Your Plantar aponeurosis images are available. Plantar aponeurosis are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Plantar aponeurosis files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for plantar aponeurosis pictures information linked to the plantar aponeurosis topic, you have come to the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
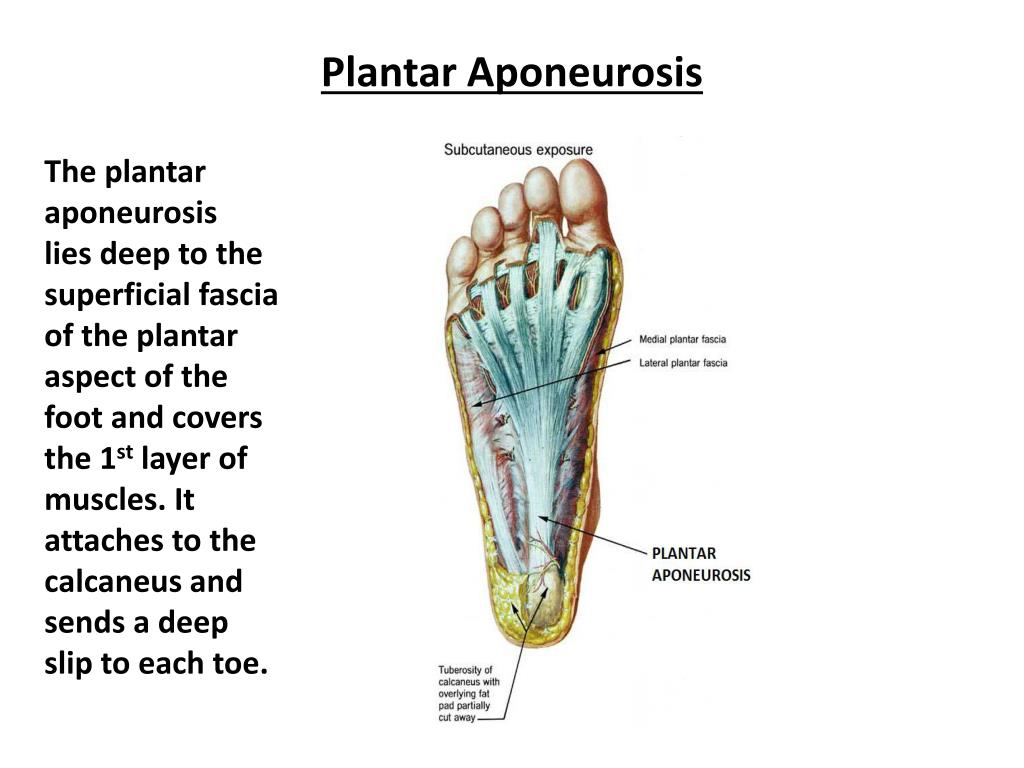
Plantar Aponeurosis. Plantar fasciitis, characterized by pain in the plantar region of the foot that is worse when initiating walking, is one of the most common causes of foot and heel pain in adults. The plantar aponeurosis (pa), or plantar fascia, is the strong, fibrous investing layer of the sole of the foot (, 1). The apex of the plantar aponeurosis is connected to the medial tubercle of calcaneum, proximal to the connection of the flexor digitorum brevis. The plantar aponeurosis (pa) originates from the calcaneal tubercle and extends to the forefoot.
 plantar aponeurosis Sports Performance Bulletin From sportsperformancebulletin.com
plantar aponeurosis Sports Performance Bulletin From sportsperformancebulletin.com
The medial and lateral parts attach to the abductor hallucis and the musculus abductor digiti quinti pedis, respectively. Doctors once thought bony growths. The plantar aponeurosis or plantar fascia as it is more colloquially known is a flat sheet of thickened, poorly vascularised and poorly innovated, deep fibrous connective tissue of the foot which can measure between 2.2 and 5.4milimetres (cardina, chhem, beauregard, aubin, & pelletier, 1996). These parts are usually categorized as “fascia”. They extend from the calcaneal tuberosity then diverge to connect to the bones, ligaments and the dermis of the skin around the distal part of the metatarsal bones. The plantar aponeurosis (pa) originates from the calcaneal tubercle and extends to the forefoot.
Arising predominantly from the calcaneal tuberosity, the plantar fascia attaches distally, through several slips, to the plantar aspect of the forefoot as well as the medial and lateral intermuscular septa.
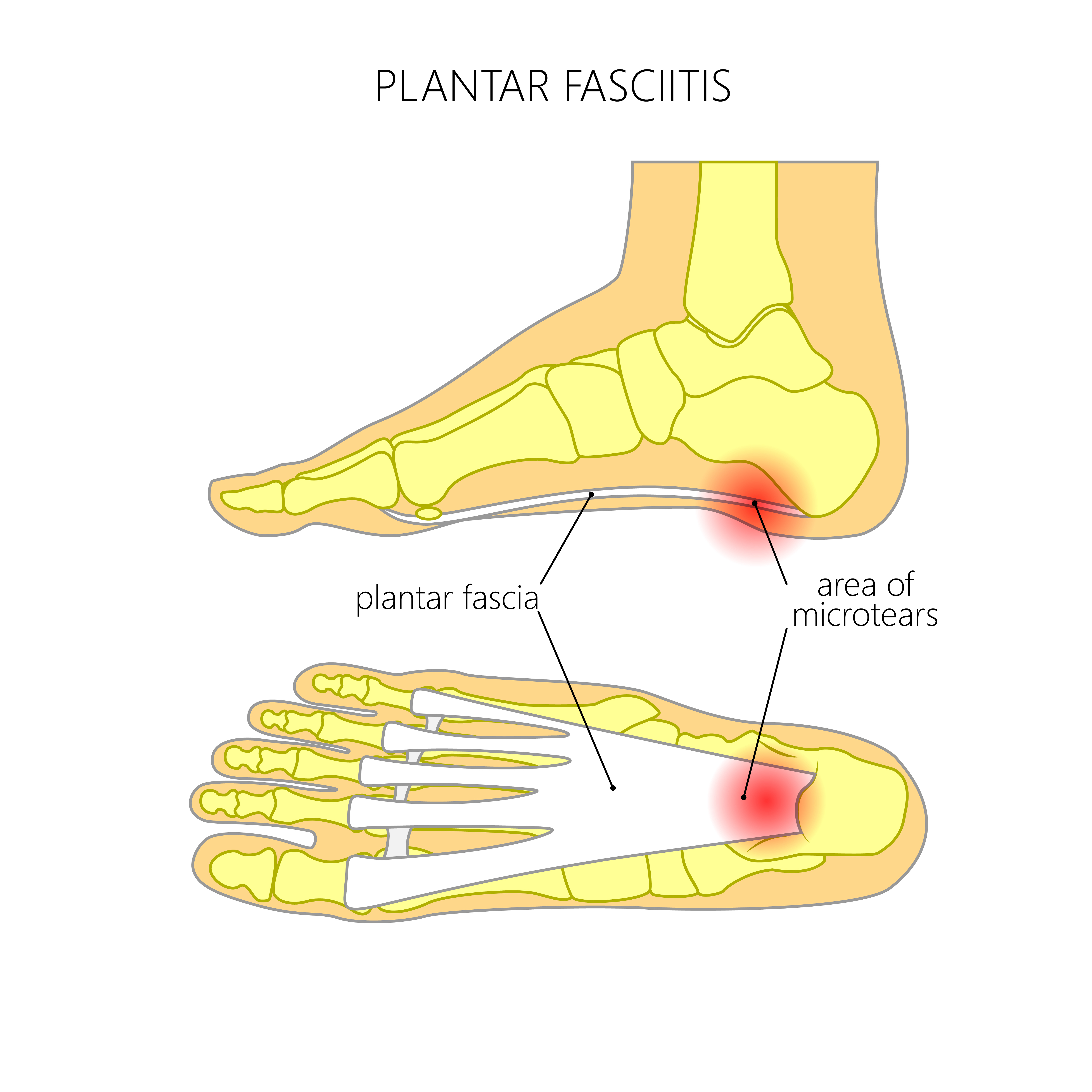
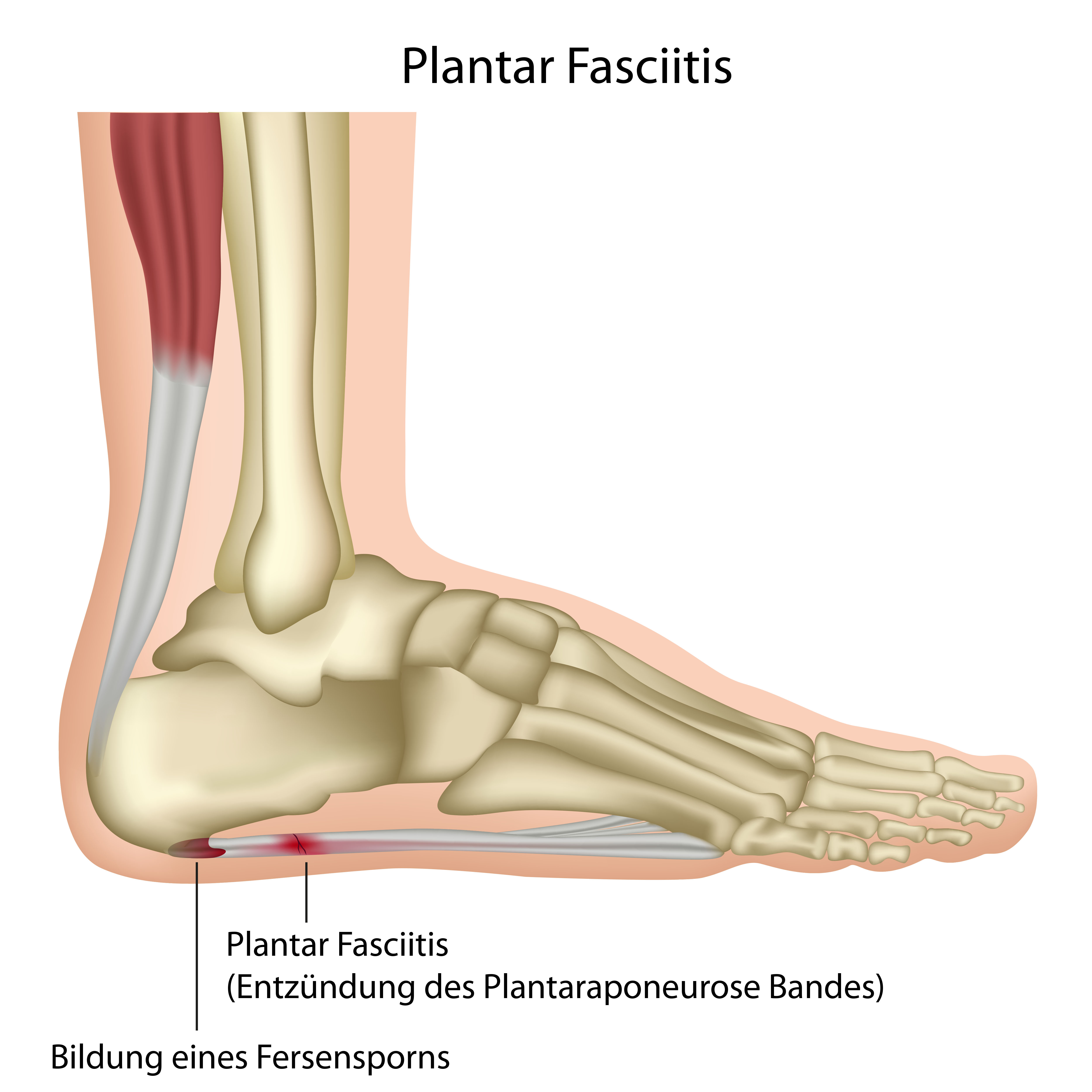
The plantar aponeurosis comprises histologically both collagen and elastic fibers arranged in a particular network The pain, mostly localised in the area of the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity, is caused by pressure in the region of the plantar aponeurosis attachment to the calcaneal bone. It radiates toward the toes from the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and provides some attachment for the short flexor muscle of the toes. Doctors once thought bony growths. The plantar aponeurosis, or plantar fascia, has received considerable attention in the scientific literature and has been shown to be the most important structure for dynamic longitudinal arch support in the foot. The plantar aponeurosis, also known as the plantar fascia, is a strong layer of white fibrous tissue located beneath the skin on the sole of the foot.
 Source: sportsperformancebulletin.com
Source: sportsperformancebulletin.com
The plantar aponeurosis (pa) originates from the calcaneal tubercle and extends to the forefoot. The plantar aponeurosis foot ankle int. It radiates toward the toes from the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and provides some attachment for the short flexor muscle of the toes. The plantar aponeurosis (pa), or plantar fascia, is the strong, fibrous investing layer of the sole of the foot (, 1). The plantar aponeurosis, also known as the plantar fascia, is a strong layer of white fibrous tissue located beneath the skin on the sole of the foot.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The aponeurosis consists of a medial, central and lateral part. See biomechanics of plantar fasciitis. This type of action is called a windlass mechanism. [ta] the thick, central portion of the fascia investing the plantar muscles; The medial and lateral parts attach to the abductor hallucis and the musculus abductor digiti quinti pedis, respectively.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The plantar aponeurosis (pa) originates from the calcaneal tubercle and extends to the forefoot. The plantar aponeurosis comprises histologically both collagen and elastic fibers arranged in a particular network of bundles and is a tough tendinous (rather than a. It radiates toward the toes from the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and provides some attachment for the short flexor muscle of the toes. The central portion, the thickest, is narrow behind and attached to the medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus, posterior to the origin of the. Plantar fasciitis, characterized by pain in the plantar region of the foot that is worse when initiating walking, is one of the most common causes of foot and heel pain in adults.
 Source: whitakerwellness.com
Source: whitakerwellness.com
It radiates toward the toes from the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and provides some attachment for the short flexor muscle of the toes. The medial and lateral parts attach to the abductor hallucis and the musculus abductor digiti quinti pedis, respectively. Arising predominantly from the calcaneal tuberosity, the plantar fascia attaches distally, through several slips, to the plantar aspect of the forefoot as well as the medial and lateral intermuscular septa. Plantar is a term used to refer to the bottom/sole of the feet. The plantar aponeurosis (pa) originates from the calcaneal tubercle and extends to the forefoot.
 Source: piedmont.org
Source: piedmont.org
The plantar aponeurosis or plantar fascia as it is more colloquially known is a flat sheet of thickened, poorly vascularised and poorly innovated, deep fibrous connective tissue of the foot which can measure between 2.2 and 5.4milimetres (cardina, chhem, beauregard, aubin, & pelletier, 1996). The plantar aponeurosis foot ankle int. Stress of repetitive trauma (more common) degenerative. Plantar is a term used to refer to the bottom/sole of the feet. It causes severe pain in the plantar surface of the heel and on the medial aspect of the foot.
 Source: naturalremedies.org
Source: naturalremedies.org
We’ll see the whole of the plantar fascia when we�ve looked at at the muscles of the foot, which we’re going to do shortly. As you walk, the plantar aponeurosis is engaged when your heel rises and the toes lift off the ground. The plantar aponeurosis, also known as the plantar fascia, is a strong layer of white fibrous tissue located beneath the skin on the sole of the foot. Plantar fasciitis, characterized by pain in the plantar region of the foot that is worse when initiating walking, is one of the most common causes of foot and heel pain in adults. The plantar aponeurosis (pa), or plantar fascia, is the strong, fibrous investing layer of the sole of the foot (, 1).
 Source: purposegames.com
Source: purposegames.com
[ta] the thick, central portion of the fascia investing the plantar muscles; It radiates toward the toes from the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and provides some attachment for the short flexor muscle of the toes. The plantar aponeurosis, also known as the plantar fascia, is a strong layer of white fibrous tissue located beneath the skin on the sole of the foot. The medial and lateral parts attach to the abductor hallucis and the musculus abductor digiti quinti pedis, respectively. The aponeurosis consists of a medial, central and lateral part.

Author m r hedrick 1 affiliation 1 emory university, emory clinic, department of orthopaedic surgery, atlanta, georgia, usa. The plantar aponeurosis, also known as the plantar fascia, is a strong layer of white fibrous tissue located beneath the skin on the sole of the foot. The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. Author m r hedrick 1 affiliation 1 emory university, emory clinic, department of orthopaedic surgery, atlanta, georgia, usa. The plantar aponeurosis in the human foot has been extensively studied and thoroughly described, in part, because of the incidence of plantar fasciitis in humans.
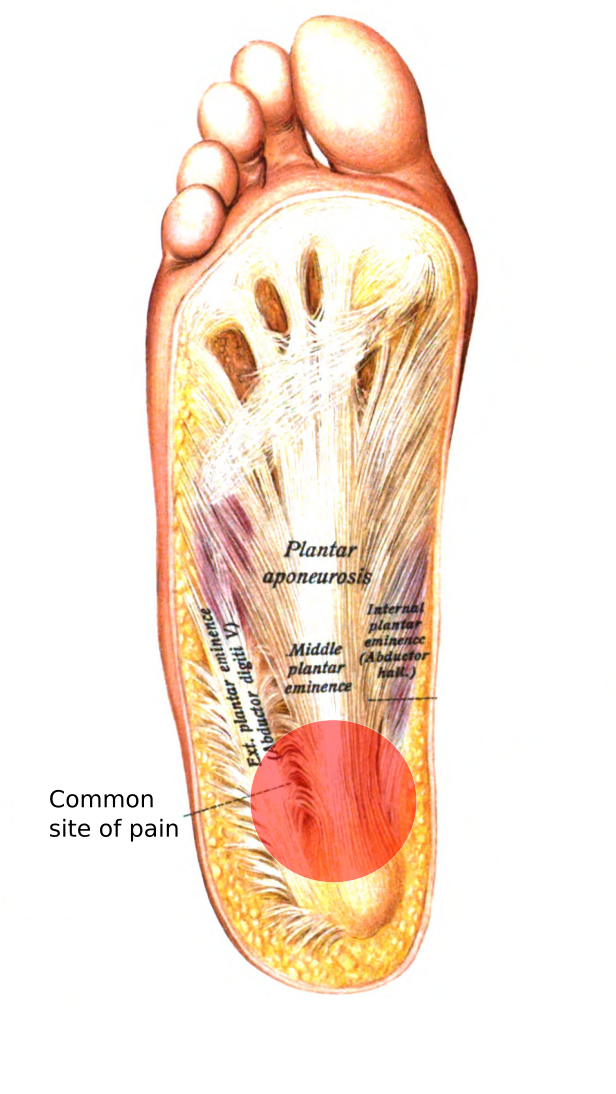 Source: idealbalanceacupuncture.blogspot.com
Source: idealbalanceacupuncture.blogspot.com
The plantar aponeurosis (pa) originates from the calcaneal tubercle and extends to the forefoot. The plantar fascia is a broad fibrous aponeurosis that originates from the medial and anterior aspects of the calcaneus, divides into five digital slips at the metatarsophalangeal joints, and inserts distally into the periosteum at the base of the proximal phalanges (figure 1). During walking, the plantar aponeurosis functions mainly during �heel rise� to �toe off. The plantar aponeurosis comprises histologically both collagen and elastic fibers arranged in a particular network of bundles and is a tough tendinous (rather than a. The bottom of the plantar aponeurosis close to the heads of the metatarsals splits into five straps, one for every toe.
 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
It causes severe pain in the plantar surface of the heel and on the medial aspect of the foot. The aponeurosis consists of a medial, central and lateral part. The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. Function of the pa is to The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot.
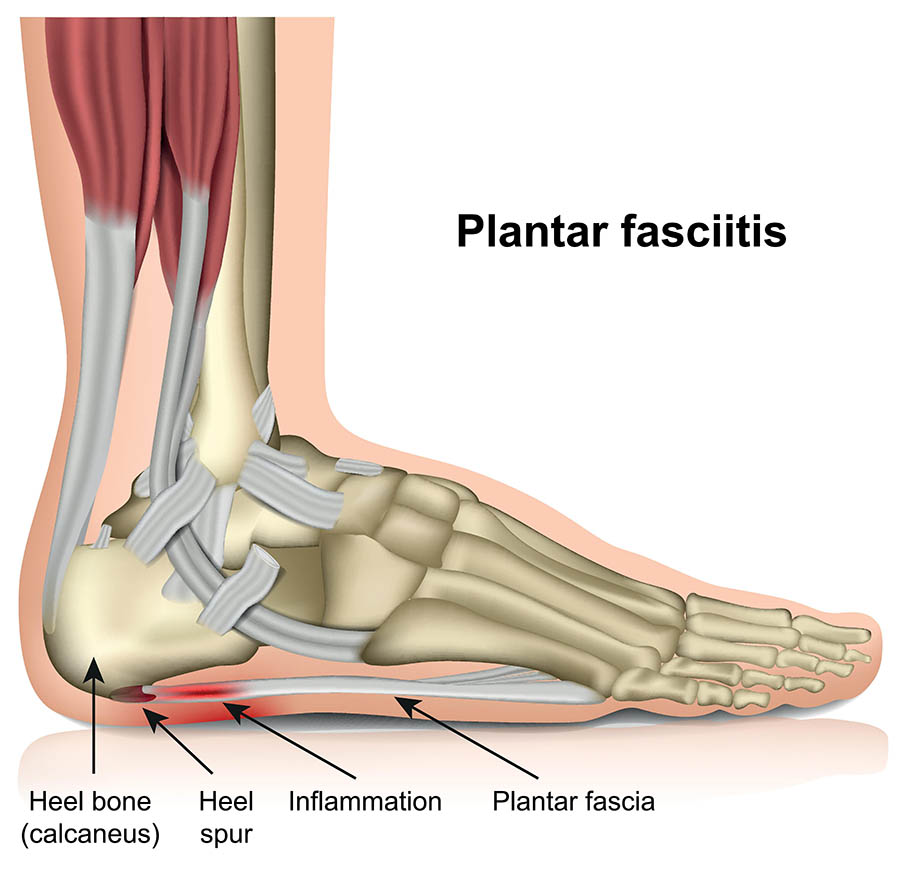 Source: dr7physioandpod.com.au
Source: dr7physioandpod.com.au
The plantar aponeurosis (pa), or plantar fascia, is the strong, fibrous investing layer of the sole of the foot (, 1). The plantar aponeurosis is triangle shaped and fills the central space of the sole. It causes severe pain in the plantar surface of the heel and on the medial aspect of the foot. See biomechanics of plantar fasciitis. Arising predominantly from the calcaneal tuberosity, the plantar fascia attaches distally, through several slips, to the plantar aspect of the forefoot as well as the medial and lateral intermuscular septa.
 Source: practicalpainmanagement.com
Source: practicalpainmanagement.com
Author m r hedrick 1 affiliation 1 emory university, emory clinic, department of orthopaedic surgery, atlanta, georgia, usa. Doctors once thought bony growths. The bottom of the plantar aponeurosis close to the heads of the metatarsals splits into five straps, one for every toe. They extend from the calcaneal tuberosity then diverge to connect to the bones, ligaments and the dermis of the skin around the distal part of the metatarsal bones. The central portion, the thickest, is narrow behind and attached to the medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus, posterior to the origin of the.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The plantar aponeurosis is the central part, and much the strongest part, of a layer of fascia, the plantar fascia, which covers the entire sole of the foot. Plantar is a term used to refer to the bottom/sole of the feet. The medial and lateral parts attach to the abductor hallucis and the musculus abductor digiti quinti pedis, respectively. It radiates toward the toes from the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and provides some attachment for the short flexor muscle of the toes. 3, 4 it is composed of three separate bands of dense connective.
Source: researchgate.net
The plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the. The aponeurosis consists of a medial, central and lateral part. During walking, the plantar aponeurosis functions mainly during �heel rise� to �toe off. The plantar aponeurosis comprises histologically both collagen and elastic fibers arranged in a particular network of bundles and is a tough tendinous (rather than a. The plantar aponeuroses occur on the plantar aspect of the foot.
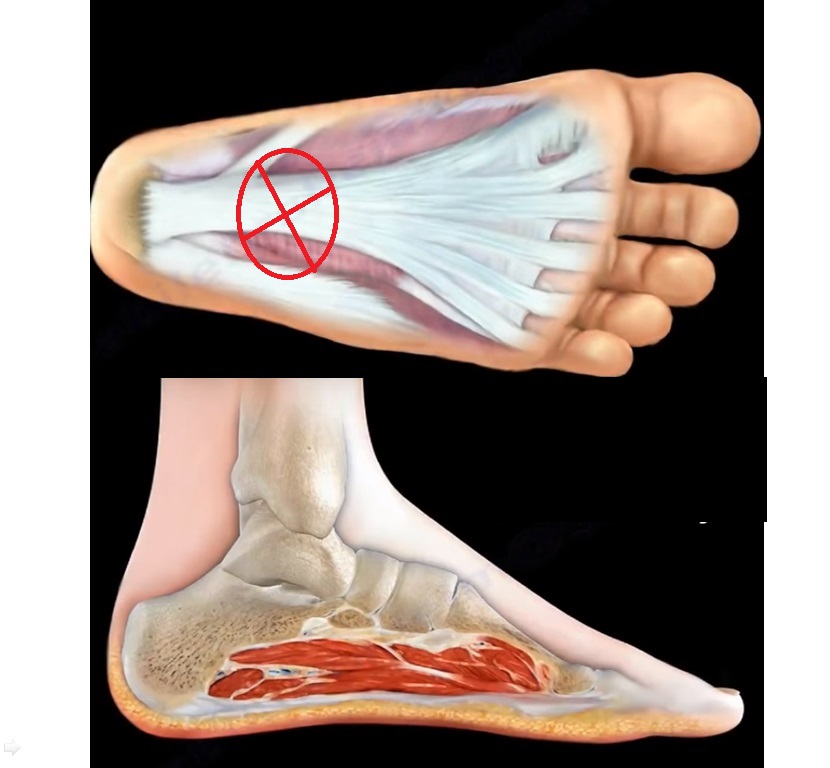 Source: orthopaedicprinciples.com
Source: orthopaedicprinciples.com
Plantar fasciitis is a condition in which the plantar aponeurosis is strained and inflamed. Plantar is a term used to refer to the bottom/sole of the feet. The plantar aponeurosis (pa) originates from the calcaneal tubercle and extends to the forefoot. Plantar fasciitis, characterized by pain in the plantar region of the foot that is worse when initiating walking, is one of the most common causes of foot and heel pain in adults. The central portion, the thickest, is narrow behind and attached to the medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus, posterior to the origin of the.
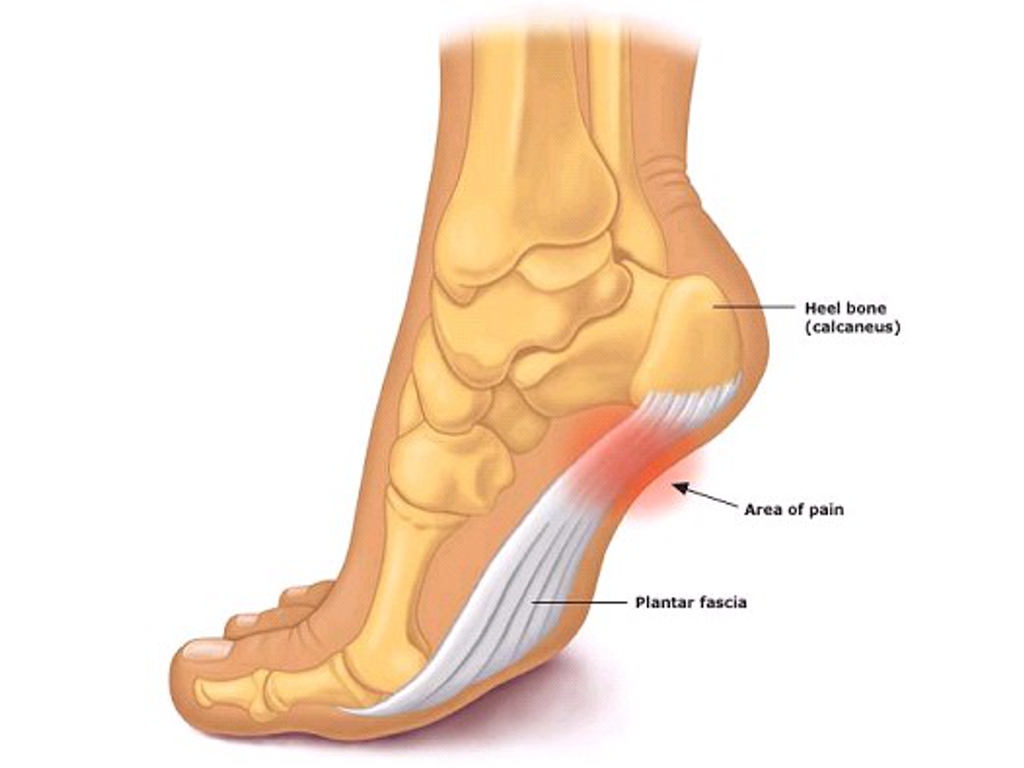 Source: americanfoot.com
Source: americanfoot.com
The plantar aponeurosis, also known as the plantar fascia, is a strong layer of white fibrous tissue located beneath the skin on the sole of the foot. The plantar aponeurosis (pa), or plantar fascia, is the strong, fibrous investing layer of the sole of the foot (, 1). It is commonly assumed that the human plantar aponeurosis is a unique adaptation to bipedalism that evolved in concert with the longitudinal arch. During walking, the plantar aponeurosis functions mainly during �heel rise� to �toe off. The plantar aponeurosis or plantar fascia as it is more colloquially known is a flat sheet of thickened, poorly vascularised and poorly innovated, deep fibrous connective tissue of the foot which can measure between 2.2 and 5.4milimetres (cardina, chhem, beauregard, aubin, & pelletier, 1996).
 Source: kintec.net
Source: kintec.net
They extend from the calcaneal tuberosity then diverge to connect to the bones, ligaments and the dermis of the skin around the distal part of the metatarsal bones. 3, 4 it is composed of three separate bands of dense connective. The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. The plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes. The medial and lateral parts attach to the abductor hallucis and the musculus abductor digiti quinti pedis, respectively.
 Source: physio-puncture.com
Source: physio-puncture.com
Stress of repetitive trauma (more common) degenerative. We’ll see the whole of the plantar fascia when we�ve looked at at the muscles of the foot, which we’re going to do shortly. Because of its combined static and dynamic role in longitudinal arch support in the foot ( , 2 , , 3 ) and the capability of allowing the loading capacity on the foot during weight bearing, abnormalities of the pa are commonly. These parts are usually categorized as “fascia”. This type of action is called a windlass mechanism.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title plantar aponeurosis by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.