Your Plant secondary compounds images are ready in this website. Plant secondary compounds are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Plant secondary compounds files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for plant secondary compounds images information connected with to the plant secondary compounds topic, you have come to the right site. Our website frequently provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Plant Secondary Compounds. They are formed from primary metabolites (see glossary) in specific pathways and are omnipresent in plants. Most pharmaceuticals are based on plant chemical structures, and secondary metabolites are widely used for recreation and stimulation (the alkaloids nicotine and cocaine; Secondary metabolism is also relevant to agriculture. Probably the largest group of secondary metabolites, phenols range from simple compounds with a single aromatic ring to complex compounds which are polymers like tannins and lignins.
 Plant Metabolism. Plant Secondary Metabolites Plants make From vdocuments.mx
Plant Metabolism. Plant Secondary Metabolites Plants make From vdocuments.mx
A bitter cyanoglycoside, sarmentosin, was characterised from several moth species in the geometridae, zygaenidae and yponomeutidae, and from the apollo butterflies, parnassius spp. They include coumarins, quinones, napthoquinones and anthraquinones, all flavonoids which give odour, scent and colour to plants. They are formed from primary metabolites (see glossary) in specific pathways and are omnipresent in plants. The distribution of pscs is heterogeneous across the plant kingdom, and these compounds exhibit extensive variation both among and within species Most pharmaceuticals are based on plant chemical structures, and secondary metabolites are widely used for recreation and stimulation (the alkaloids nicotine and cocaine; 4 rows plant secondary compounds (pscs) organic compounds typically formed from primary metabolites in.
They are formed from primary metabolites (see glossary) in specific pathways and are omnipresent in plants.
The concept of secondary metabolite was first defined by albrecht kossel, nobel prize winner for physiology or medicine in 1910 [ 2 ]. Secondary chemicals are important in plant use by humans. It is not possible to deduce the sequence of events in the evolution of plant secondary compounds from the fossil record because few compounds have survived: Plant secondary compounds in soil and their role in belowground species interactions knowledge of the effect of plant secondary compounds (pscs) on belowground interactions in the more diffuse community of species living outside the rhizosphere is sparse compared with what we know about how pscs affect aboveground interactions. 4 rows plant secondary compounds (pscs) organic compounds typically formed from primary metabolites in. Each of these broad classes is comprised of many thousands of different individual compounds and this diversity is one of the primary challenges associated with studying the ecological roles of psm.
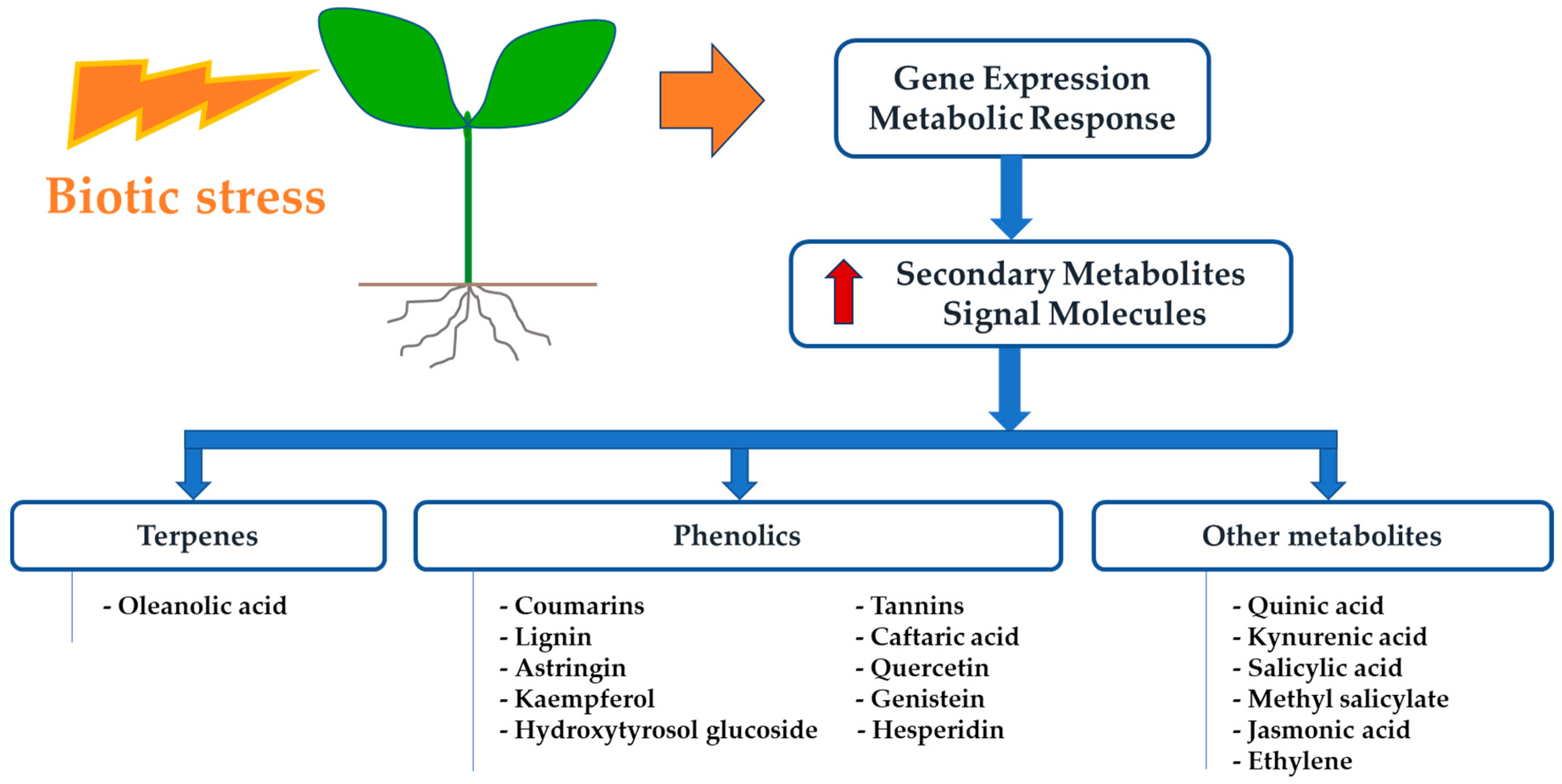 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Secondary plant metabolites are produced by plants via different primary metabolic pathways. They were thus described by czapek in the second edition of his 1921 textbook plant biochemistry and this view persisted into the 1970s. However, secondary metabolites are crucial for plant survival when competing in surrounding environments in various ways—fighting against herbivores and pathogens, an. Plants produce a wide diversity of secondary metabolites (sm) which serve them as defense compounds against herbivores, and other plants and microbes, but also as signal compounds. Secondary metabolism is also relevant to agriculture.
![New Page 1 [www.uky.edu] New Page 1 [www.uky.edu]](http://www.uky.edu/~dhild/biochem/26/secondaryc.gif) Source: uky.edu
Source: uky.edu
Affiliation 1 department of biological sciences. Authors howard v cornell 1 , bradford a hawkins. Based on their biosynthetic origins, plant secondary metabolites can be divided into three major groups: Plant secondary metabolites can be distinguished roughly into three classes of chemical compounds, namely alkaloids, phenolic compounds and terpenes. These defenses are most frequently chemical, with an array of plant secondary compounds identified to date [ 1, 2, 3 ].
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Herbivores have to survive exposure to the chemically challenging or toxic environments of their host plants and have in turn evolved various ways to overcome plant defenses or even use them for their own benefit. As a result of metabolic activity, plants produce primary and secondary compounds. These defenses are most frequently chemical, with an array of plant secondary compounds identified to date [ 1, 2, 3 ]. Herbivore responses to plant secondary compounds: Secondary plant compounds are extracted and utilized in the manufacturing and production of medicines, flavouring, recreational drugs and essential oils.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Probably the largest group of secondary metabolites, phenols range from simple compounds with a single aromatic ring to complex compounds which are polymers like tannins and lignins. Secondary compounds in plants are major contributors to the chemical diversity of nature. It is not possible to deduce the sequence of events in the evolution of plant secondary compounds from the fossil record because few compounds have survived: By contrast, a number of lepidopteran species store the same compounds though feeding upon taxonomically diverse plant species. The first secondary compounds to be characterised were those accumulating in relatively high concentration and this led to the view that they were probably �excretory products� or �end products of metabolism�.
 Source: faculty.uca.edu
Source: faculty.uca.edu
As a result of metabolic activity, plants produce primary and secondary compounds. Each of these broad classes is comprised of many thousands of different individual compounds and this diversity is one of the primary challenges associated with studying the ecological roles of psm. They are formed from primary metabolites (see glossary) in specific pathways and are omnipresent in plants. The first secondary compounds to be characterised were those accumulating in relatively high concentration and this led to the view that they were probably �excretory products� or �end products of metabolism�. Affiliation 1 department of biological sciences.
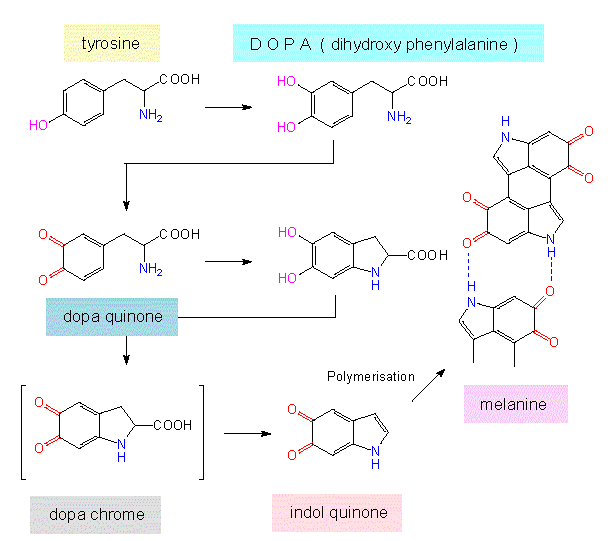 Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
They include coumarins, quinones, napthoquinones and anthraquinones, all flavonoids which give odour, scent and colour to plants. This chapter focuses on secondary compounds (metabolites) and the way that the production of secondary metabolites can be elicited by biotic and abiotic. Plants produce a wide diversity of secondary metabolites (sm) which serve them as defense compounds against herbivores, and other plants and microbes, but also as signal compounds. Secondary metabolism, producing substances that have no known direct function in basic metabolism, and are often. Secondary compounds in plants are major contributors to the chemical diversity of nature.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Major secondary compounds in temperate and tropical forage plants occur in the phenolic fraction and include condensed and hydrolysable tannins, phenolic monomers and lignin. A bitter cyanoglycoside, sarmentosin, was characterised from several moth species in the geometridae, zygaenidae and yponomeutidae, and from the apollo butterflies, parnassius spp. Secondary compounds in plants are major contributors to the chemical diversity of nature. As a result of metabolic activity, plants produce primary and secondary compounds. Secondary chemicals are important in plant use by humans.
 Source: fdocuments.in
Source: fdocuments.in
Major secondary compounds in temperate and tropical forage plants occur in the phenolic fraction and include condensed and hydrolysable tannins, phenolic monomers and lignin. They include coumarins, quinones, napthoquinones and anthraquinones, all flavonoids which give odour, scent and colour to plants. Secondary metabolism is also relevant to agriculture. They are also the compounds that are nutritionally vital and essential for health. Primary functions abstract pdf more abstract many natural products supposed by ecologists to exist as secondary metabolic products for protection of plants exist in dynamic equilibrium, with rapid turnover rates, involving cycles that include primary products such as sugars and amino acids.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Affiliation 1 department of biological sciences. They are formed from primary metabolites (see glossary) in specific pathways and are omnipresent in plants. Authors howard v cornell 1 , bradford a hawkins. They are also the compounds that are nutritionally vital and essential for health. Based on their biosynthetic origins, plant secondary metabolites can be divided into three major groups:
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
The distribution of pscs is heterogeneous across the plant kingdom, and these compounds exhibit extensive variation both among and within species [1]. Probably the largest group of secondary metabolites, phenols range from simple compounds with a single aromatic ring to complex compounds which are polymers like tannins and lignins. However, secondary metabolites are crucial for plant survival when competing in surrounding environments in various ways—fighting against herbivores and pathogens, an. The distribution of pscs is heterogeneous across the plant kingdom, and these compounds exhibit extensive variation both among and within species [1]. They were thus described by czapek in the second edition of his 1921 textbook plant biochemistry and this view persisted into the 1970s.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Secondary compounds in plants are major contributors to the chemical diversity of nature. Probably the largest group of secondary metabolites, phenols range from simple compounds with a single aromatic ring to complex compounds which are polymers like tannins and lignins. The study of such plant use is called ethnopharmacology. By contrast, a number of lepidopteran species store the same compounds though feeding upon taxonomically diverse plant species. Secondary metabolism, producing substances that have no known direct function in basic metabolism, and are often.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Secondary plant metabolites are numerous chemical compounds produced by the plant cell through metabolic pathways derived from the primary metabolic pathways. Each of these broad classes is comprised of many thousands of different individual compounds and this diversity is one of the primary challenges associated with studying the ecological roles of psm. Primary functions abstract pdf more abstract many natural products supposed by ecologists to exist as secondary metabolic products for protection of plants exist in dynamic equilibrium, with rapid turnover rates, involving cycles that include primary products such as sugars and amino acids. A test of phytochemical coevolution theory am nat. Secondary plant compounds are extracted and utilized in the manufacturing and production of medicines, flavouring, recreational drugs and essential oils.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Secondary chemicals are important in plant use by humans. Based on their biosynthetic origins, plant secondary metabolites can be divided into three major groups: This chapter focuses on secondary compounds (metabolites) and the way that the production of secondary metabolites can be elicited by biotic and abiotic. Plants produce a wide diversity of secondary metabolites (sm) which serve them as defense compounds against herbivores, and other plants and microbes, but also as signal compounds. (papilionidae), although each species feeds on different.
 Source: fdocuments.in
Source: fdocuments.in
They were thus described by czapek in the second edition of his 1921 textbook plant biochemistry and this view persisted into the 1970s. Secondary compounds in plants (allelochemicals) as promoters of human biological variability annual review of anthropology vol. Each of these broad classes is comprised of many thousands of different individual compounds and this diversity is one of the primary challenges associated with studying the ecological roles of psm. Major secondary compounds in temperate and tropical forage plants occur in the phenolic fraction and include condensed and hydrolysable tannins, phenolic monomers and lignin. Secondary compounds in plants are major contributors to the chemical diversity of nature.
 Source: myknowledgehunt.com
Source: myknowledgehunt.com
The ability of plants to compete and survive is therefore profoundly affected by the ecological functions of their secondary metabolites. Herbivore responses to plant secondary compounds: We have investigated food choice in individual fallow deer (dama dama) The distribution of pscs is heterogeneous across the plant kingdom, and these compounds exhibit extensive variation both among and within species [1]. Primary functions abstract pdf more abstract many natural products supposed by ecologists to exist as secondary metabolic products for protection of plants exist in dynamic equilibrium, with rapid turnover rates, involving cycles that include primary products such as sugars and amino acids.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Secondary compounds are historically called secondary to differentiate them from primary compounds, which are directly involved in plant growth, development, and reproduction. Most pharmaceuticals are based on plant chemical structures, and secondary metabolites are widely used for recreation and stimulation (the alkaloids nicotine and cocaine; Secondary compounds are historically called secondary to differentiate them from primary compounds, which are directly involved in plant growth, development, and reproduction. Secondary compounds in plants are major contributors to the chemical diversity of nature. Affiliation 1 department of biological sciences.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Secondary plant compounds are extracted and utilized in the manufacturing and production of medicines, flavouring, recreational drugs and essential oils. Based on their biosynthetic origins, plant secondary metabolites can be divided into three major groups: Major secondary compounds in temperate and tropical forage plants occur in the phenolic fraction and include condensed and hydrolysable tannins, phenolic monomers and lignin. The concept of secondary metabolite was first defined by albrecht kossel, nobel prize winner for physiology or medicine in 1910 [ 2 ]. They were thus described by czapek in the second edition of his 1921 textbook plant biochemistry and this view persisted into the 1970s.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Major secondary compounds in temperate and tropical forage plants occur in the phenolic fraction and include condensed and hydrolysable tannins, phenolic monomers and lignin. They are also the compounds that are nutritionally vital and essential for health. Herbivores have to survive exposure to the chemically challenging or toxic environments of their host plants and have in turn evolved various ways to overcome plant defenses or even use them for their own benefit. Authors howard v cornell 1 , bradford a hawkins. Condensed tannins (ct) bind to plant
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant secondary compounds by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






