Your Plantar foot anatomy images are ready. Plantar foot anatomy are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Plantar foot anatomy files here. Get all free vectors.
If you’re searching for plantar foot anatomy images information related to the plantar foot anatomy topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
Plantar Foot Anatomy. (fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements: The central muscles of the foot sole lie within the central compartment between the muscles of the big and little toe. All the muscles are innervated either by the medial plantar nerve or the lateral plantar nerve, which are both branches of the tibial nerve. The ligament, which runs along the sole of the foot, from the heel to.
 TREATMENTS IN AYURVEDA MY CLINICAL EXPERIENCES Plantar From vaidyaveekshan.blogspot.com
TREATMENTS IN AYURVEDA MY CLINICAL EXPERIENCES Plantar From vaidyaveekshan.blogspot.com
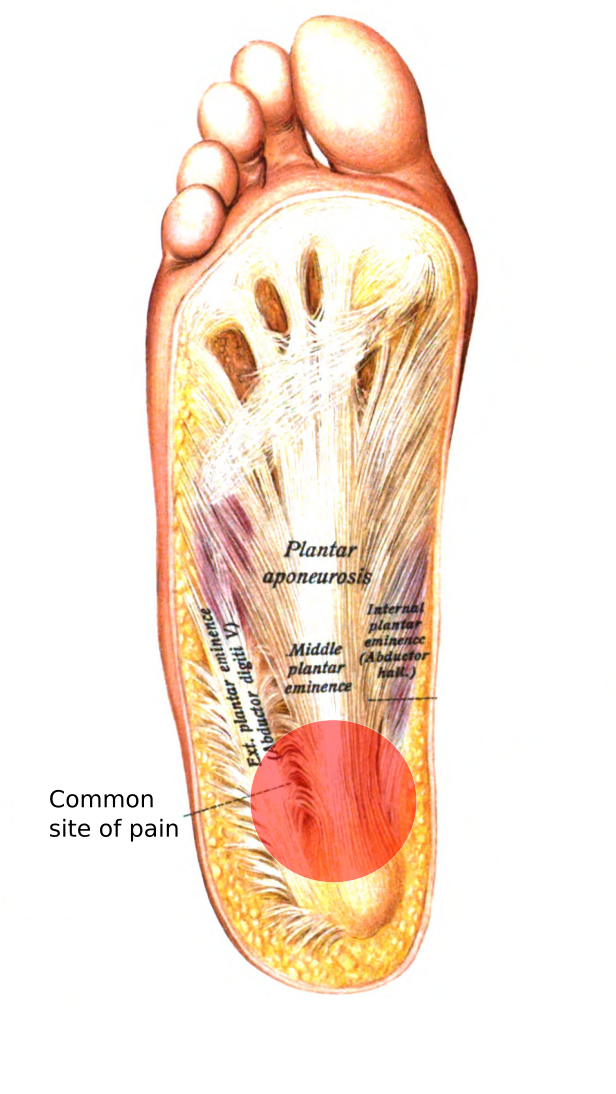
Normal bands today’s post is again a video on mri of the plantar fascia anatomy. The main tendon of the foot is the achilles tendon, which runs from the calf muscle to the heel. Lateral plantar muscles (inferior view) the lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles. The plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes. The plantar fascia is the investing fascial layer of the anterior (plantar) aspect of the foot that originates from the os calcis and inserts through a complex. The compartment comprises numerous short foot muscles in different layers.
A bursa may develop at the spur and this may also become inflamed
Lateral plantar muscles (inferior view) the lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles. The compartment comprises numerous short foot muscles in different layers. Their muscle bellies form the surface of the lateral foot sole (ball of the little toe). Note that all of these muscles cross and act upon more than one joint. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate [ clarification needed ] organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. This image shows the anatomy of the plantar foot and is labeled with corresponding identification tags.
 Source: ergonx.com.au
Source: ergonx.com.au
Plantar warts can be painful and difficult to treat. (fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements: In this article, we review the normal anatomy of the plantar tendons, including the peroneus longus, flexor hallucis longus (fhl), flexor digitorum longus (fdl), and posterior tibial tendons. Pain plantar surface of the heel and medial aspect of foot; Its role is to support the head of the talus.
 Source: trialexhibitsinc.com
Source: trialexhibitsinc.com
The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. A bursa may develop at the spur and this may also become inflamed In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate [ clarification needed ] organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot, and individually to control movement of the digits. Their muscle bellies form the surface of the lateral foot sole (ball of the little toe).
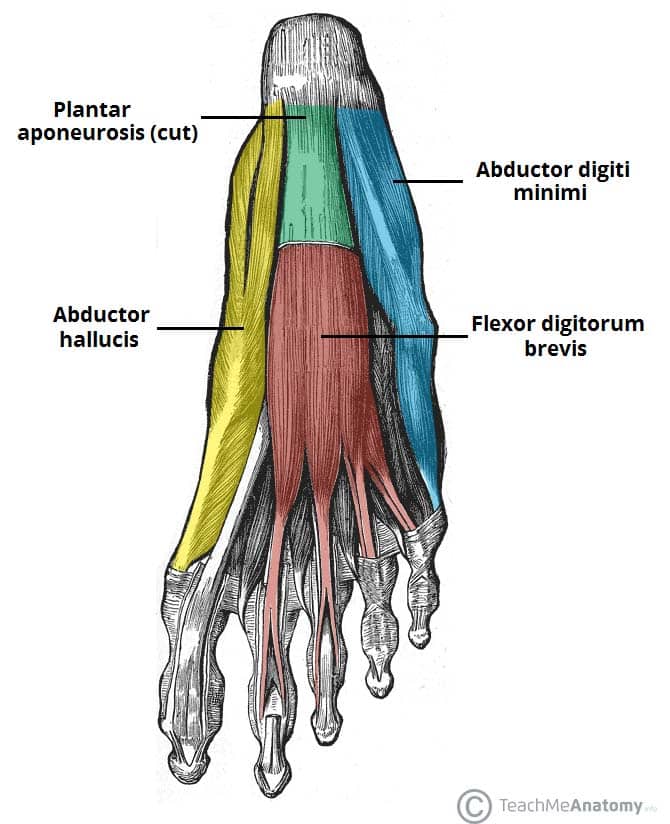 Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Source: teachmeanatomy.info
What does palmar mean in anatomy? The muscular anatomy of the plantar foot is composed of the plantar fascia as well as intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. A bursa may develop at the spur and this may also become inflamed These two branches provide sensation to the entire sole of the foot,. The plantar fascia provides strength for walking and assists with balance.
 Source: saragerow.com
Source: saragerow.com
Oblique and transverse heads of the adductor hallucis. The plantar fascia provides strength for walking and assists with balance. What does palmar mean in anatomy? (fig.23) dorsiflexion (refer fig.24) abduction spreading the toes apart. (fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements:
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Plantar warts can be painful and difficult to treat. The achilles tendon makes it possible to run, jump, climb stairs and stand on your toes. Oblique and transverse heads of the adductor hallucis. What does palmar mean in anatomy? They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot, and individually to control movement of the digits.
 Source: humanbodyhelp.com
Source: humanbodyhelp.com
Their muscle bellies form the surface of the lateral foot sole (ball of the little toe). If chronic, it will present with ecchymosis and edema in a patient with underlying plantar fasciitis. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate [ clarification needed ] organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. (fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements: The achilles tendon makes it possible to run, jump, climb stairs and stand on your toes.
 Source: pinterest.ca
Source: pinterest.ca
The tibial nerve controls all the muscles behind the tibia and fibula in the back part of the calf (deep and superficial posterior compartment muscles). The tibial nerve controls all the muscles behind the tibia and fibula in the back part of the calf (deep and superficial posterior compartment muscles). It arises opposite the 1st metatarsal interspace from the venous arch of the 1st interspace. The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. Lateral plantar muscles (inferior view) the lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles.
 Source: idealbalanceacupuncture.blogspot.com
Source: idealbalanceacupuncture.blogspot.com
Lateral plantar muscles (inferior view) the lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles. Its thick central part, the plantar aponeurosis, is bound by thinner lateral portions. The lateral (or external) plantar pedicle is longer (12 cm), curved, and larger because it is located between the two muscle layers of the sole of the foot, and thus is compressed during contraction. Its role is to support the head of the talus. Anatomy of the foot and ankle (refer fig.22) plantar flexion bending the toes towards the sole of the foot.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The main tendon of the foot is the achilles tendon, which runs from the calf muscle to the heel. The plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes. (fig.23) dorsiflexion (refer fig.24) abduction spreading the toes apart. What does palmar mean in anatomy? The central muscles of the foot sole lie within the central compartment between the muscles of the big and little toe.
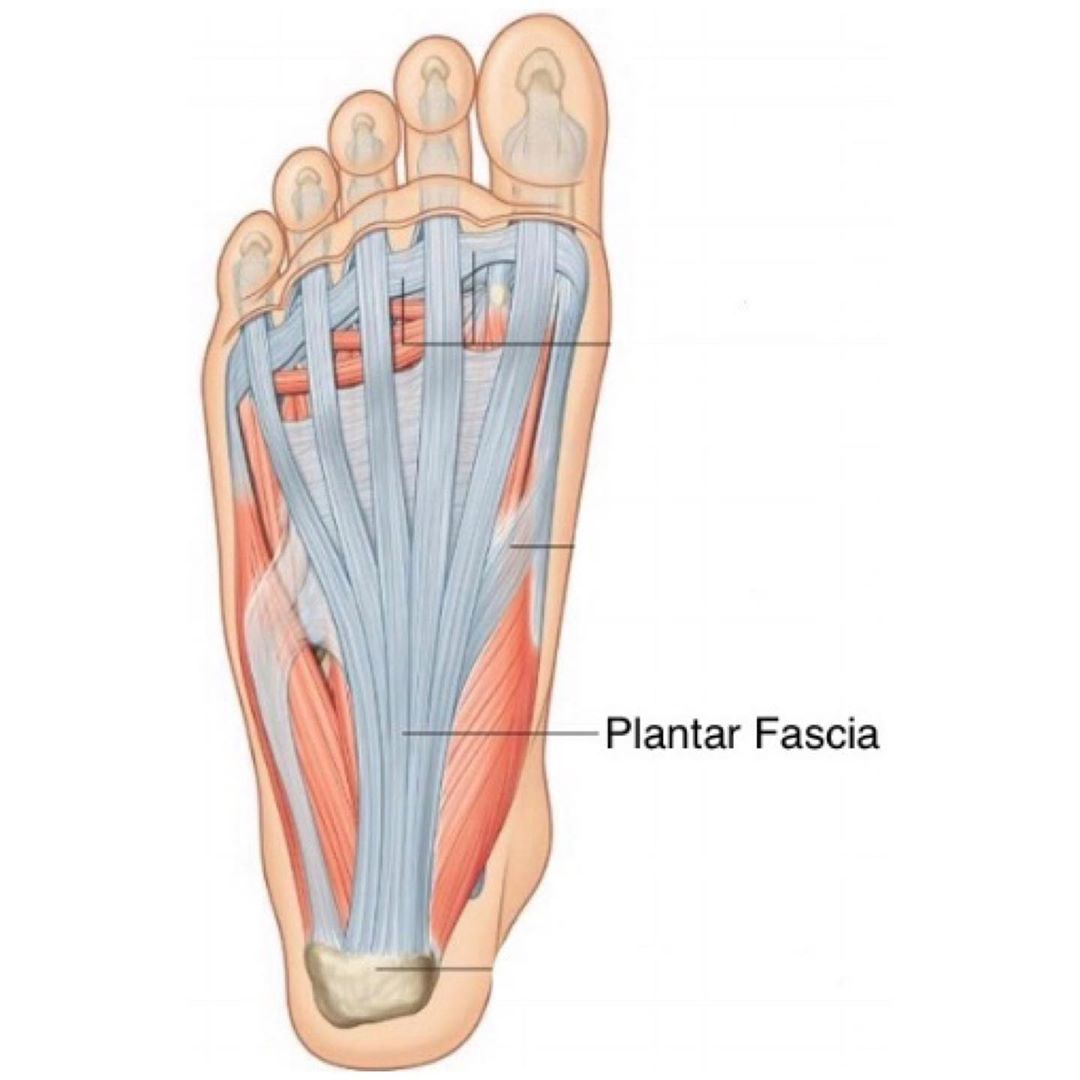 Source: stefanduell.tumblr.com
Source: stefanduell.tumblr.com
If chronic, it will present with ecchymosis and edema in a patient with underlying plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia provides strength for walking and assists with balance. Plantar fascial tears can occur acutely or chronically. This is a ligament that connects the calcaneus to the talus. The plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes.
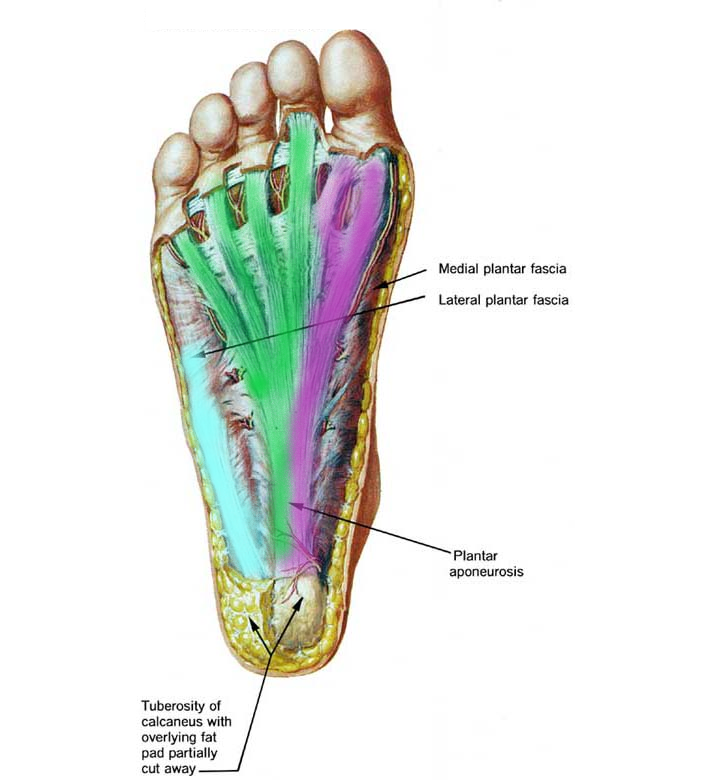 Source: sportspodiatry.com.au
Source: sportspodiatry.com.au
Muscle anatomy of the plantar foot. This image shows the anatomy of the plantar foot and is labeled with corresponding identification tags. Flexor hallucis brevis muscle (medial head and lateral head ). (fig.23) dorsiflexion (refer fig.24) abduction spreading the toes apart. This is the longest ligament of the foot that runs from the heel to the toes to form the arch.
 Source: pinterest.co.uk
Source: pinterest.co.uk
It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. The compartment comprises numerous short foot muscles in different layers. The plantar fascia provides strength for walking and assists with balance. We are looking at how to identify the 3 bands of the plantar fascia and which band is most important in plantar fasciitis. (fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements:
 Source: joionline.net
Source: joionline.net
The achilles tendon makes it possible to run, jump, climb stairs and stand on your toes. Plantar warts can be painful and difficult to treat. This is the part of the foot that protects the sole from injury and supports and stabilizes the arch (with the help of the posterior tibial tendon). (fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements: The muscular anatomy of the plantar foot is composed of the plantar fascia as well as intrinsic and extrinsic muscles.
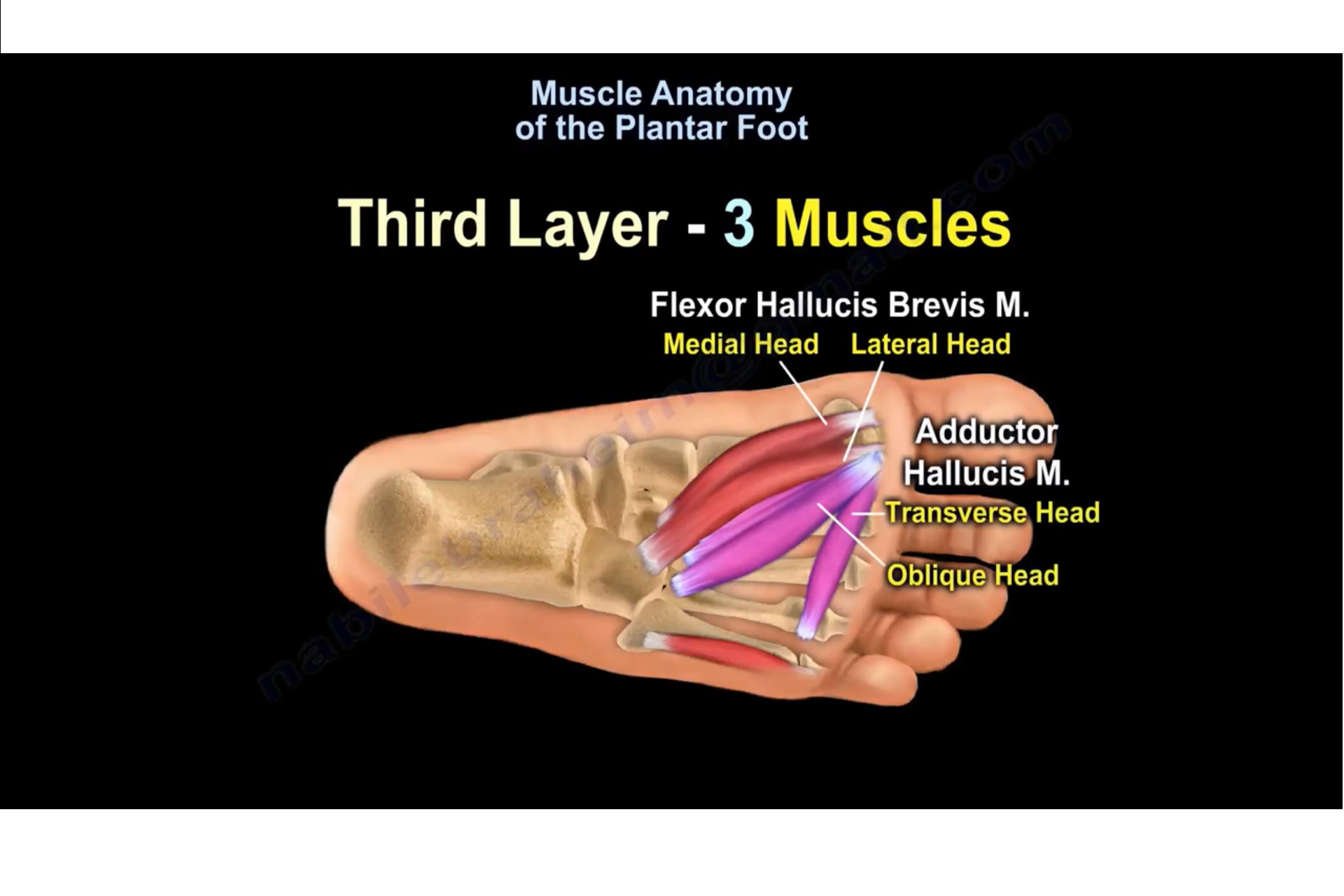 Source: orthopaedicprinciples.com
Source: orthopaedicprinciples.com
Their muscle bellies form the surface of the lateral foot sole (ball of the little toe). The tibial nerve controls all the muscles behind the tibia and fibula in the back part of the calf (deep and superficial posterior compartment muscles). Muscles of the plantar foot are divided into four layers:first la. (fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements: It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion.
 Source: vaidyaveekshan.blogspot.com
Source: vaidyaveekshan.blogspot.com
The plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate [ clarification needed ] organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. Lateral plantar muscles (inferior view) the lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles. They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot, and individually to control movement of the digits. The main ligaments of the foot are:
 Source: highmarkhealth.org
Source: highmarkhealth.org
Muscle anatomy of the plantar foot. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate [ clarification needed ] organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. Muscles of the plantar foot are divided into four layers:first la. Feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. Its role is to support the head of the talus.
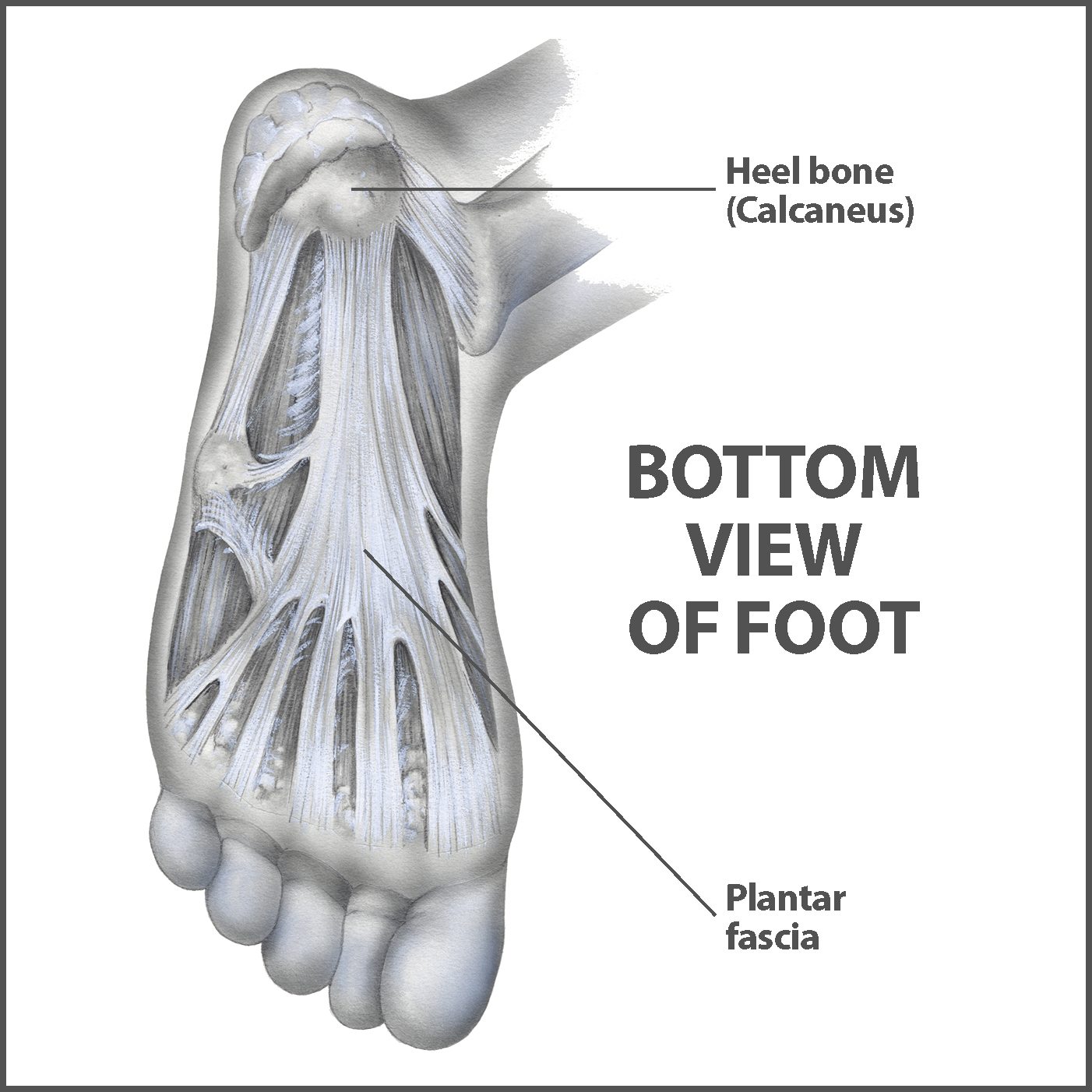 Source: floridaortho.com
Source: floridaortho.com
(fig.22) plantar flexion the toes allow four different movements: The plantar fascia is located deep to the superficial fascia and is divided into three bands (medial, central, and lateral). This movement normally accompanies plantar The plantar fascia provides strength for walking and assists with balance. The anatomy of the foot.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This is a ligament that connects the calcaneus to the talus. They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot, and individually to control movement of the digits. The achilles tendon makes it possible to run, jump, climb stairs and stand on your toes. The plantar fascia, or plantar aponeurosis, forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes. Anterior posterior plantar view of foot peroneus longus peroneus brevis
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title plantar foot anatomy by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.