Your Plastids in plant cell images are available. Plastids in plant cell are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Plastids in plant cell files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for plastids in plant cell images information linked to the plastids in plant cell keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Plastids In Plant Cell. In any event, so as to understand the coordinated regulatory mechanisms between plastids and nucleus, it is crucial to learn a lot of things from cornucopia of eubacterial molecular biology. For land plants, the number of plastids has been shown to be relatively high per cell ranging from 30 to 40 and 100 to 150 in diploid cells. Plastids originated by an endosymbiotic event still maintain a number of prokaryotic features, although they are now an integral part of plant cells. Chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts are the three main types of plastids in plant cells.chloroplasts contain pigments called chlorophyll to produce glucose inside the cell.
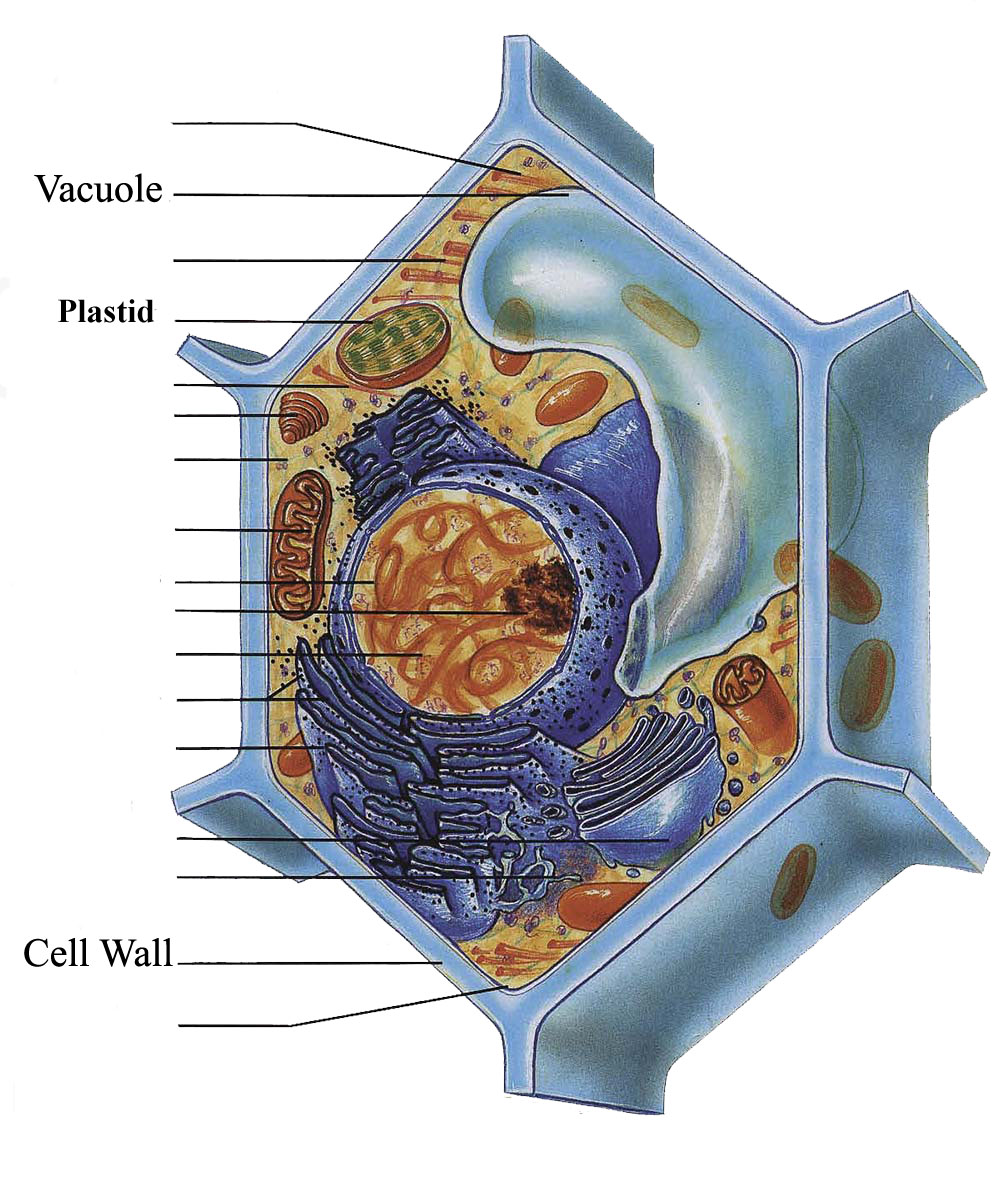 Biology 107 Home Page From homework.sdmesa.edu
Biology 107 Home Page From homework.sdmesa.edu
Plastids are major organelles (larger green, orange, red, or colorless organelles) found in most of the plant cells and euglenoids and occur in variety of shapes and sizes. Plastids were discovered and named by e. Why plastids are absent in animal cell? These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell. Plastids are found in the cells of plants and algae that are responsible for manufacturing and storing food. In some plant cells, plastids in the plant cytosol may be connected to each other via long thin protrusions arising from the envelope called stromules.
The plastids of plants are also simpler when compared to those found in other organisms like algae.
Haeckel (1866) introduced the term plasmid. Plastids are the largest cell organelle in plants. Plastids are responsible for manufacturing and storing of food. Plastids are an important group of plant cellular organelles and comprise one of the primary features that distinguish plant cells from those of other eukaryotes. In some plant cells, plastids in the plant cytosol may be connected to each other via long thin protrusions arising from the envelope called stromules. Schimper was the first to deliver a clear definition.
 Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Plastids in plant cell are in charge of food production and storage. Plastids are double membre bounded cytoplasmic organneles found in all plant cells and in euglenoides. The chloroplasts contain a green pigment chlorophyll that is responsible for the process of photosynthesis. Why plastids are absent in animal cell? Plastids also contain their own dna.
 Source: pagestronic.com
Source: pagestronic.com
Plastids also act as storage devices for starch and help in the synthesis of various molecules like fatty acids and terpene. All plastids, including chloroplasts, develop from proplastids, small (0.5 to 1 μm in diameter) undifferentiated organelles present in the rapidly dividing cells of plant roots and shoots. Haeckel (1866) introduced the term plasmid. Why plastids are absent in animal cell? Due to their large size they are easily observed under the microscope.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Plastids are major organelles (larger green, orange, red, or colorless organelles) found in most of the plant cells and euglenoids and occur in variety of shapes and sizes. Learn more about types, structure & functions of plastids at vedantu.com Of primary importance to plant cell function is the appropriate distribution of plastids during cell division, and in different organisms this creates different challenges. In their roles, the different types of plastids contribute to plant metabolism thus promoting plant growth and development. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Which is the largest cell organelle present in plant cell? Process by which plants breathe, eat and drink Plastids are found in almost all cells of the plant body either in the form of colorless plastids or colored plastids or proplastids. Plastids are double membre bounded cytoplasmic organneles found in all plant cells and in euglenoides. The plastids of plants are also simpler when compared to those found in other organisms like algae.
 Source: homework.sdmesa.edu
Source: homework.sdmesa.edu
These frequently contain photosynthetic pigments as well as other pigments that can modify the colour of the cell. As plastids bear some specific pigments, they impart specific colours to the plants. Plastids also contain their own dna. In any event, so as to understand the coordinated regulatory mechanisms between plastids and nucleus, it is crucial to learn a lot of things from cornucopia of eubacterial molecular biology. Proplastids then develop into the various types of mature plastids according to the needs of differentiated cells.
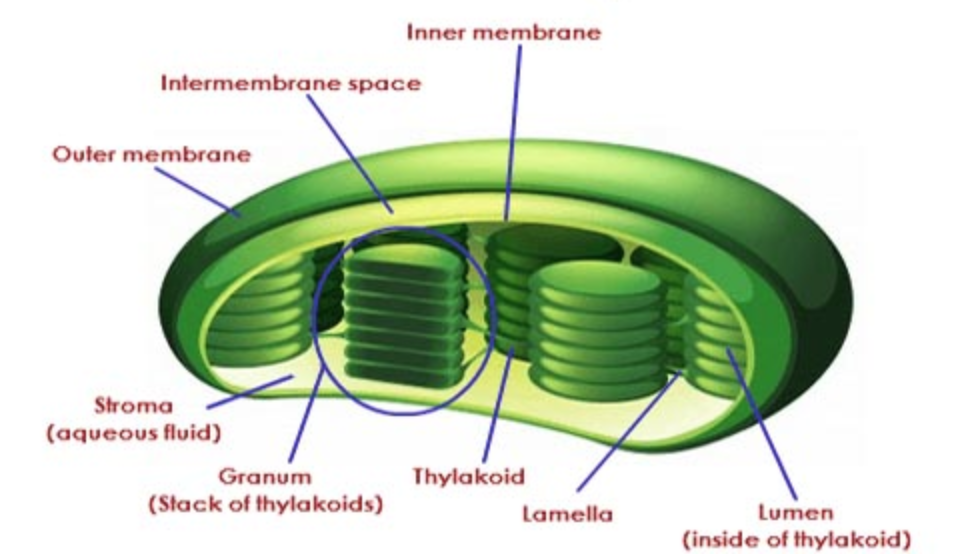 Source: classnotes.org.in
Source: classnotes.org.in
Thought to have evolved from independent unicellular organisms that lived symbiotically with plants over a billion years ago, they contain a large number of genes and manufacture a number of proteins. Plastids are the largest cell organelle in plants. For example unicellular algae, such as chlamydomonas or c. These stromules also facilitate communication and signaling between plastids. These frequently contain photosynthetic pigments as well as other pigments that can modify the colour of the cell.
 Source: wisegeek.com
Source: wisegeek.com
These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell. Haeckel (1866) introduced the term plasmid. Plastids are specialized structures within plant cells that manufacture and store food and pigments for the cell. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell. For land plants, the number of plastids has been shown to be relatively high per cell ranging from 30 to 40 and 100 to 150 in diploid cells.
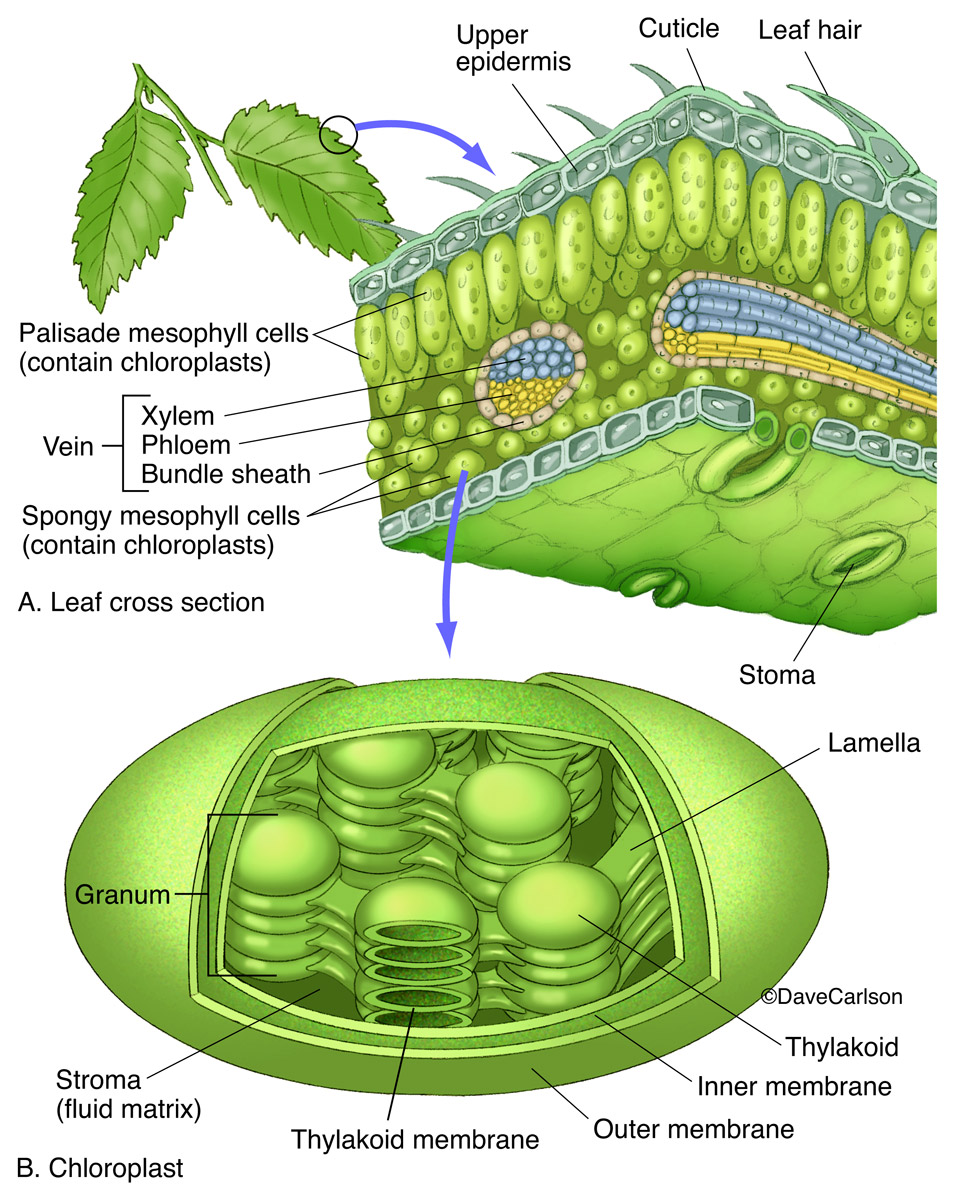 Source: carlsonstockart.com
Source: carlsonstockart.com
As plastids bear some specific pigments, they impart specific colours to the plants. Plastids were discovered and named by e. These stromules also facilitate communication and signaling between plastids. Plastids are double membre bounded cytoplasmic organneles found in all plant cells and in euglenoides. Like the mitochondria, plastids also have their own dna and ribosomes.
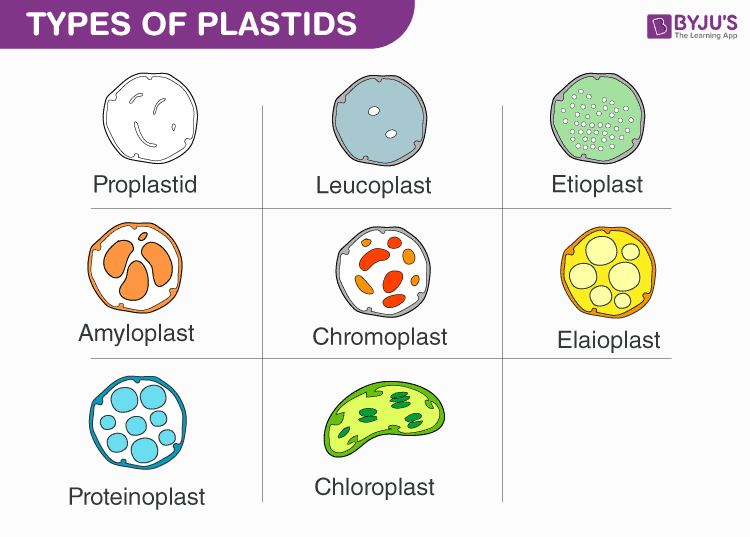 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Why plastids are absent in animal cell? These stromules also facilitate communication and signaling between plastids. Merolae, have only one chloroplast per cell and so coordination of cell and chloroplast division is essential to. Plastids were discovered and named by ernst haeckel, but a. Plastids are found in almost all cells of the plant body either in the form of colorless plastids or colored plastids or proplastids.

Plastids are double membre bounded cytoplasmic organneles found in all plant cells and in euglenoides. The chloroplasts contain a green pigment chlorophyll that is responsible for the process of photosynthesis. Plastids were discovered and named by ernst haeckel, but a. In some plant cells, plastids in the plant cytosol may be connected to each other via long thin protrusions arising from the envelope called stromules. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell.
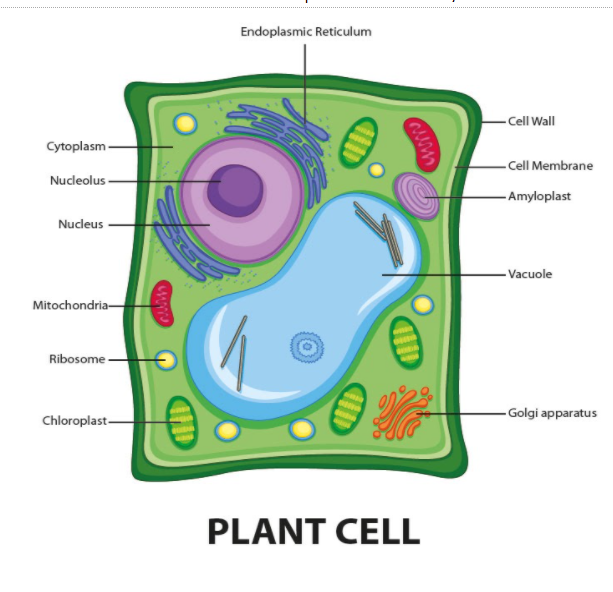 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Due to their large size they are easily observed under the microscope. Chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts are the three main types of plastids in plant cells.chloroplasts contain pigments called chlorophyll to produce glucose inside the cell. Due to their large size they are easily observed under the microscope. Which is the largest cell organelle present in plant cell? In some plant cells, plastids in the plant cytosol may be connected to each other via long thin protrusions arising from the envelope called stromules.
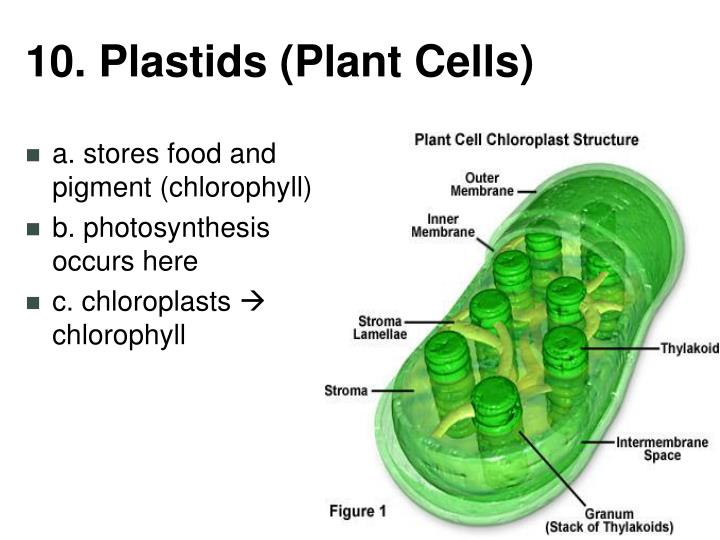 Source: diagram.oyajino.com
Source: diagram.oyajino.com
Thought to have evolved from independent unicellular organisms that lived symbiotically with plants over a billion years ago, they contain a large number of genes and manufacture a number of proteins. Plastids are a class of small organelles that contain pigment or food and are found in the cytoplasm of cells. These frequently contain photosynthetic pigments as well as other pigments that can modify the colour of the cell. All plastids, including chloroplasts, develop from proplastids, small (0.5 to 1 μm in diameter) undifferentiated organelles present in the rapidly dividing cells of plant roots and shoots. The chloroplasts contain a green pigment chlorophyll that is responsible for the process of photosynthesis.
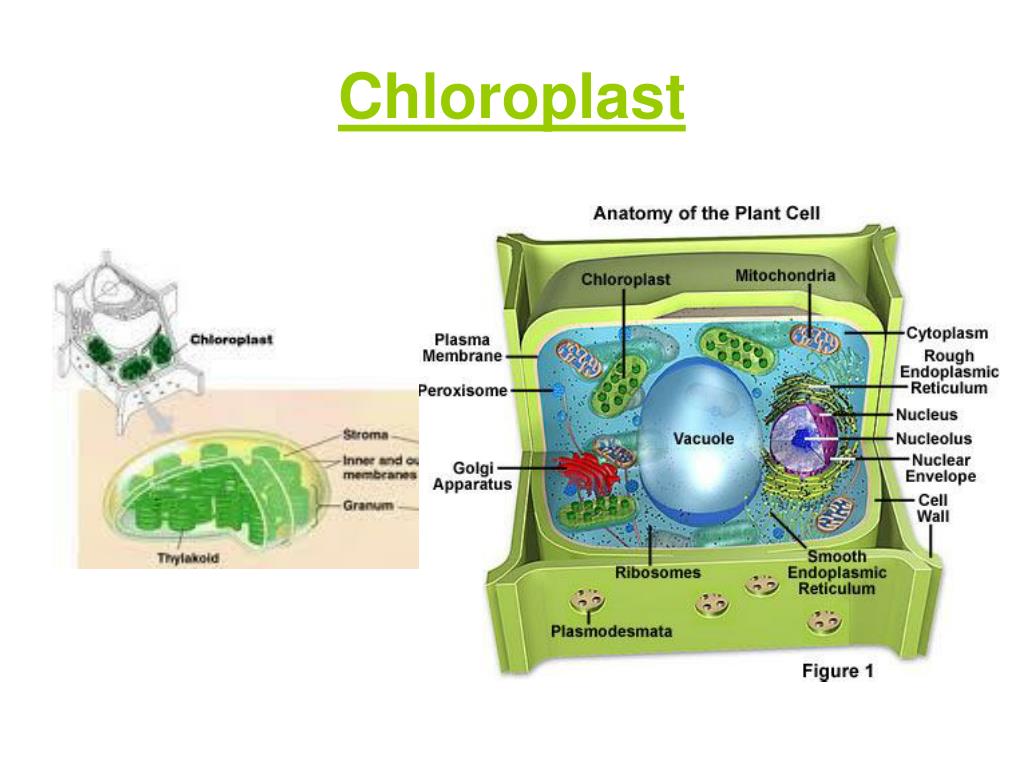 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The chloroplasts contain a green pigment chlorophyll that is responsible for the process of photosynthesis. In some plant cells, plastids in the plant cytosol may be connected to each other via long thin protrusions arising from the envelope called stromules. Mayer and schimper first used the term plastid. Plastids are the largest cell organelle in plants. Plastids also contain their own dna.
 Source: funscience.in
Source: funscience.in
Process by which plants breathe, eat and drink Plastids are responsible for manufacturing and storing of food. Plastids also act as storage devices for starch and help in the synthesis of various molecules like fatty acids and terpene. All plastids, including chloroplasts, develop from proplastids, small (0.5 to 1 μm in diameter) undifferentiated organelles present in the rapidly dividing cells of plant roots and shoots. They are easily observed under light microscope.
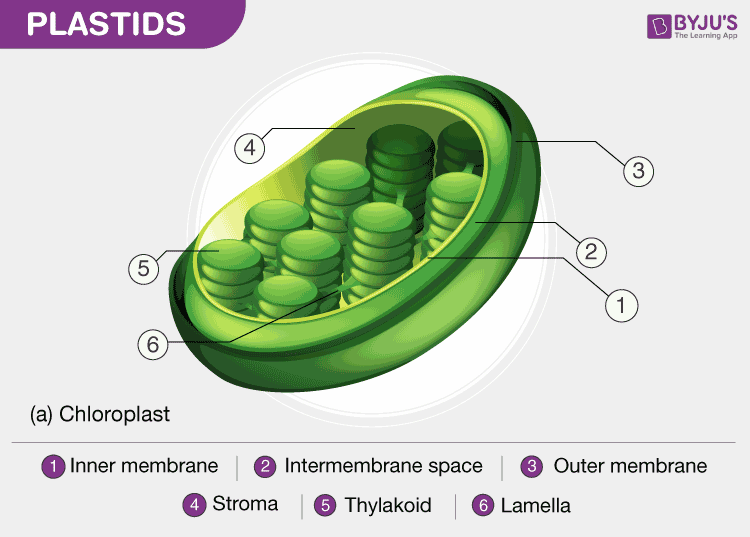 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Thought to have evolved from independent unicellular organisms that lived symbiotically with plants over a billion years ago, they contain a large number of genes and manufacture a number of proteins. Of primary importance to plant cell function is the appropriate distribution of plastids during cell division, and in different organisms this creates different challenges. Merolae, have only one chloroplast per cell and so coordination of cell and chloroplast division is essential to. Plastids in plant cell are in charge of food production and storage. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell.
 Source: abcworksheet.com
Source: abcworksheet.com
Merolae, have only one chloroplast per cell and so coordination of cell and chloroplast division is essential to. Plastids originated by an endosymbiotic event still maintain a number of prokaryotic features, although they are now an integral part of plant cells. Learn more about types, structure & functions of plastids at vedantu.com The chloroplasts contain a green pigment chlorophyll that is responsible for the process of photosynthesis. For land plants, the number of plastids has been shown to be relatively high per cell ranging from 30 to 40 and 100 to 150 in diploid cells.
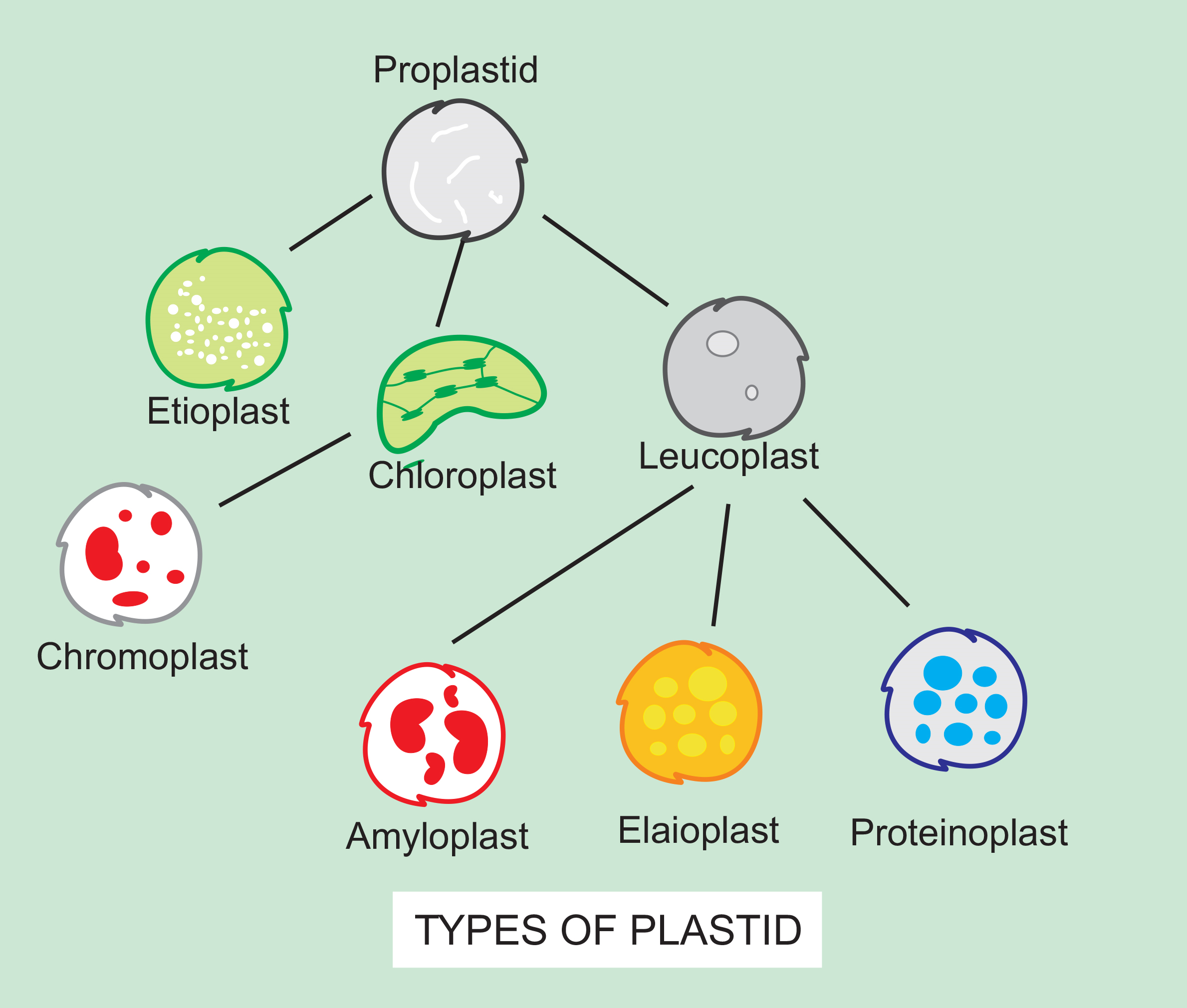 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
For example unicellular algae, such as chlamydomonas or c. Plastids also contain their own dna. Responsible for photosynthesis photosynthesis : Plastids are an important group of plant cellular organelles and comprise one of the primary features that distinguish plant cells from those of other eukaryotes. Like the mitochondria, plastids also have their own dna and ribosomes.
 Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
As plastids bear some specific pigments, they impart specific colours to the plants. For land plants, the number of plastids has been shown to be relatively high per cell ranging from 30 to 40 and 100 to 150 in diploid cells. Plastids originated by an endosymbiotic event still maintain a number of prokaryotic features, although they are now an integral part of plant cells. In their roles, the different types of plastids contribute to plant metabolism thus promoting plant growth and development. Plastids also contain their own dna.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title plastids in plant cell by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







