Your Plantar anatomy images are available in this site. Plantar anatomy are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Plantar anatomy files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for plantar anatomy images information linked to the plantar anatomy topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Plantar Anatomy. At mr imaging, the course of the. As the muscle crosses both the knee and ankle joints, it weakly assists with knee and plantar flexion. This consists of five long metatarsal bones and five shorter bones that form the toes (phalanges). Various terms have been used to describe plantar fasciitis, including jogger’s heel, tennis heel, policeman’s.
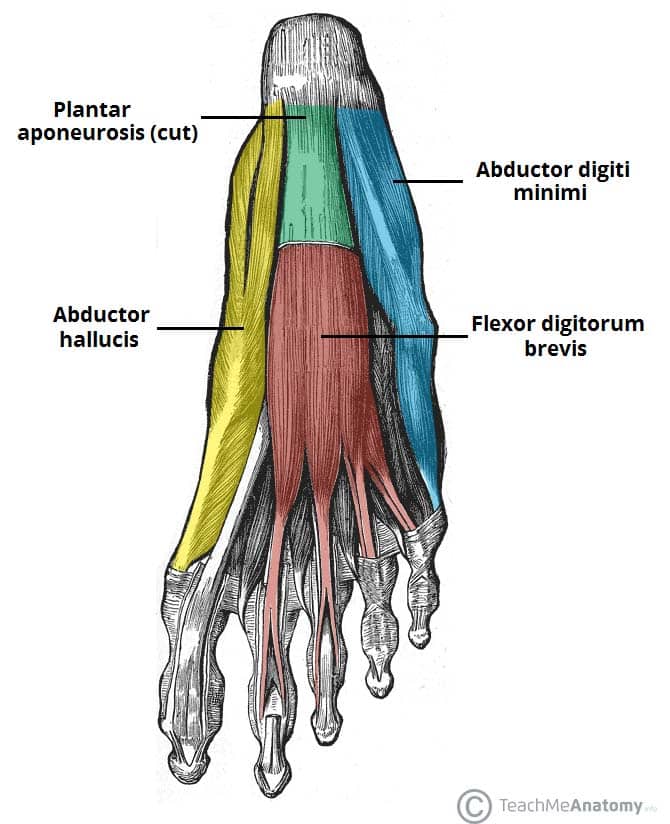 Muscles of the Foot Dorsal Plantar TeachMeAnatomy From teachmeanatomy.info
Muscles of the Foot Dorsal Plantar TeachMeAnatomy From teachmeanatomy.info
The plantar fascia is a complex structure that extends from the medial calcaneal tubercle (the heel bone) to the proximal phalanges of the toes (the bone at the base of the toe) at the metatarsophalangeal (mtp) joints. Helping people find foot comfort, since 1999. [adjective] of or relating to the sole of the foot. Learn about anatomical directional terminology used for the limbs, hands, and feet, and explore the differences between palmar, dorsal, and plantar aspects, and the definition of. Arising predominantly from the calcaneal tuberosity, the plantar fascia attaches distally, through several slips, to the plantar… The pain may be substantial, resulting in the alteration of daily activities.
Plantar fasciitis is the pain caused by degenerative irritation at the insertion of the plantar fascia on the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity.
Plantar fasciitis is the pain caused by degenerative irritation at the insertion of the plantar fascia on the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity. The anatomy of the foot. My favorites (0) shopping guide. It forms a small fusiform belly, from 7 to 10 cm. On the dorsal aspect, the. Learn about anatomical directional terminology used for the limbs, hands, and feet, and explore the differences between palmar, dorsal, and plantar aspects, and the definition of.
 Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Source: teachmeanatomy.info
The fascia consists of three parts, medial, lateral and the central part, respectively.[1] My favorites (0) shopping guide. It is a thick connective tissue, that functions to support and protect the underlying vital structures of the foot. Long, ending in a long slender tendon which crosses obliquely between the two muscles of the. Helping people find foot comfort, since 1999.
 Source: newtonrunning.com
Source: newtonrunning.com
Although the plantar fascia (pf) has been studied quite well from a biomechanical viewpoint, its microscopic. All the muscles are innervated either by the medial plantar nerve or the lateral plantar nerve, which are both branches of the tibial nerve. Plantar plate (bottom) the plantar plate extends from the metatarsal neck to the base of the proximal phalanx and is an important stabilizer of the mtp joints. Plantar fascia anatomy and its relationship with achilles tendon and paratenon abstract. The medial plantar nerve supplies the plantar aspects of the first, second, third and medial half of the fourth metatarsophalangeal joint.
 Source: humanbodyhelp.com
Source: humanbodyhelp.com
When the foot rolls off the ground during walking, the toes dorsiflex and pull on the plantar fascia. However, in humans, the plantaris comes nowhere near it. Long, ending in a long slender tendon which crosses obliquely between the two muscles of the. As the muscle crosses both the knee and ankle joints, it weakly assists with knee and plantar flexion. There are 10 intrinsic muscles located in the sole of the foot.
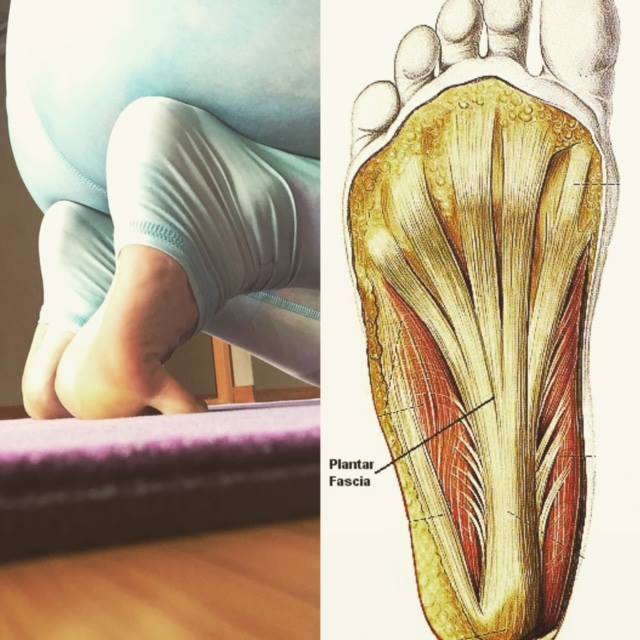 Source: saragerow.com
Source: saragerow.com
Plantar flexion is the movement that occurs at the ankle where the foot is pointed downwards. An anatomical study of 200 (cadaveric) feet injected with latex demonstrated that lejars’ concept of the venous sole of the foot is incorrect: Anatomy of the plantar fascia. Anatomy of the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot.
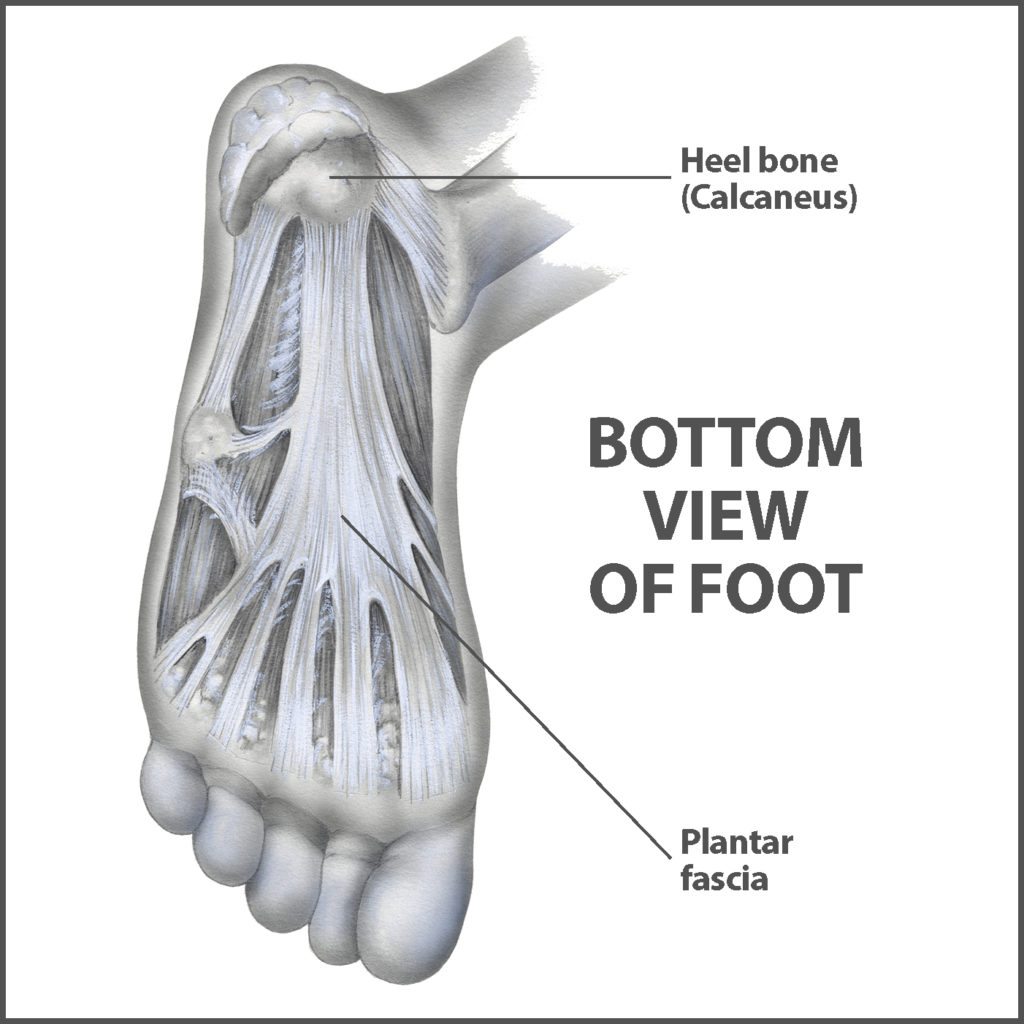 Source: floridaortho.com
Source: floridaortho.com
Although the plantar fascia (pf) has been studied quite well from a biomechanical viewpoint, its microscopic. The lateral plantar artery (a. These fibers are mostly longitudinal but also transverse. 5.9 anatomy of the plantar fascia scott wearing the plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes. Authors carla stecco 1 , marco corradin, veronica macchi, aldo morra, andrea porzionato, carlo biz, raffaele de caro.
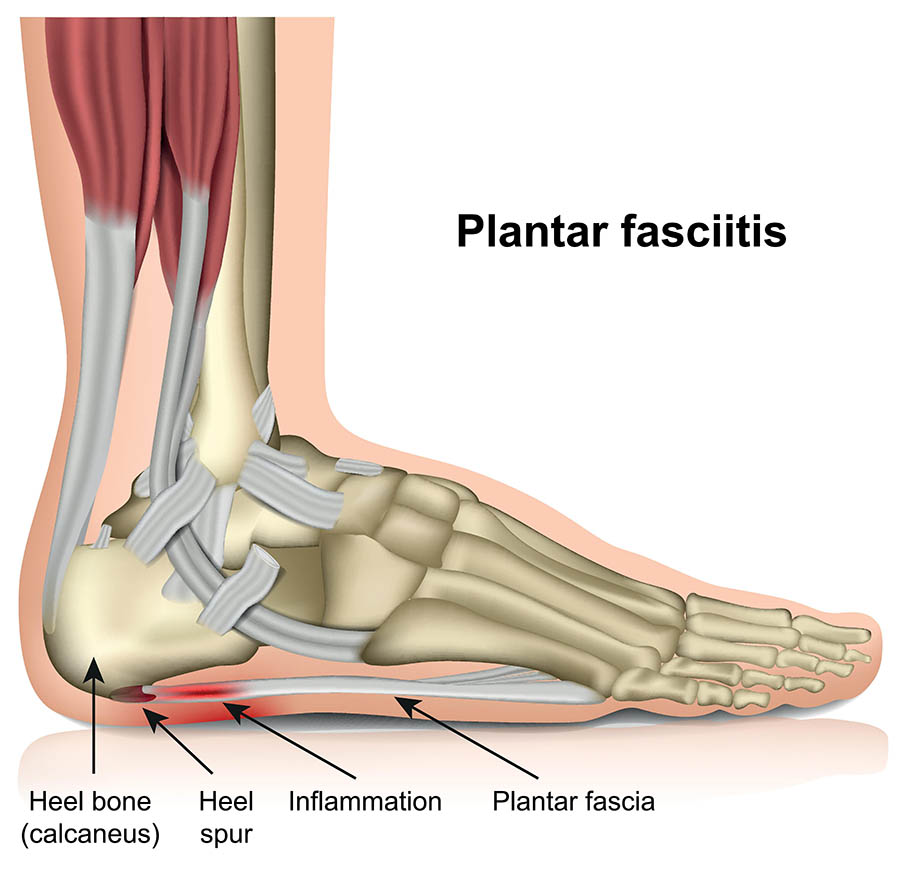 Source: dr7physioandpod.com.au
Source: dr7physioandpod.com.au
The muscles of the plantar aspect are. However, in humans, the plantaris comes nowhere near it. They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot, and individually to control movement of the digits. Anatomy of the plantar fascia. This image shows the anatomy of the plantar foot and is labeled with corresponding identification tags.
 Source: pinterest.ca
Source: pinterest.ca
There are 10 intrinsic muscles located in the sole of the foot. [adjective] of or relating to the sole of the foot. The muscles of the plantar aspect are. External plantar artery), much larger than the medial, passes obliquely lateralward and forward to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.it then turns medialward to the interval between the bases of the first and second metatarsal bones, where it unites with the deep plantar branch of the dorsalis pedis artery, thus. Plantar fascia anatomy and its relationship with achilles tendon and paratenon j anat.
 Source: ergonx.com.au
Source: ergonx.com.au
The medial plantar nerve supplies the plantar aspects of the first, second, third and medial half of the fourth metatarsophalangeal joint. Authors carla stecco 1 , marco corradin, veronica macchi, aldo morra, andrea porzionato, carlo biz, raffaele de caro. We are looking at how to identify the 3 bands of the plantar fascia and which band is most important in plantar fasciitis. Learn about anatomical directional terminology used for the limbs, hands, and feet, and explore the differences between palmar, dorsal, and plantar aspects, and the definition of. It is the opposite of dorsiflexion, which is pointing the foot upwards.
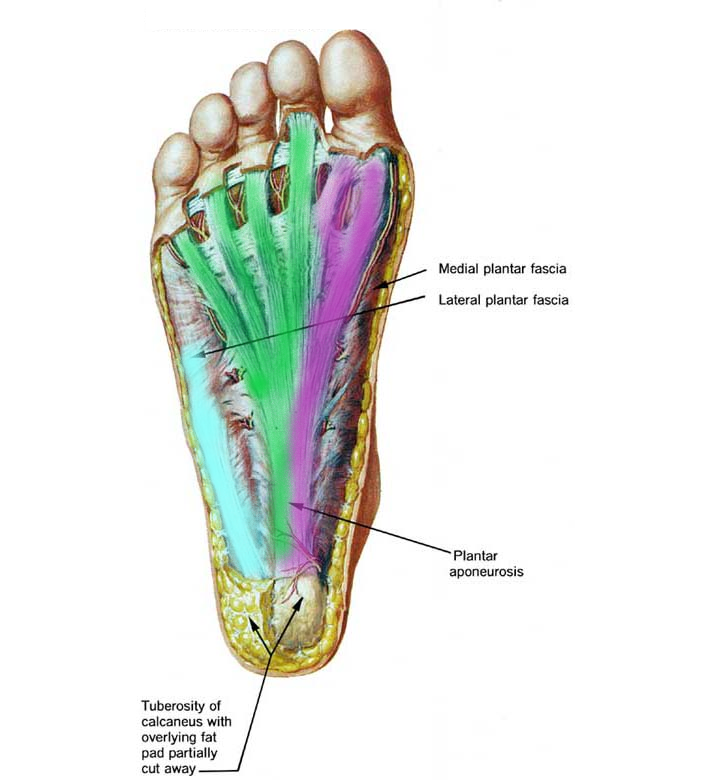 Source: sportspodiatry.com.au
Source: sportspodiatry.com.au
Plantar flexion is the movement that occurs at the ankle where the foot is pointed downwards. The plantar aponeurosis is the modification of deep fascia, which covers the sole. The plantar fascia is a complex structure that extends from the medial calcaneal tubercle (the heel bone) to the proximal phalanges of the toes (the bone at the base of the toe) at the metatarsophalangeal (mtp) joints. The plantar fascia (pf) can undergo a form of pathological degeneration called. The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue ( aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom ( plantar side) of the foot.
 Source: hybridpainrelief.com
Source: hybridpainrelief.com
Learn about anatomical directional terminology used for the limbs, hands, and feet, and explore the differences between palmar, dorsal, and plantar aspects, and the definition of. 5.9 anatomy of the plantar fascia scott wearing the plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes. Plantar flexion is the movement that occurs at the ankle where the foot is pointed downwards. The fascia is thick centrally, known as aponeurosis and is thin along the sides. Tendon disorders along the plantar aspect of the foot may lead to significant symptoms but are often clinically misdiagnosed.
 Source: kinetichealthcalgary.blogspot.com
Source: kinetichealthcalgary.blogspot.com
Anatomy of the plantar fascia. Plantar definition, of or relating to the sole of the foot. Various terms have been used to describe plantar fasciitis, including jogger’s heel, tennis heel, policeman’s. The plantar aponeurosis is the modification of deep fascia, which covers the sole. Muscles of the plantar foot are divided into four layers:first la.
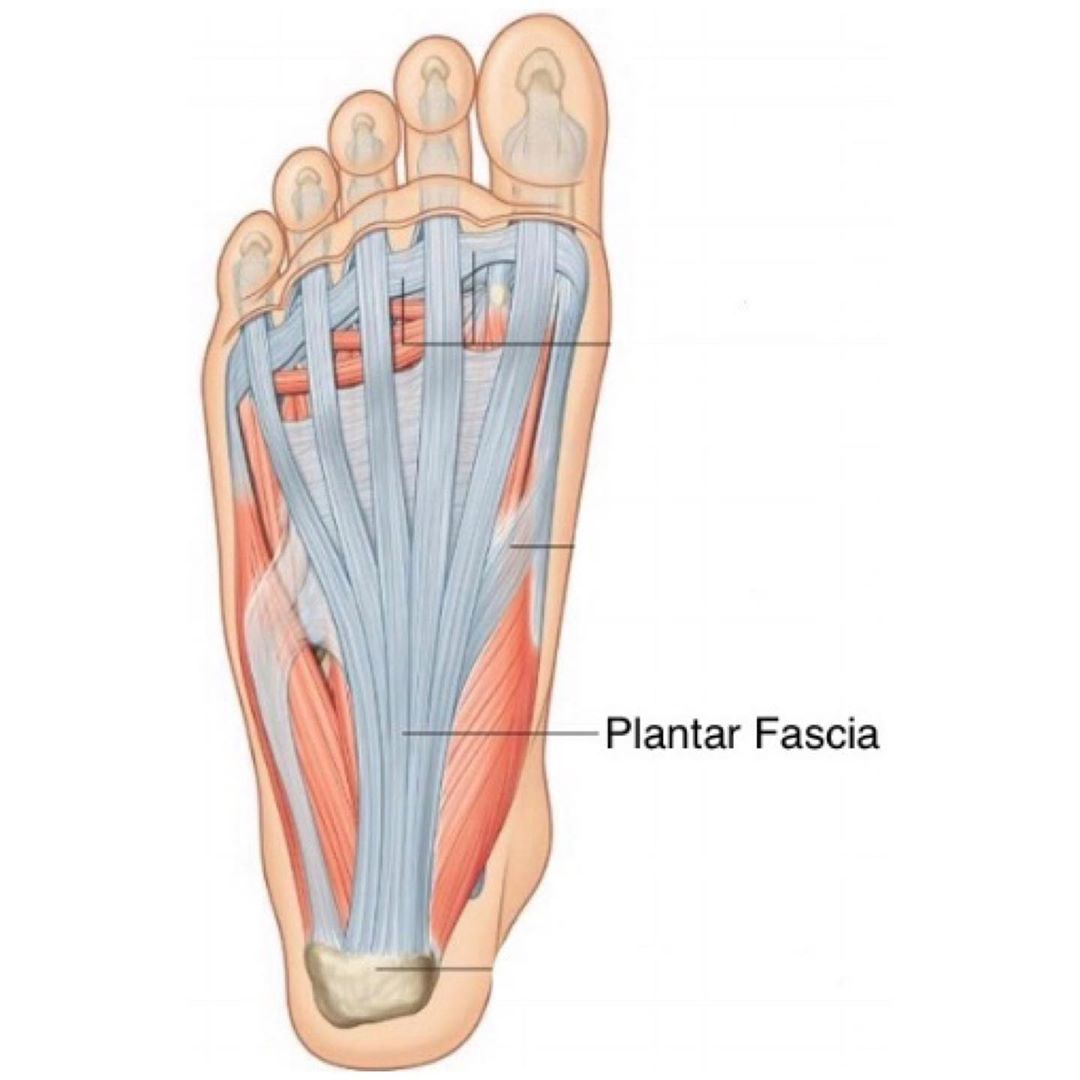 Source: stefanduell.tumblr.com
Source: stefanduell.tumblr.com
[adjective] of or relating to the sole of the foot. This article will cover the anatomy and functions of the plantaris muscle. Plantar fasciitis is the pain caused by degenerative irritation at the insertion of the plantar fascia on the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity. Learn about anatomical directional terminology used for the limbs, hands, and feet, and explore the differences between palmar, dorsal, and plantar aspects, and the definition of. The muscles of the plantar aspect are.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Plantaris gets its name because in many mammals it inserts into the plantar aponeurosis. Tendon disorders along the plantar aspect of the foot may lead to significant symptoms but are often clinically misdiagnosed. This consists of five long metatarsal bones and five shorter bones that form the toes (phalanges). The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. Plantar fascia anatomy and its relationship with achilles tendon and paratenon j anat.
 Source: step1.medbullets.com
Source: step1.medbullets.com
There are 10 intrinsic muscles located in the sole of the foot. Anatomy of the plantar fascia. The lateral half of the fourth joint and the fifth joint are innervated by digital branches of the lateral plantar nerve. However, in humans, the plantaris comes nowhere near it. For example when you go up onto your toes.
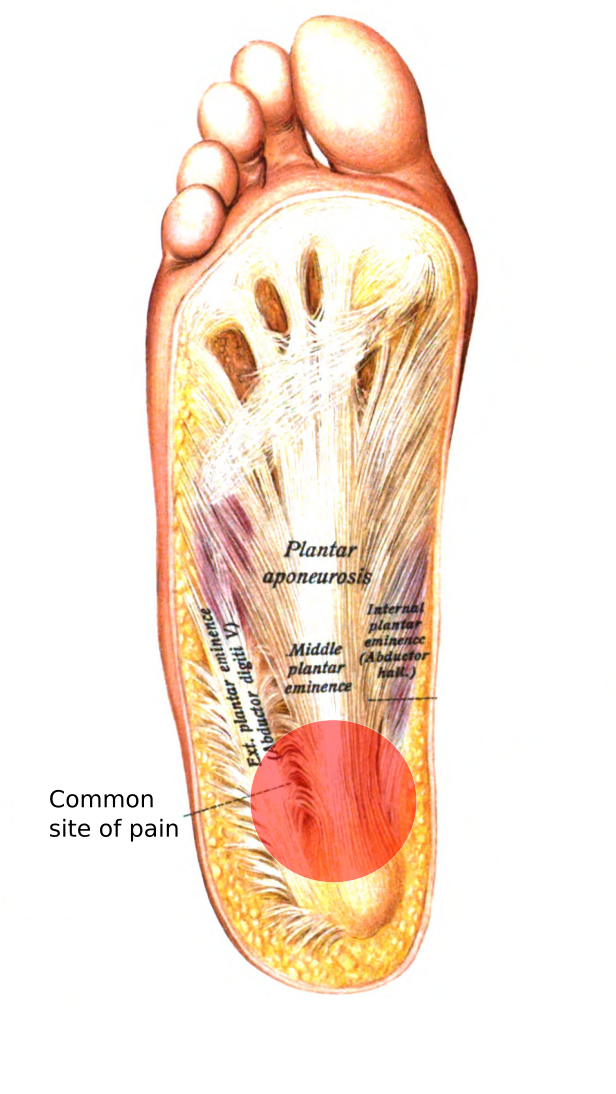 Source: idealbalanceacupuncture.blogspot.com
Source: idealbalanceacupuncture.blogspot.com
Plantaris gets its name because in many mammals it inserts into the plantar aponeurosis. The fascia is thick centrally, known as aponeurosis and is thin along the sides. For example when you go up onto your toes. The anatomy of the foot. This image shows the anatomy of the plantar foot and is labeled with corresponding identification tags.
 Source: candent.ca
Source: candent.ca
The lateral half of the fourth joint and the fifth joint are innervated by digital branches of the lateral plantar nerve. This article will cover the anatomy and functions of the plantaris muscle. Anatomy of the plantar fascia. Arising predominantly from the calcaneal tuberosity, the plantar fascia attaches distally, through several slips, to the plantar… The plantaris is placed between the gastrocnemius and soleus.
 Source: bjsm.bmj.com
Source: bjsm.bmj.com
Plantar fascia anatomy and its relationship with achilles tendon and paratenon j anat. These fibers are mostly longitudinal but also transverse. On the dorsal aspect, the. Posteriorly it attaches to the medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus, proximal to flexor digitorum brevis.it is narrow and thick at this attachment and becomes more. The plantar fascia or plantar aponeurosis is a dense collection of collagen fibers on the sole (plantar surface) of the foot.
 Source: vaidyaveekshan.blogspot.com
Source: vaidyaveekshan.blogspot.com
The medial plantar nerve supplies the plantar aspects of the first, second, third and medial half of the fourth metatarsophalangeal joint. Learn about anatomical directional terminology used for the limbs, hands, and feet, and explore the differences between palmar, dorsal, and plantar aspects, and the definition of. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the muscle anatomy of the plantar foot. This is the 2nd video in our series on mri of the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is not a nerve, tendon or muscle, but rather a strong fibrous tissue (figure 16).
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plantar anatomy by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







