called plant parasitic nematodes (ppn) and are ubiquitous in agricultural soils. Potato rot nematode ditylenchus destructor is.
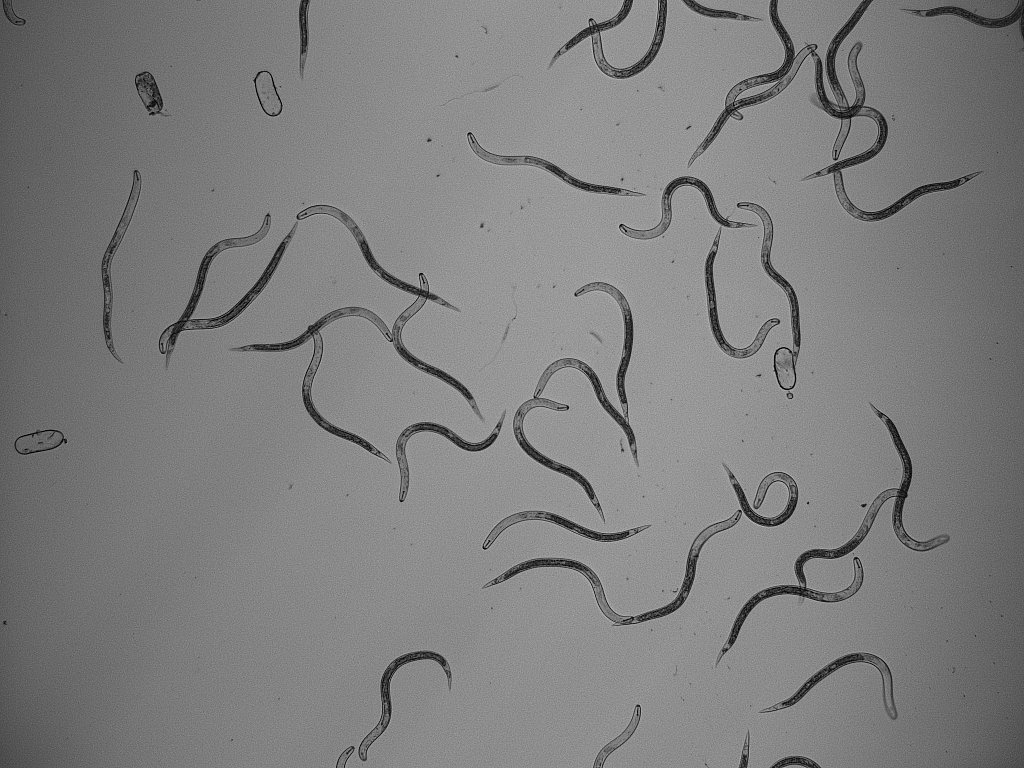 Source: neurivo.com
Source: neurivo.com
In case of endoparasitic nematodes, three moults occur with in the host plant. Potato rot nematode ditylenchus destructor is. Although worldwide recognition of nematodes as important cause of plant. This means that if the host dies, the nematodes will disperse to search for other plants. The duration of the different juvenile stages is highly variable.
 Source: ag.umass.edu
Source: ag.umass.edu
Plant diseases caused by nematodes. These dangerous nematodes feed on plant roots, which ultimately damages the plant and severely impacts plant growth. Plant parasitic nematodes typically live in soil and feed on cells in plant roots. Potato rot nematode ditylenchus destructor is. Crop damage is the result of a complex interaction of the environment, initial nematode populations at planting.
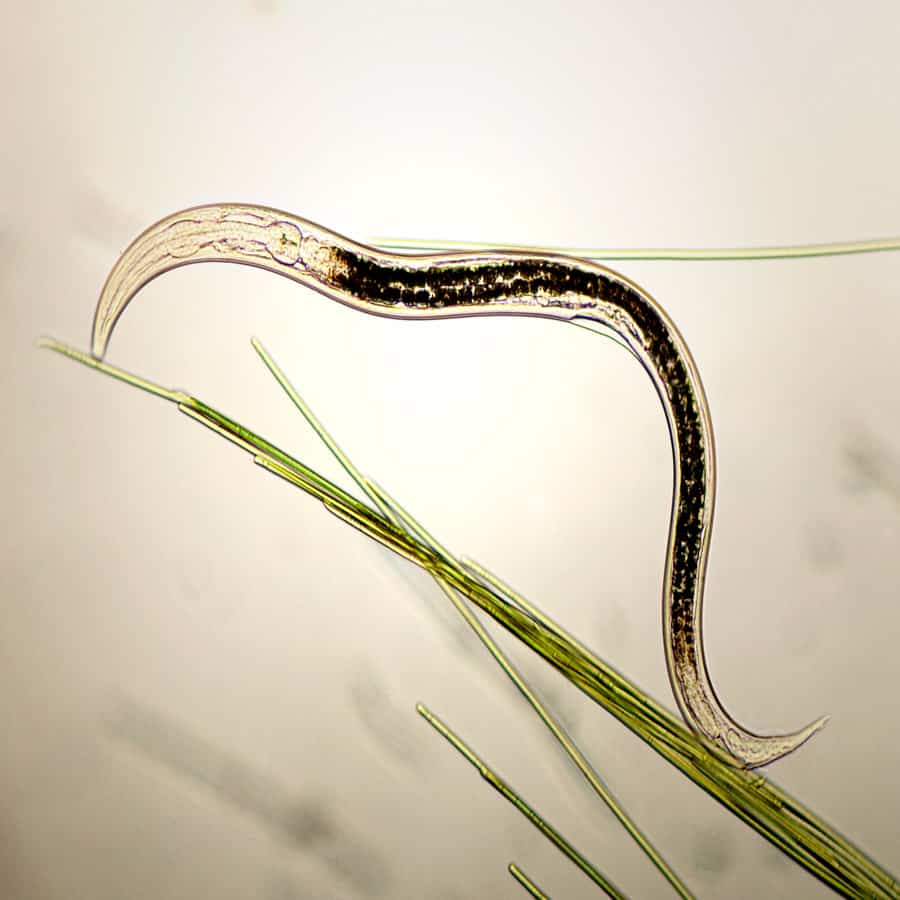 Source: dudutech.com
Source: dudutech.com
Defence priming involves the release in the apoplast of toxic molecules derived from reactive species or secondary metabolism. Globodera pallida is the predominant potato cyst nematode (pcn) that is found in more than 90% of the nematode. Nematodes that damage plant roots are often called parasites. It has been found that nematodes, alone or in combination with other soil microorganisms, infect almost every part of the plant, including roots, stems, leaves, fruits and seeds. Plant parasitic nematodes feed on living plant tissues, using an oral stylet, a spearing device somewhat like a hypodermic needle, to puncture host cells.
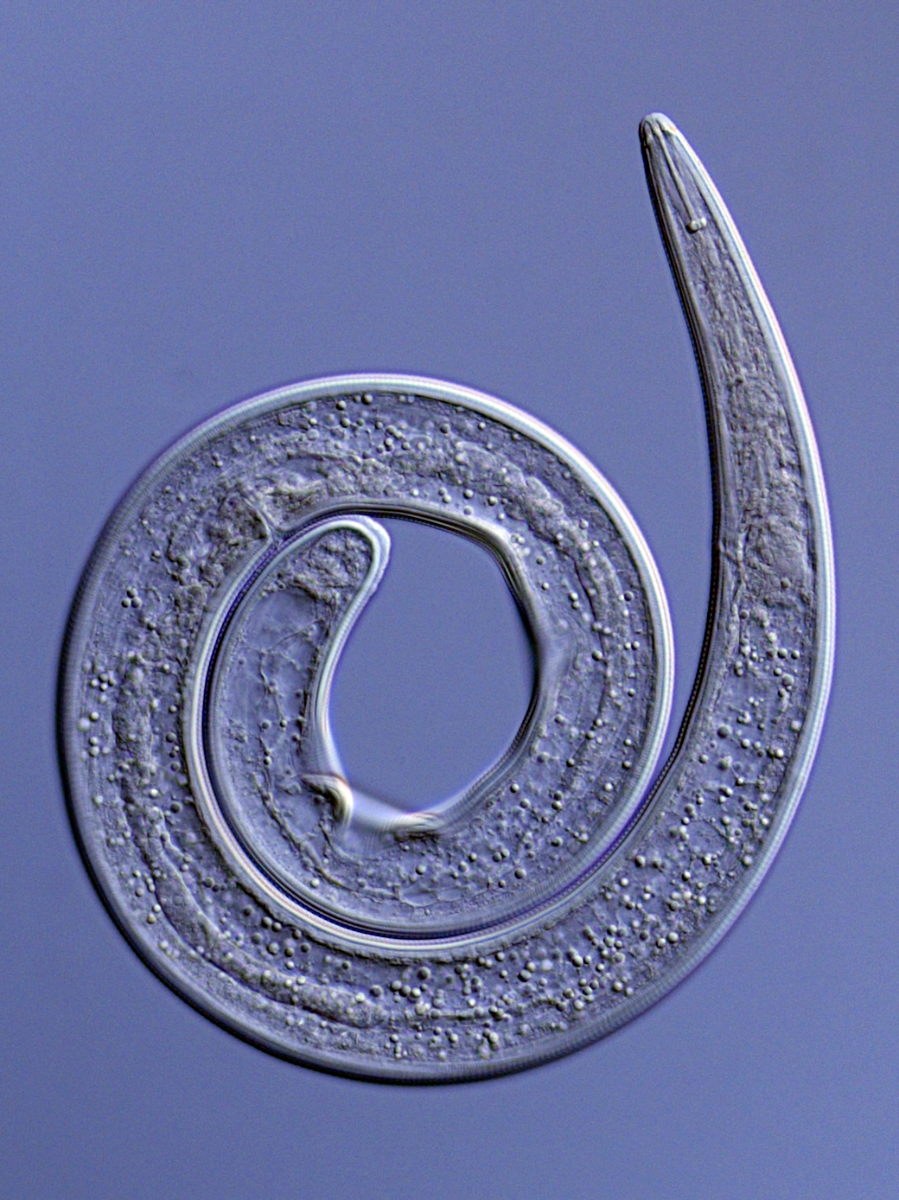 Source: fera.co.uk
Source: fera.co.uk
Globodera pallida is the predominant potato cyst nematode (pcn) that is found in more than 90% of the nematode. Globodera pallida is the predominant potato cyst nematode (pcn) that is found in more than 90% of the nematode. Many, probably all, plant nematodes inject enzymes into a host cell before feeding to partially digest the cell contents before they are sucked into the gut. In case of endoparasitic nematodes, three moults occur with in the host plant. Plant parasitic nematodes in subtropical and tropical agriculture, edited by richard sikora, danny coyne, johannes hallman and patricia timper, is available now from the cabi bookshop.
 Source: today.agrilife.org
Source: today.agrilife.org
In this study, we investigated the changes in sterols of agricultural important crops, brassica juncea (brown mustard), cucumis sativus (cucumber), glycine max (soybean), solanum lycopersicum. Many, probably all, plant nematodes inject enzymes into a host cell before feeding to partially digest the cell contents before they are sucked into the gut. The duration of the different juvenile stages is highly variable. The life cycle of a nematode includes eggs, juveniles and adults, and they can overwinter at any of these stages. Infection by plant nematodes damages the plant and causes a reduction in water uptake, leaf expansion, and.
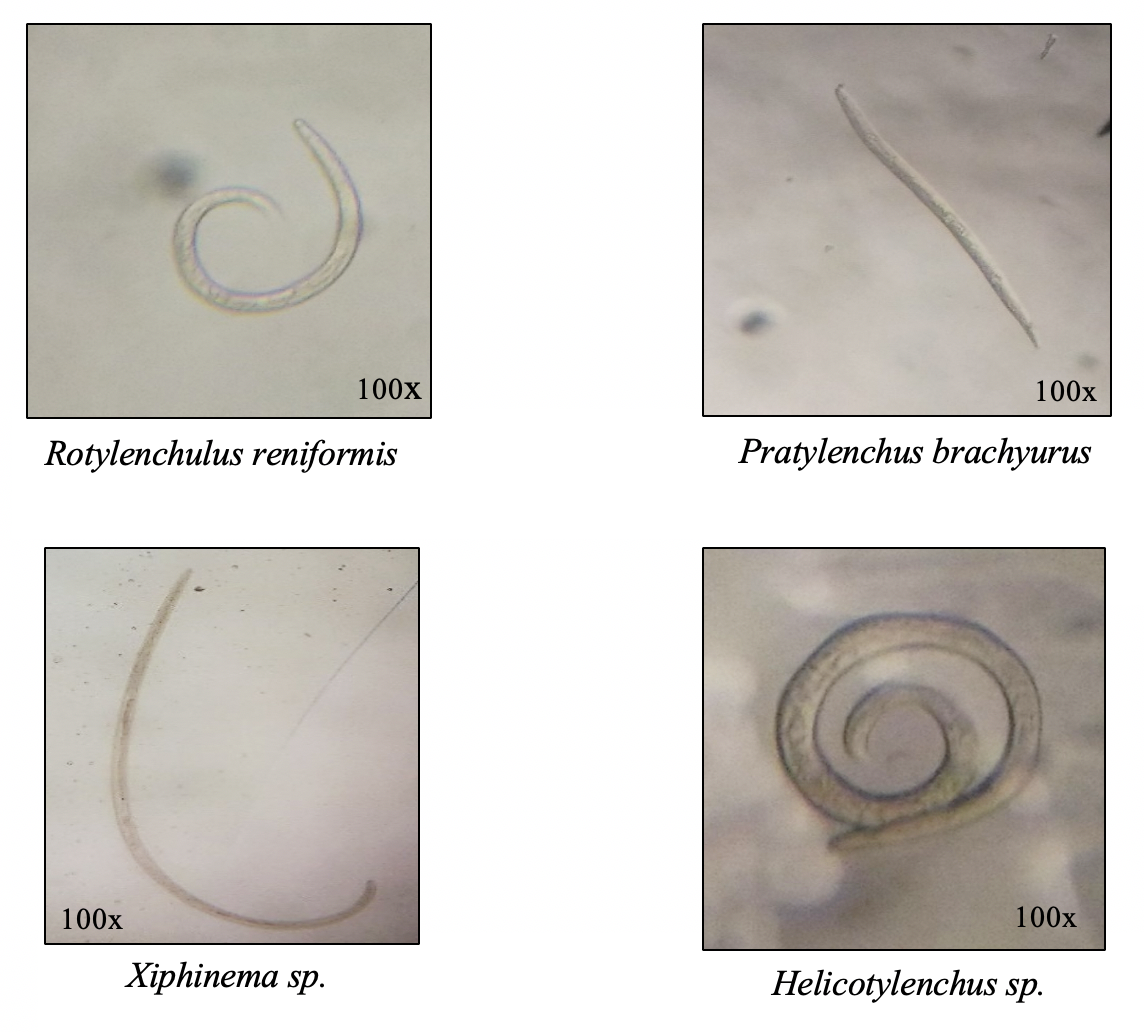 Source: vsu.edu.ph
Source: vsu.edu.ph
Although worldwide recognition of nematodes as important cause of plant. Gonad development starts in the first juvenile stage before. In this study, we investigated the changes in sterols of agricultural important crops, brassica juncea (brown mustard), cucumis sativus (cucumber), glycine max (soybean), solanum lycopersicum. Gheysen & mitchum, 2019), endomycorrhizal fungi (le marquer et al., 2019), and other fungi and bacteria (ronald & joe, 2018) have been shown to secrete molecules mimicking plant Although worldwide recognition of nematodes as important cause of plant.
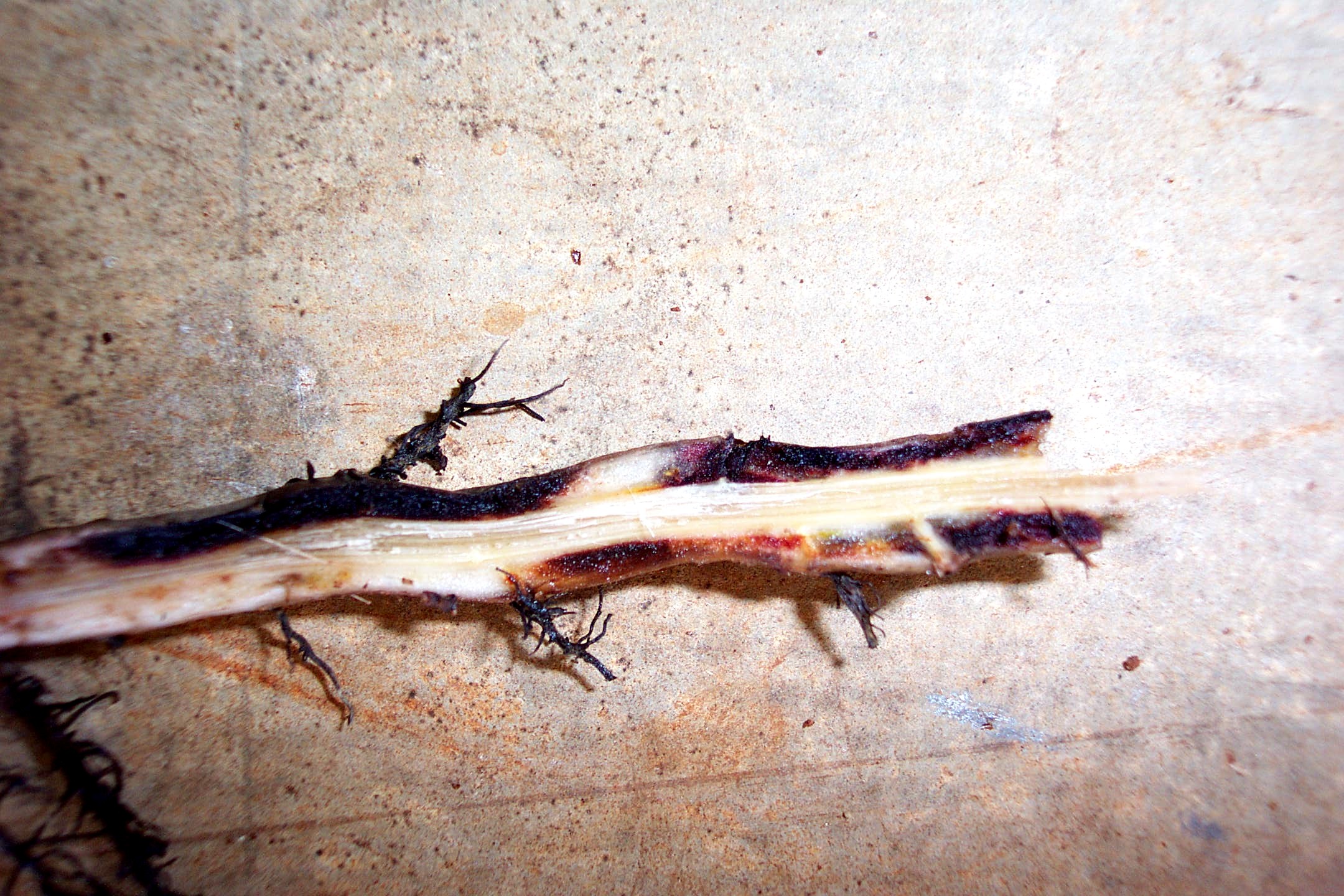 Source: abgc.org.au
Source: abgc.org.au
Of the hundreds of different kinds of nematodes that infect plants, only a dozen or so species. This means that if the host dies, the nematodes will disperse to search for other plants. These dangerous nematodes feed on plant roots, which ultimately damages the plant and severely impacts plant growth. The duration of the different juvenile stages is highly variable. Some nematodes feed within leaves.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Herbivore nematodes are found in the orders rhabditida, dorylaimida, and triplonchida. Every plant species has at least one nematode species that parasitizes it. Nematodes that damage plant roots are often called parasites. In general they can be classified as either being migratory or sedentary. Potato rot nematode ditylenchus destructor is.
 Source: cropperagra.com
Source: cropperagra.com
The immature stage of the nematode called as juvenile. Chemical nematicides have been employed with varying degrees of success, but their implementation can be cumbersome, and furthe. Nematodes that feed on plant parts are called plant parasitic nematodes (ppn) and are ubiquitous in agricultural soils. All plant parasitic nematodes have a protrusible hollow stylet or spear. Globodera pallida is the predominant potato cyst nematode (pcn) that is found in more than 90% of the nematode.
 Source: scivit.de
Source: scivit.de
In general they can be classified as either being migratory or sedentary. Although worldwide recognition of nematodes as important cause of plant. Plant parasitic nematode species and their distribution. Crop damage is the result of a complex interaction of the environment, initial nematode populations at planting. This means that if the host dies, the nematodes will disperse to search for other plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The immature stage of the nematode called as juvenile. Of the hundreds of different kinds of nematodes that infect plants, only a dozen or so species. Plant parasitic nematodes feed on living plant tissues, using an oral stylet, a spearing device somewhat like a hypodermic needle, to puncture host cells. It has been found that nematodes, alone or in combination with other soil microorganisms, infect almost every part of the plant, including roots, stems, leaves, fruits and seeds. Covering all aspects of practical plant nematology in subtropical and tropical agriculture, the third edition of this definitive global reference work is fully revised and in full colour throughout.
 Source: lsuagcenter.com
In case of endoparasitic nematodes, three moults occur with in the host plant. Nematodes that damage plant roots are often called parasites. Nematodes damaging to potatoes occur in both of these groupings: Globodera pallida is the predominant potato cyst nematode (pcn) that is found in more than 90% of the nematode. It covers the presence, distribution, symptomology and management of all economically important plant parasitic nematodes damaging the world’s major food and cash crops.
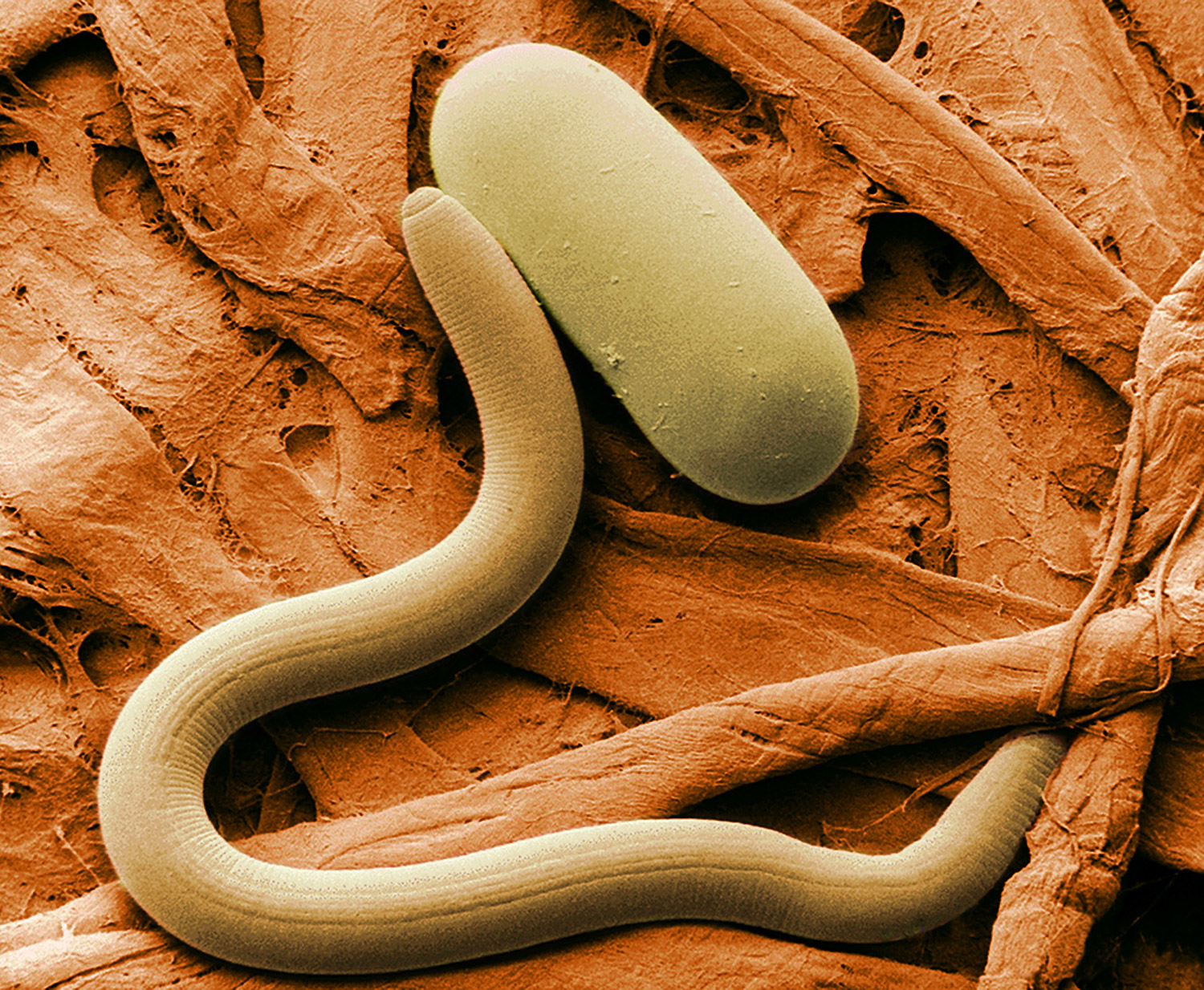 Source: coolgalapagos.com
Source: coolgalapagos.com
Plant parasitic nematodes typically live in soil and feed on cells in plant roots. In plant parasitic nematodes, there are four juvenile stages and an adult stage. The immature stage of the nematode called as juvenile. Covering all aspects of practical plant nematology in subtropical and tropical agriculture, the third edition of this definitive global reference work is fully revised and in full colour throughout. Gheysen & mitchum, 2019), endomycorrhizal fungi (le marquer et al., 2019), and other fungi and bacteria (ronald & joe, 2018) have been shown to secrete molecules mimicking plant
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant parasitic nematodes by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






