Your Plant traits images are available in this site. Plant traits are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Plant traits files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for plant traits pictures information connected with to the plant traits keyword, you have visit the ideal blog. Our website always gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Plant Traits. To identify which category of plant traits best predicted the correlations to herbivore susceptibility, we pooled effect sizes into moderator subgroups of plant traits among five major functional categories: Another characteristic of plants is that they do not voluntarily move, though they may grow branches in a particular direction. They are eukaryotic, multicellular and autotrophic organisms. Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c 3 grasslands.
 Plant economics spectrum theory holds true within ferns From botany.one
Plant economics spectrum theory holds true within ferns From botany.one
We selected 11 plant functional traits to measure on each species in the experiment. Plant traits edit page content. Plant functional traits are the features (morphological, physiological, phenological) that represent ecological strategies and determine. They form tissues, have multiple cells and create food through photosynthesis, which is the process of turning sunlight into energy. The plant kingdom has the following characteristic. The easiest method of plant genetic modification (see operational definitions in chapter 1), used by our nomadic ancestors and continuing today, is simple selection.that is, a genetically heterogeneous population of plants is inspected, and “superior” individuals—plants with the most desired traits, such as improved palatability and yield—are selected for.
Made of cells (with dna, cell wall, chloroplasts) 2.
Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c 3 grasslands. Examples include leaf mass per unit area (lma), which estimates the. Plant trait frameworks are mainly based on principles of resource capture, abiotic stress (in)tolerance, competitive ability and dispersal strategies (e.g. To identify which category of plant traits best predicted the correlations to herbivore susceptibility, we pooled effect sizes into moderator subgroups of plant traits among five major functional categories: Plant traits each trait has information regarding the trait category (morphology, reproduction, phenology, ecology), type (qualitative or quantitative), value type (integer, real, enumerated) or units whenever applicable. The plant cell contains a rigid cell wall.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Another characteristic of plants is that they do not voluntarily move, though they may grow branches in a particular direction. The plant cell contains a rigid cell wall. We selected 11 plant functional traits to measure on each species in the experiment. Functional diversity in ecosystems has traditionally been studied using aboveground plant traits. Another characteristic of plants is that they do not voluntarily move, though they may grow branches in a particular direction.
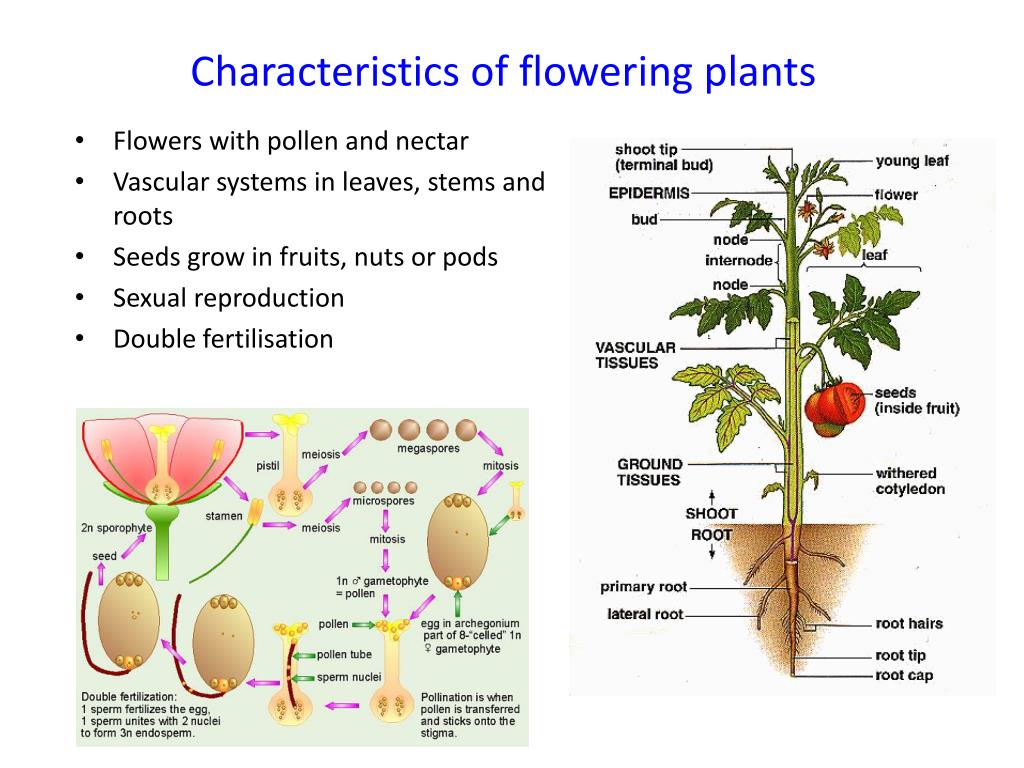 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
To identify which category of plant traits best predicted the correlations to herbivore susceptibility, we pooled effect sizes into moderator subgroups of plant traits among five major functional categories: Variation in plant functional traits, and trait syndromes, has proven useful for tackling. Plant characteristics plants are autotrophs; Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c 3 grasslands. Despite the known effect of plant traits on the microbial community composition, their effects on the microbial functional diversity are only starting to.
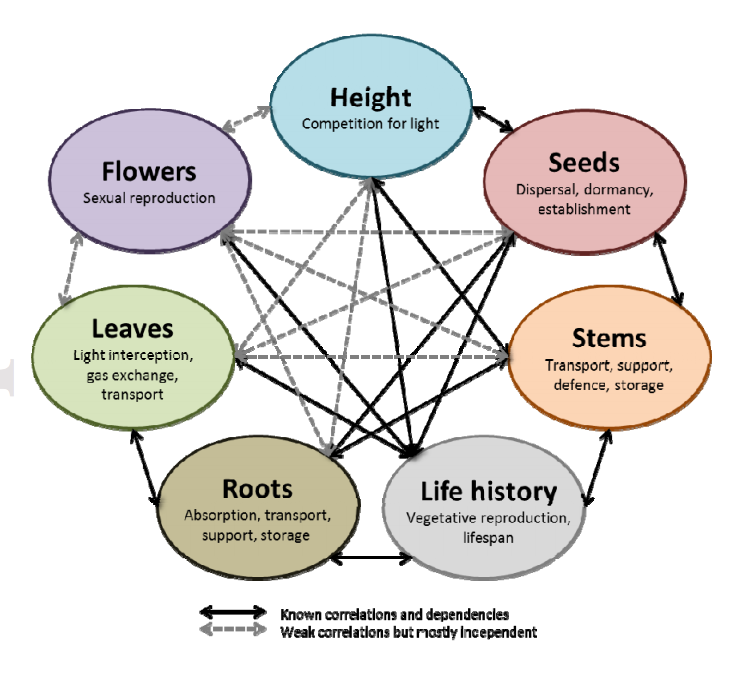 Source: evol-eco.blogspot.com
Source: evol-eco.blogspot.com
Plant trait frameworks are mainly based on principles of resource capture, abiotic stress (in)tolerance, competitive ability and dispersal strategies (e.g. Traits and corresponding values are defined as follows: In the field of plant ecophysiology, the term “functional trait” has multiple overlapping definitions ().however, functional traits are generally considered aspects of plant phenotypes that influence growth, survival, and reproduction by mediating interactions with the biotic and abiotic environment; Ptns can be applied across individuals of a species, or across species within or across communities, and can highlight. The essential characteristics of plants.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Plant traits each trait has information regarding the trait category (morphology, reproduction, phenology, ecology), type (qualitative or quantitative), value type (integer, real, enumerated) or units whenever applicable. The use of plant traits to predict ecosystem functions has been gaining growing attention. Shoots consist of simple repeated units exhibiting serial homology. However, plants need to balance a number of functional requirements; In the field of plant ecophysiology, the term “functional trait” has multiple overlapping definitions ().however, functional traits are generally considered aspects of plant phenotypes that influence growth, survival, and reproduction by mediating interactions with the biotic and abiotic environment;
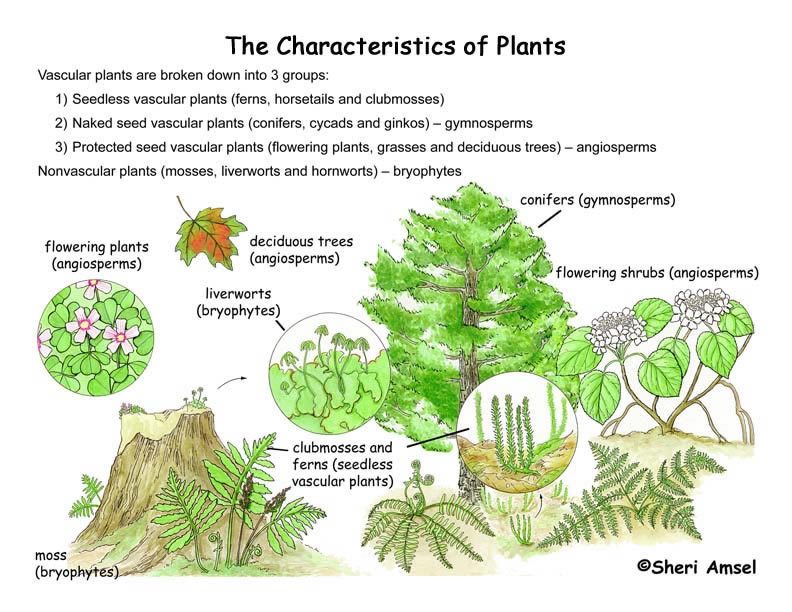 Source: exploringnature.org
Source: exploringnature.org
Plants have chloroplast and chlorophyll pigment, which is required for photosynthesis. Plant functional traits are the features (morphological, physiological, phenological) that represent ecological strategies and determine. Another characteristic of plants is that they do not voluntarily move, though they may grow branches in a particular direction. And (v) primary chemistry and physiology. Plant characteristics plants are autotrophs;
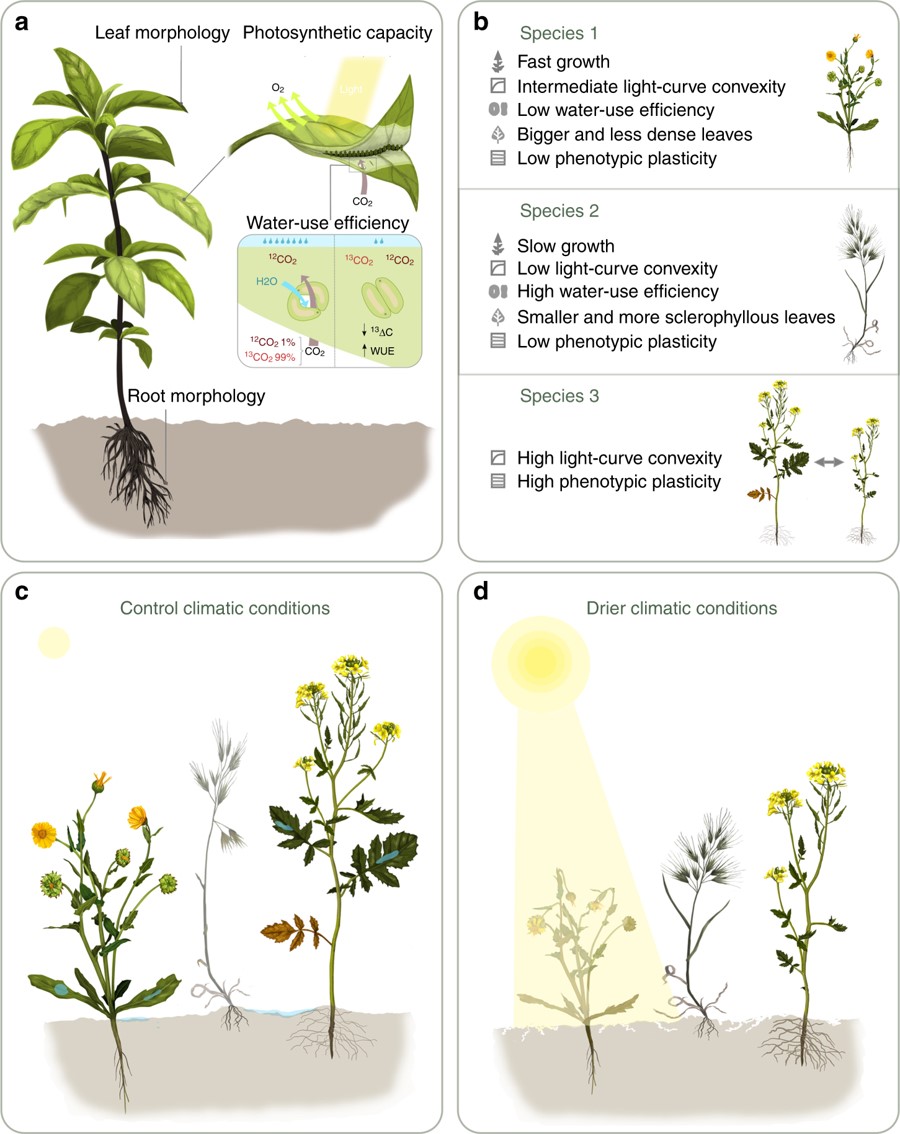 Source: plantae.org
Source: plantae.org
The use of plant traits to predict ecosystem functions has been gaining growing attention. Plant characteristics plants are autotrophs; Pathfinder roleplaying game core rulebook ↓ attributes. They are eukaryotic, multicellular and autotrophic organisms. We selected 11 plant functional traits to measure on each species in the experiment.
 Source: botany.one
Source: botany.one
Kingdom plantae includes all the plants. Another characteristic of plants is that they do not voluntarily move, though they may grow branches in a particular direction. Plants have chloroplast and chlorophyll pigment, which is required for photosynthesis. Shoots consist of simple repeated units exhibiting serial homology. Plant trait frameworks are mainly based on principles of resource capture, abiotic stress (in)tolerance, competitive ability and dispersal strategies (e.g.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Plants are multicellular, primarily terrestrial organisms descended from green algae. Body plan (cells to organ systems) 3. Made of cells (with dna, cell wall, chloroplasts) 2. Shoots consist of simple repeated units exhibiting serial homology. The easiest method of plant genetic modification (see operational definitions in chapter 1), used by our nomadic ancestors and continuing today, is simple selection.that is, a genetically heterogeneous population of plants is inspected, and “superior” individuals—plants with the most desired traits, such as improved palatability and yield—are selected for.
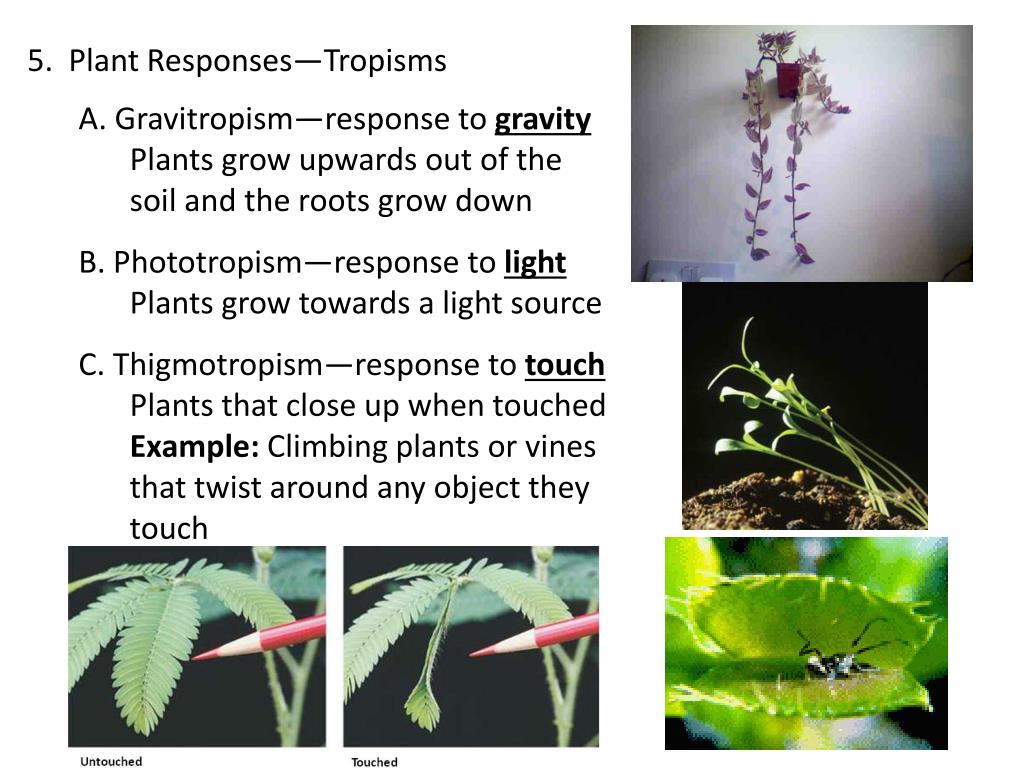 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Another characteristic of plants is that they do not voluntarily move, though they may grow branches in a particular direction. Plants are eukaryotic, meaning their cells have a nucleus. They produce their own food. Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c. Plant growth is indeterminate and adapted to gather diffuse resources.
 Source: philschatz.com
Source: philschatz.com
The use of plant traits to predict ecosystem functions has been gaining growing attention. In the field of plant ecophysiology, the term “functional trait” has multiple overlapping definitions ().however, functional traits are generally considered aspects of plant phenotypes that influence growth, survival, and reproduction by mediating interactions with the biotic and abiotic environment; Plants have chloroplast and chlorophyll pigment, which is required for photosynthesis. Plant traits—the morphological, anatomical, physiological, biochemical and phenological characteristics of plants—determine how plants respond to environmental factors, affect other trophic levels, and influence ecosystem. Kingdom plantae includes all the plants.
 Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Plant growth is indeterminate and adapted to gather diffuse resources. We selected 11 plant functional traits to measure on each species in the experiment. Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c 3 grasslands. Plant traits—the morphological, anatomical, physiological, biochemical and phenological characteristics of plants—determine how plants respond to environmental factors, affect other trophic levels, and influence ecosystem. Examples include leaf mass per unit area (lma), which estimates the.
 Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c 3 grasslands. Plant functional traits are the features (morphological, physiological, phenological) that represent ecological strategies and determine how plants respond to environmental factors, affect other trophic levels and influence ecosystem properties. Plant trait measurements are needed for evaluating ecological responses to environmental conditions and for ecosystem process model development, parameterization, and. Despite the known effect of plant traits on the microbial community composition, their effects on the microbial functional diversity are only starting to. They do so via photosynthesis, which is the process of making nutrients such as sugars from light energy and carbon dioxide.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
We selected 11 plant functional traits to measure on each species in the experiment. Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c 3 grasslands. Pathfinder roleplaying game core rulebook ↓ attributes. Ptns can be applied across individuals of a species, or across species within or across communities, and can highlight. Traits and corresponding values are defined as follows:

Plant functional traits are the features (morphological, physiological, phenological) that represent ecological strategies and determine how plants respond to environmental factors, affect other trophic levels and influence ecosystem properties. Plants have chloroplast and chlorophyll pigment, which is required for photosynthesis. Plant functional traits are the features (morphological, physiological, phenological) that represent ecological strategies and determine. Functional diversity in ecosystems has traditionally been studied using aboveground plant traits. Plant growth is indeterminate and adapted to gather diffuse resources.
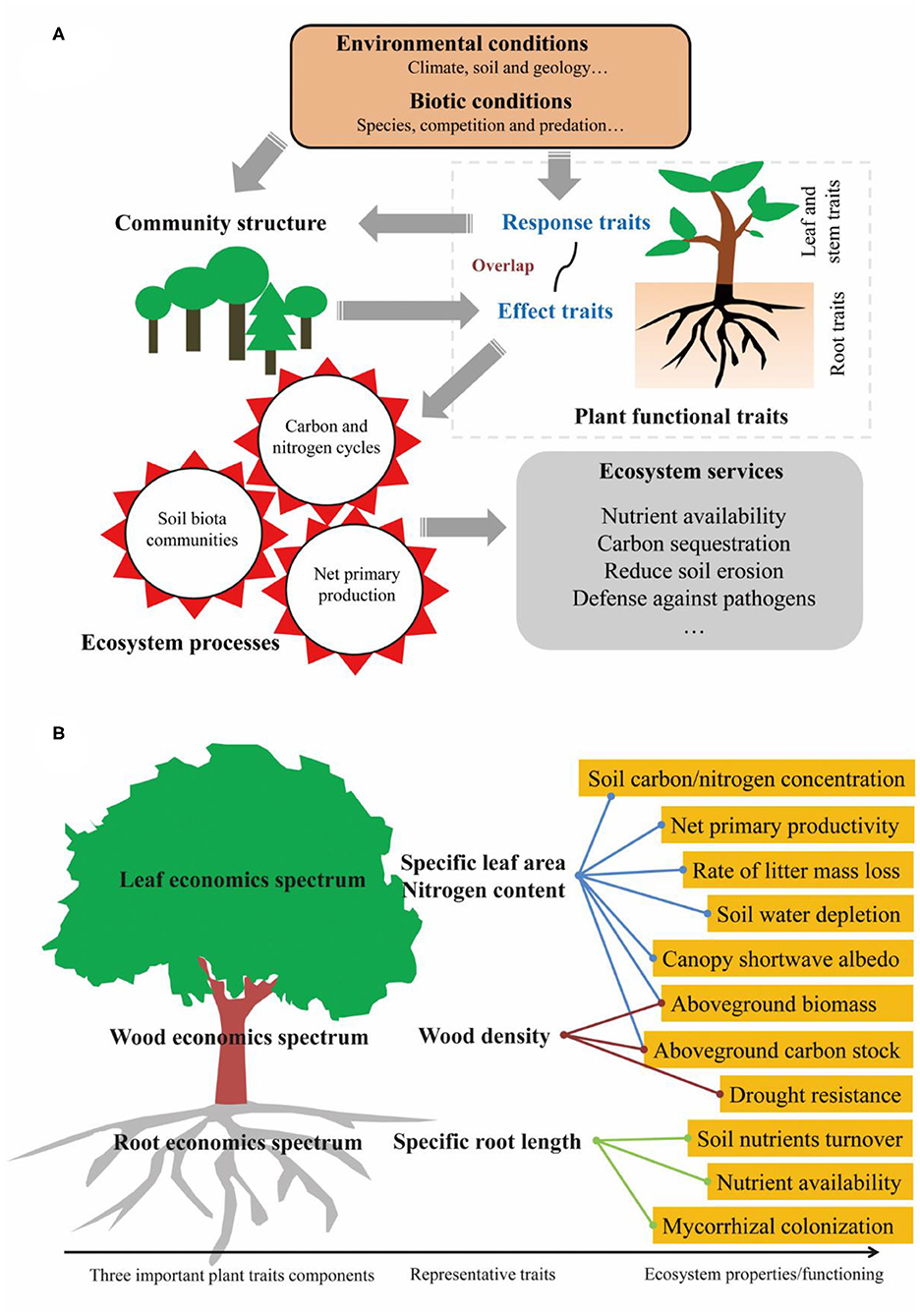 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Plant traits and soil fertility mediate productivity losses under extreme drought in c. The use of plant traits to predict ecosystem functions has been gaining growing attention. Plant growth is indeterminate and adapted to gather diffuse resources. Variation in plant functional traits, and trait syndromes, has proven useful for tackling. Traits and corresponding values are defined as follows:
 Source: petmarmoset.com
Source: petmarmoset.com
They are eukaryotic, multicellular and autotrophic organisms. Plant trait networks (ptns) clarify complex relationships among traits, enable the calculation of metrics for the topology of trait coordination and the importance of given traits in ptns, and how. Plant trait frameworks are mainly based on principles of resource capture, abiotic stress (in)tolerance, competitive ability and dispersal strategies (e.g. They produce their own food. The easiest method of plant genetic modification (see operational definitions in chapter 1), used by our nomadic ancestors and continuing today, is simple selection.that is, a genetically heterogeneous population of plants is inspected, and “superior” individuals—plants with the most desired traits, such as improved palatability and yield—are selected for.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Variation in plant functional traits, and trait syndromes, has proven useful for tackling. Responses of six key plant traits to temperature across five different study types including: The essential characteristics of plants. Body plan (cells to organ systems) 3. They are eukaryotic, multicellular and autotrophic organisms.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Plant functional traits are the features (morphological, physiological, phenological) that represent ecological strategies and determine how plants respond to environmental factors, affect other trophic levels and influence ecosystem properties. Plant trait measurements are needed for evaluating ecological responses to environmental conditions and for ecosystem process model development, parameterization, and. The essential characteristics of plants. Traits and corresponding values are defined as follows: Plants are eukaryotic, meaning their cells have a nucleus.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plant traits by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







